-
Android热修复1
定义
在我们应用上线后出现bug需要及时修复时,不用再发新的安装包,只需要发布补丁包,在客户无感知下修复调bug。
热修复解决方案
市场上的热修复方案很多,其中比较出名的有腾讯的Tinker、阿里的AndFix、美团的Robust以及QZone的超级补丁方案。
下面,我们比较下各个方案的优缺点。Tinker QZone AndFix Robust 类替换 yes yes no no So替换 yes no no no 资源替换 yes yes no no 全平台支持 yes yes yes yes 即时生效 no no yes yes 性能损耗 较小 较大 较小 较小 补丁包大小 较小 较大 一般 一般 开发透明 yes yes no no 复杂度 较低 较低 复杂 复杂 gradle支持 yes no no no Rom体积 较大 较小 较小 较小 成功率 较高 较高 一般 最高 - AndFix
在native动态替换java层的方法,通过native层hookjava层的代码。具体的流程类似于下面的流程图所示。

举个例子:我们有一个补丁包,里面有一个Test类。我们拿到补丁包之后通过类加载、反射的方式将补丁包中Test类的test方法替换原apk中有bug的Test类的test方法。至于,AndFix用JNI的方式来实现是因为java层的反射是无法将方法、属性进行赋值替换的。
public class Test{ @MethodReplace (class="'com.xxx.test",method="test") //表示该方法要替换的有bug的类名以及方法 public void test (){ //..... } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

- Robust
对于每个函数都在编译打包阶段自动插入一段代码。类似于代理,将方法执行的代码重定向到另一个方法中。
//编写的代码 @Modify //改动代码后手动添加注解用于补丁包生成 public long getIndex(){ return 100; } //经过插桩后实际执行的代码 public long getIndex(){ if(redirect!=null){ //修复 return 。。。 } return 100; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
-
Tinker
Tinker通过计算对比指定的Base Apk中的dex与修改后的Apk中的dex的区别,补丁包中的内容即为两者差分的描述。
运行时将Base Apk中的dex与补丁包进行合成,重启后加载全新的合成后的dex文件。

-
QZone
原理与Tinker差不多,这里就不多加介绍了
上面介绍的各种热修复框架,虽然实现的方式不一样,但是底层技术都是一样的,都运用了类加载、反射等技术。因此,我们有必要了解下android的类加载机制
双亲委托机制
某个类加载器在加载类时,首先将加载任务委托给父类加载器,依次递归,如果父类加载器可以完成类加载任务,就成功返回;只有父类加载器无法完成此加载任务或者没有父类加载器时,才自己去加载。
具体,我们看下ClassLoader类的源码就知道了。@Override protected Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { //有加载过的类,就用缓存的 Class<?> clazz = findLoadedClass(className); if (clazz == null) { clazz = findClass(className); } return clazz; } protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) { ClassLoader loader; if (this == BootClassLoader.getInstance()) loader = null; else loader = this; return VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass(loader, name); } @Override protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { return Class.classForName(name, false, null); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
优点:
- 避免重复加载,当父类加载器已经加载了该类的时候,就没有必要让子ClassLoader再加载一次。
- 安全性考虑,防止核心API库被随意篡改。
热修复流程
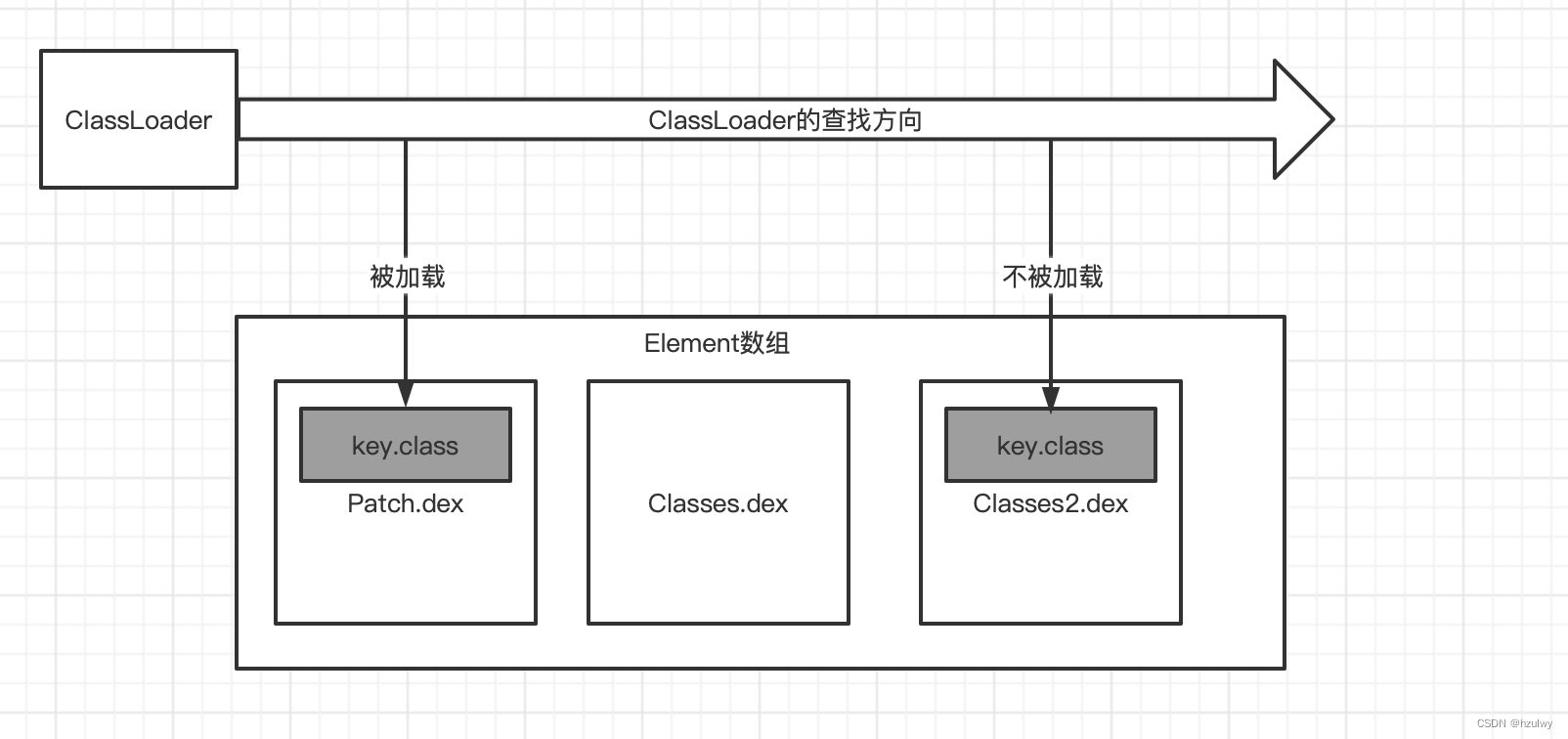
- 把Bug修复掉后,先生成类的class文件;
- 执行命令:dx --dex --ouput=patch.jar xxx.class //将class文件转成dex文件或jar文件(dex文件和jar文件都是一样的)
- 获取到当前应用的PathClassloader;
- 反射获取到DexPathList属性对象pathList;
- 反射修改pathList的dexElements
1.把补丁包patch.dex转化为Elementl (patch)
2 获得pathList的dexElements属性 (old)
3.patch+dexElements合并,并反射赋值给pathList的dexElements
下面我们列举一个案例来说明一下:
使用反射进行热修复案例
首先,我们创建一个lib模块,用于存放我们实现热修复功能相关的代码。
- ShareReflectUtil(反射工具类)
package com.brett.lib; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; public class ShareReflectUtil { /** * 从 instance 到其父类 找 name 属性 * * @param instance * @param name * @return * @throws NoSuchFieldException */ public static Field findField(Object instance, String name) throws NoSuchFieldException { for (Class<?> clazz = instance.getClass(); clazz != null; clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()) { try { //查找当前类的 属性(不包括父类) Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(name); if (!field.isAccessible()) { field.setAccessible(true); } return field; } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { // ignore and search next } } throw new NoSuchFieldException("Field " + name + " not found in " + instance.getClass()); } /** * 从 instance 到其父类 找 name 方法 * * @param instance * @param name * @return * @throws NoSuchFieldException */ public static Method findMethod(Object instance, String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException { for (Class<?> clazz = instance.getClass(); clazz != null; clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()) { try { Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(name, parameterTypes); if (!method.isAccessible()) { method.setAccessible(true); } return method; } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { // ignore and search next } } throw new NoSuchMethodException("Method " + name + " with parameters " + Arrays.asList(parameterTypes) + " not found in " + instance.getClass()); } /** * @param instance * @param fieldName * @param patchElements 补丁的Element数组 * @throws NoSuchFieldException * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws IllegalAccessException */ public static void expandFieldArray(Object instance, String fieldName, Object[] patchElements) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { //拿到 classloader中的dexelements 数组 Field jlrField = findField(instance, fieldName); //old Element[] Object[] oldElements = (Object[]) jlrField.get(instance); //合并后的数组 Object[] newElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(oldElements.getClass().getComponentType(), oldElements.length + patchElements.length); // 先拷贝新数组 System.arraycopy(patchElements, 0, newElements, 0, patchElements.length); System.arraycopy(oldElements, 0, newElements, patchElements.length, oldElements.length); //修改 classLoader中 pathList的 dexelements jlrField.set(instance, newElements); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- BrettFix
package com.brett.lib; import android.app.Application; import android.os.Build; import android.util.Log; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Brett.li on 2022/7/31. */ public class BrettFix { private static final String TAG = "BrettFix"; public static void installPatch(Application application, File patch){ List<File> patchs = new ArrayList<>(); if(patch.exists()){ patchs.add(patch); } //1.获取程序的PathClassLoader对象 ClassLoader classLoader = application.getClassLoader(); //2.反射获取PathClassLoader父类BaseDexClassLoader的pathList对象 try { Field pathListField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(classLoader,"pathList"); Object pathList = pathListField.get(classLoader); //3.反射获取pathList的dexElements对象(oldElement) Field dexElementsField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(pathList, "dexElements"); Object[] oldElements = (Object[]) dexElementsField.get(pathList); //4、把补丁包变成Element数组:patchElement(反射执行makePathElements) Object[] patchElements = null; if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) { Method makePathElements = ShareReflectUtil.findMethod(pathList, "makePathElements", List.class, File.class, List.class); ArrayList<IOException> ioExceptions = new ArrayList<>(); patchElements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(pathList, patchs, application.getCacheDir(), ioExceptions); } else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) { Method makePathElements = ShareReflectUtil.findMethod(pathList, "makeDexElements", ArrayList.class, File.class, ArrayList.class); ArrayList<IOException> ioExceptions = new ArrayList<>(); patchElements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(pathList, patchs, application.getCacheDir(), ioExceptions); } //5、合并patchElement+oldElement = newElement (Array.newInstance) //创建一个新数组,大小 oldElements+patchElements // int[].class.getComponentType() ==int.class Object[] newElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(oldElements.getClass().getComponentType(), oldElements.length + patchElements.length); System.arraycopy(patchElements, 0, newElements, 0, patchElements.length); System.arraycopy(oldElements, 0, newElements, patchElements.length, oldElements.length); //6、反射把oldElement赋值成newElement dexElementsField.set(pathList, newElements); Log.e(TAG,"========"); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
完成上面两个功能之后,我们直接在application中调用installPatch方法即可。
package com.brett.myapplication; import android.app.Application; import android.content.Context; import android.util.Log; import androidx.multidex.MultiDex; import com.brett.common.RecordPathManager; import com.brett.lib.BrettFix; import com.brett.test.TestActivity; import com.brett.test1.Test1Activity; import java.io.File; /** * Created by Brett.li on 2022/6/22. */ public class MyApplication extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); } @Override protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) { super.attachBaseContext(base); MultiDex.install(this); BrettFix.installPatch(this,new File(this.getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath()+"/patch.jar")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
接着,我们在Mainactivity中,调用一个会报错的方法来模拟崩溃的情况。
package com.brett.myapplication; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Utils.test(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
package com.brett.myapplication; import android.util.Log; /** * Created by Brett.li on 2022/7/31. */ public class Utils { public static void test(){ throw new IllegalStateException("出错了"); // Log.e("BrettFix","bug修复了"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
这样,在没有补丁包(patch.jar)的情况下,我们的程序一执行到MainActivity就会崩溃。
接着,我们修复test方法,然后将其编译为class文件(直接在原文件上修改,然后点击android studio的rebuild project即可)。等待编译结束就能在build文件夹下面找到Utils.class文件,之后再使用dx命令将class文件打包成jar包。
注意:如何使用dx命令也是有学问的,初学者可能会遇到找不到相关类的错误。
类似于下面这种报错。

正解是,建议将Utils.class文件的从com开始的目录都copy到同一个目录下,然后再cd到该目录下再使用dx命令。
如下图所示,笔者将com/brett/myapplication/Utils.class文件全部copy到桌面。然后cd到桌面再使用dx命令,这样就能确保dx命令不报错。

最后,我们实际测试下,但我们的手机cache目录中没有patch.jar文件时,我们运行下程序。


接着,我们往cache目录下放入patch.jar文件然后杀掉进程,重启app。记住,一定要重启app,这种依靠classloader来实现的热修复是无法及时生效的哦。

这样,我们就成功地将原有的有bug的Utils类替换掉了。AndroidN混合编译
上面,我们实现的热修复功能貌似很完美但是在androidN手机上分分钟崩溃了。原因在于androidN使用了混合编译的功能。这主要涉及到android虚拟机相关的知识。
我们都知道,DVM是实现了JVM规范的专用于android平台的虚拟机,默认使用CMS垃圾回收器,于JVM运行class字节码不同,DVM执行的是已转换为.dex格式的java应用程序。Dex文件是很多class文件处理压缩后的产物,最终可以在android运行时环境执行。JVM的指令集基于栈,DVM是基于寄存器(执行效率高)。
ART(兼容DVM),android4中引入的一个开发者选项,也是android5.0及更高版本的默认模式,在应用安装的时候,Ahead-of-Time(AOT)预编译字节码到机器语言。应用程序安装会变慢,但是执行效率更高,启动更快。
在DVM下,应用运行需要解释执行,常用热点代码(频繁运行的代码)通过即时编译器(JIT)在运行时将字节码转为机器码,运行效率低。预编译可以明显改善电池续航,因为应用程序每次运行时不用重复编译,从而减少cpu的使用频率,降低能耗。
因此,ART是采用了控件换时间(增加了机器码的空间)的方式,提高效率。
注意:机器码是与cpu架构有关,每一种架构的cpu都有与之对应的指令集,因此无法跨平台。- dexopt
在DVM中虚拟机在加载一个dex文件时,会对dex文件进行验证和优化的操作,其中dex文件的优化结果变成了odex文件,这个文件和dex文件很像,知识使用了一些优化的操作码。 - dex2oat
ART预编译机制,在安装时对dex文件执行dexopt优化后,再将odex进行AOT,编译为OAT(实际上ELF文件)可执行文件(机器码)。相比做过dexopt优化,直接将dex文件转换为OAT要花费更长的时间。
androidN之后,常用的则是混合编译的方式
- 最初安装应用时不进行任何AOT编译(安装速度变快),运行过程中解释执行,对经常执行的方法进行JIT,经过JIT编译之后记录到Profile文件中,类似做了一个缓存。
- 当设备闲置或充电时,编译守护进程会根据Profile文件对常用代码进行AOT编译,下次运行直接使用。底层是通过findLoadedClass0(c++)方法实现的。
根据类加载的原理,此时类已经被加载了无法替换。
混合编译热修复解决方案
既然,是在classloader进行处理,那么将我们替换成我们自己的不就可以了吗?这里则是参考了Tinker的修复思路,代码也是抄Tinker的,毕竟我们要站在巨人的肩膀上嘛。
package com.brett.lib; import android.app.Application; import android.content.Context; import android.content.res.Resources; import android.os.Build; import android.util.Log; import java.io.File; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.List; import dalvik.system.DexFile; public class ClassLoaderInjector { public static void inject(Application app, ClassLoader oldClassLoader, List<File> patchs) throws Throwable { //创建我们自己的加载器 ClassLoader newClassLoader = createNewClassLoader(app, oldClassLoader, patchs); doInject(app, newClassLoader); Log.e("BrettFix","=============="); } private static ClassLoader createNewClassLoader(Context context, ClassLoader oldClassLoader, List<File> patchs) throws Throwable { /** * 1、先把补丁包的dex拼起来 */ // 获得原始的dexPath用于构造classloader StringBuilder dexPathBuilder = new StringBuilder(); String packageName = context.getPackageName(); boolean isFirstItem = true; for (File patch : patchs) { //添加:分隔符 /xx/a.dex:/xx/b.dex if (isFirstItem) { isFirstItem = false; } else { dexPathBuilder.append(File.pathSeparator); } dexPathBuilder.append(patch.getAbsolutePath()); } /** * 2、把apk中的dex拼起来 */ //得到原本的pathList Field pathListField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(oldClassLoader, "pathList"); Object oldPathList = pathListField.get(oldClassLoader); //dexElements Field dexElementsField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(oldPathList, "dexElements"); Object[] oldDexElements = (Object[]) dexElementsField.get(oldPathList); //从Element上得到 dexFile Field dexFileField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(oldDexElements[0], "dexFile"); for (Object oldDexElement : oldDexElements) { String dexPath = null; DexFile dexFile = (DexFile) dexFileField.get(oldDexElement); if (dexFile != null) { dexPath = dexFile.getName(); } if (dexPath == null || dexPath.isEmpty()) { continue; } if (!dexPath.contains("/" + packageName)) { continue; } if (isFirstItem) { isFirstItem = false; } else { dexPathBuilder.append(File.pathSeparator); } dexPathBuilder.append(dexPath); } String combinedDexPath = dexPathBuilder.toString(); /** * 3、获取apk中的so加载路径 */ // app的native库(so) 文件目录 用于构造classloader Field nativeLibraryDirectoriesField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(oldPathList, "nativeLibraryDirectories"); List<File> oldNativeLibraryDirectories = (List<File>) nativeLibraryDirectoriesField.get(oldPathList); StringBuilder libraryPathBuilder = new StringBuilder(); isFirstItem = true; for (File libDir : oldNativeLibraryDirectories) { if (libDir == null) { continue; } if (isFirstItem) { isFirstItem = false; } else { libraryPathBuilder.append(File.pathSeparator); } libraryPathBuilder.append(libDir.getAbsolutePath()); } String combinedLibraryPath = libraryPathBuilder.toString(); //创建自己的类加载器 ClassLoader result = new BrettClassLoader(combinedDexPath, combinedLibraryPath, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()); return result; } private static void doInject(Application app, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Throwable { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader); Context baseContext = (Context) ShareReflectUtil.findField(app, "mBase").get(app); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 26) { ShareReflectUtil.findField(baseContext, "mClassLoader").set(baseContext, classLoader); } Object basePackageInfo = ShareReflectUtil.findField(baseContext, "mPackageInfo").get(baseContext); ShareReflectUtil.findField(basePackageInfo, "mClassLoader").set(basePackageInfo, classLoader); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 27) { Resources res = app.getResources(); try { ShareReflectUtil.findField(res, "mClassLoader").set(res, classLoader); final Object drawableInflater = ShareReflectUtil.findField(res, "mDrawableInflater").get(res); if (drawableInflater != null) { ShareReflectUtil.findField(drawableInflater, "mClassLoader").set(drawableInflater, classLoader); } } catch (Throwable ignored) { // Ignored. } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
package com.brett.lib; import dalvik.system.PathClassLoader; /** * Created by Brett.li on 2022/7/31. */ public class BrettClassLoader extends PathClassLoader { public BrettClassLoader(String dexPath, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) { super(dexPath, librarySearchPath, parent); } @Override protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { return super.loadClass(name, resolve); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
public static void installPatch(Application application, File patch){ List<File> patchs = new ArrayList<>(); if(patch.exists()){ patchs.add(patch); } //1.获取程序的PathClassLoader对象 ClassLoader classLoader = application.getClassLoader(); //替换成我们自己的classloader if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) { try { ClassLoaderInjector.inject(application, classLoader, patchs); } catch (Throwable throwable) { } // return; } //2.反射获取PathClassLoader父类BaseDexClassLoader的pathList对象 try { Field pathListField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(classLoader,"pathList"); Object pathList = pathListField.get(classLoader); //3.反射获取pathList的dexElements对象(oldElement) Field dexElementsField = ShareReflectUtil.findField(pathList, "dexElements"); Object[] oldElements = (Object[]) dexElementsField.get(pathList); //4、把补丁包变成Element数组:patchElement(反射执行makePathElements) Object[] patchElements = null; if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) { Method makePathElements = ShareReflectUtil.findMethod(pathList, "makePathElements", List.class, File.class, List.class); ArrayList<IOException> ioExceptions = new ArrayList<>(); patchElements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(pathList, patchs, application.getCacheDir(), ioExceptions); } else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) { Method makePathElements = ShareReflectUtil.findMethod(pathList, "makeDexElements", ArrayList.class, File.class, ArrayList.class); ArrayList<IOException> ioExceptions = new ArrayList<>(); patchElements = (Object[]) makePathElements.invoke(pathList, patchs, application.getCacheDir(), ioExceptions); } //5、合并patchElement+oldElement = newElement (Array.newInstance) //创建一个新数组,大小 oldElements+patchElements // int[].class.getComponentType() ==int.class Object[] newElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(oldElements.getClass().getComponentType(), oldElements.length + patchElements.length); System.arraycopy(patchElements, 0, newElements, 0, patchElements.length); System.arraycopy(oldElements, 0, newElements, patchElements.length, oldElements.length); //6、反射把oldElement赋值成newElement dexElementsField.set(pathList, newElements); Log.e(TAG,"========"); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
如此,便解决了androidN混合编译的问题。
- AndFix
-
相关阅读:
python开发之个人微信号的二次开发
智能指针shared_from_this
Sping Security前后端分离两种方案
【链表专题】
发UPS国际快递到墨西哥的收费标准
【无标题】
FS4059B ESOP8 输入5V升压充电8.4V1.5A两串锂电池充电IC
程序设计与算法(三)C++面向对象程序设计笔记 第五周 继承
【简易 教程:Pytorch 配置 GPU版本】
每日一面系列之Spring中@Autowired和@Inject注解的区别?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36828822/article/details/126085974
