-
服装图像分类
活动地址:CSDN21天学习挑战赛
学习的最大理由是想摆脱平庸,早一天就多一份人生的精彩;迟一天就多一天平庸的困扰。各位小伙伴,如果您:
想系统/深入学习某技术知识点…
一个人摸索学习很难坚持,想组团高效学习…
想写博客但无从下手,急需写作干货注入能量…
热爱写作,愿意让自己成为更好的人…创作计划
**
1,机缘A,分享服装分类实验
B,日常学习中的记录
C,通过服装分类项目进行技术交流2,收获
A,获得了10粉丝的关注
B,获得了20的赞、阅读量等
C,认识和了解了服装分类作者的想法和经验
…3,日常
- 创作已经是我学习的一部分了
- 有限的时间下,利用周二、四、六进行博客创作,其余时间用来学习
4,憧憬
创作规划是学习TensorFlow图像分类方法,模型调优,使错误率减小
**
学习计划
**
1,学习目标掌握 TensorFlow图像分类方法
2,学习内容
A,搭建TensorFlow开发环境
B,掌握 matplotlib绘图方法
C,掌握训练方法 ,损失函数的选择3,学习时间
周一至周五晚上 7 点—晚上9点
周六下午 6点-下午 9 点
周日下午 6 点-下午 9 点4,学习产出
技术笔记 1 遍
CSDN技术博客 10 篇
学习的vlog 视频 2 个**
学习日记
**
1,学习知识点服装分类方法,模型结构,数据集的结构
2,学习遇到的问题
调整数据格式、为标签编号,选择样本测试
3,学习的收获
学会了识别数据集的方式、数据可视化、使用模型预测
4,实操
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, models import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() # 将像素的值标准化至0到1的区间内。 train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0 print(train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape) #调整数据到我们需要的格式 train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1)) test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1)) print(train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape) class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] plt.figure(figsize=(20,10)) for i in range(20): plt.subplot(5,4,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]]) plt.show() model = models.Sequential([ layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)), # 卷积层 layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层 layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层 layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层2,2*2采样 layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层 layers.Flatten(), # Flatten层 layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 全连接层 layers.Dense(10) # 输出层 ]) model.summary() model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=['accuracy']) history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10, validation_data=(test_images, test_labels)) acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1) plt.plot(epochs, acc, label='accuracy') plt.plot(epochs,val_acc, label = 'val_accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.ylim([0.5, 1]) plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.show() test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2) print(test_loss,test_acc) #测试 print('选择一个样本:',class_names[test_labels[5]]) pre = model.predict(test_images) print('预测值:',class_names[np.argmax(pre[5])])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
输出:
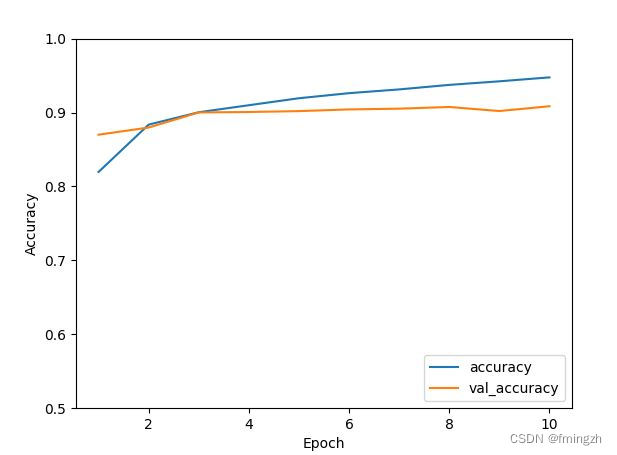
0.28127503395080566 0.9085000157356262
选择一个样本: Trouser
预测值: Trouser分析:可以看出训练集和验证集的精确率相似,拟合效果较好。预测错误率为28%,精确率为90.6%。训练效果较好。对模型选择测试集上的一个样本进行测试,结果正确。
-
相关阅读:
【问题记录与解决】jupyter notebook 无法重命名,无法运行测试代码 || jupyter notebook 中常用的两个快捷键。
js高级属性
C#实现的曲线方法
tsne可视化cnn模型
Java网络编程
Web网页实现多路播放RTSP视频流(使用WebRTC)
App自动化测试持续集成效率提高50%
Zynq UltraScale+ XCZU9EG 纯VHDL解码 IMX214 MIPI 视频,2路视频拼接输出,提供vivado工程源码和技术支持
基于SSM的流浪狗收容领养管理平台设计与实现
linux学习(5)—— 项目部署
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/misterfm/article/details/126109187
