-
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Given the
headof a linked list, remove thenthnode from the end of the list and return its head.Example 1:
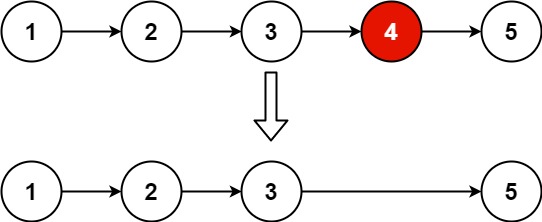
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1 Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
1.傻瓜办法:
- /**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * struct ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode *next;
- * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
- * };
- */
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
- ListNode*curr=head;
- int count=0;
- while(curr!=NULL){
- count++;
- curr=curr->next;
- }
- int cnt=count-n+1;
- struct ListNode*dummyHead=new ListNode(0,head);
- struct ListNode*pre=dummyHead;
- count=0;
- while(pre->next!=NULL){
- count++;
- if(count==cnt){
- pre->next=pre->next->next;
- }else{
- pre=pre->next;
- }
- }
- ListNode*ret=dummyHead->next;
- delete dummyHead;
- return ret;
- }
- };
注意:
我的这种方法是最容易想到的,先遍历一遍链表得到链表长度,需要注意的一点只有count++放的位置了。
2.快慢指针:
- /**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * struct ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode *next;
- * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
- * };
- */
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
- ListNode*dummyHead=new ListNode(0,head);
- ListNode*fast=dummyHead;
- ListNode*slow=dummyHead;
- n++;
- while(n--)fast=fast->next;
- while(fast!=NULL){
- fast=fast->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- }
- slow->next=slow->next->next;
- ListNode*temp=dummyHead->next;
- delete dummyHead;
- return temp;
- }
- };
注意:
1.中心思想:fast比slow多走n步,但是这会导致slow最后指向的位置刚好是要删除的,所以fast应该比slow多走n+1步,保证当fast==NULL的时候,slow是要被删除的倒数第n个位置的前一个位置。(fast和slow始终距离n+1)
2.C++代码要手动释放new的节点内存
- The number of nodes in the list is
-
相关阅读:
JAVA 基础学习笔记 (6)访问权限修饰符
Linux命令--在后台运行程序--方法/实例
Java中将字符串ArrayList转换为数组的四种方法
Logstash实现MySql数据近实时同步ElasticSearch搜索服务
用递归函数和栈操作逆序栈
PHP即刻送达同城派送小程序系统
STM32解析航模遥控器的PPM信号
使用 Vite 插件开发构建 Tampermonkey 用户脚本
平衡二叉树基本操作(AVL平衡二叉树)
REVA再创NFT托管新记录!Boodles等企业相继入局
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80161204/article/details/139829172