-
js深浅拷贝
引用关系
我们知道,像对象这种复杂数据类型,在定义它的时候我们所指定的变量只会存储这个对象的地址,我们通过这个地址来寻找对象并且操作它,而将这个变量赋值给其他变量时,复制的也仅仅只是地址,对象本身并没有被复制,当我们通过某一个变量去修改对象的成员时,另一个对它保持引用的变量也会同步的更新

这种仅仅通过等于号赋值的操作我们称之为浅拷贝
与浅拷贝相对应则是深拷贝深拷贝
深拷贝不同于浅拷贝,通过深拷贝得到的对象更像以下这种形式

我们如果想要达到深拷贝的话需要自己封装函数实现基本实现
我们定义一个deepClone函数,这个函数会传入一个值,我们并确定现在传入的是什么值,如果是一个基本类型的值我们需要直接将其返回,如果是一个复杂数据类型的值我们需要将其深度克隆之后返回一个新对象
function deepClone(originObject) { let newObject = null function getType(item) { let typeValue if (Array.isArray(item)) { typeValue = "array" } else if (item === null || (typeof item !== "function" && typeof item !== "object" && typeof item !== "symbol")) { typeValue = "common" } else { typeValue = typeof item } return typeValue } return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
我们在函数内部定义了一个getType函数,这个函数用于获得传入值的类型,我们规定:有array,common,object,function,symbol这几种类型,我们接下来将定义一个新函数用于遍历我们传入的originObject,不管它此刻是否为复杂数据类型
function deepClone(originObject) { let newObject = null function _deepClone(originObject) { if (getType(originObject) === "common") { return originObject } const newObject = getType(originObject) === "array" ? [] : {} for (const key in originObject) { } return newObject } newObject = _deepClone(originObject) return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
在函数最开始,我们需要先判断传入的值是否为基本数据类型即common,如果是common类型我们就需要直接返回
接下来我们需要知道传入的值是一个数组还是对象,根据getType拿到的类型不同我们对newObject定义了不同的初值
接下来万事俱备,我们只需完善for循环内部的代码就行function deepClone(originObject) { let newObject = null function _deepClone(originObject) { if (getType(originObject) === "common") { return originObject } const newObject = getType(originObject) === "array" ? [] : {} for (const key in originObject) { const currentObject = originObject[key] const type = getType(currentObject) switch (type) { case "object": case "symbol": case "array": default: } } return newObject } newObject = _deepClone(originObject) return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
我们首先得到了每次循环遍历的属性值currentObject,如果是数组的话得到的则是下标对应的元素
然后我们开始判断这个值的类型是什么,再使用switch来分类处理类型处理
具体而言switch会有四种情况
- object
如果得到的类型是object则需要继续调用_deepClone函数,直到类型不是object - symbol
如果得到了symbol,那我们则需要重新生成一个symbol变量,并传入原先symbol的描述 - array
如果传入的类型是一个array,那我们需要继续调用_deepClone函数,直到类型不是array - 其他情况
如common和function,这些类型的元素我们默认是不对其进行克隆的,一是common本身返回的就是一个新的字面量,二是函数本身没有拷贝的必要
综上所述,我们能得到以下代码
function deepClone(originObject) { let newObject = null function _deepClone(originObject) { if (getType(originObject) === "common") { return originObject } const newObject = getType(originObject) === "array" ? [] : {} for (const key in originObject) { const currentObject = originObject[key] const type = getType(currentObject) switch (type) { case "object": newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) break case "symbol": newObject[key] = Symbol(currentObject.description) break; case "array": newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) break default: newObject[key] = currentObject break } } return newObject } newObject = _deepClone(originObject) return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
循环引用
然而在对象中还有一种奇特的现象,那就是对象中保持了对自身的引用
即const obj = {} obj.self = obj- 1
- 2
这种现象被称作循环引用,我们的深拷贝需要解决这种情况
在switch的四种情况中,我们可以看出循环引用发生当type为object时,那我们可以写出以下代码function deepClone(originObject) { const set = new WeakSet() let newObject = null function _deepClone(originObject) { if (getType(originObject) === "common") { return originObject } const newObject = getType(originObject) === "array" ? [] : {} for (const key in originObject) { const currentObject = originObject[key] const type = getType(currentObject) switch (type) { case "object": if (set.has(currentObject)) { newObject[key] = currentObject } else { set.add(currentObject) newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) } break case "symbol": newObject[key] = Symbol(currentObject.description) break; case "array": newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) break default: newObject[key] = currentObject break } } return newObject } newObject = _deepClone(originObject) return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
我们使用一个set来记录目前已经存在的对象,如果这个对象以存在于set,那么我们就不继续递归
但是如果使用set的话会有一个问题,其对于自身元素保持着强引用,当变量被赋值为null时此对象也不会被GC回收,因为此时的set还对对象保持着引用,解决方法要么是在_deepClone调用完后手动释放set,要么使用weakSet
具体关于set和weakSet的内容可以看我这篇文章
set与weakSetkey为symbol时
最后还有一个问题,当对象的key为symbol时此属性无法被for…in遍历,所以我们需要对此额外处理
function deepClone(originObject) { let newObject = null function _deepClone(originObject) { newObject = _deepClone(originObject) const symbols = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(originObject) for (const symbol of symbols) { newObject[symbol] = _deepClone(originObject[symbol]) } return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
最后我们得到了完整的深拷贝函数
function deepClone(originObject) { const set = new WeakSet() let newObject = null function getType(item) { let typeValue if (Array.isArray(item)) { typeValue = "array" } else if (item === null || (typeof item !== "function" && typeof item !== "object" && typeof item !== "symbol")) { typeValue = "common" } else { typeValue = typeof item } return typeValue } function _deepClone(originObject) { if (getType(originObject) === "common") { return originObject } const newObject = getType(originObject) === "array" ? [] : {} for (const key in originObject) { const currentObject = originObject[key] const type = getType(currentObject) switch (type) { case "object": if (set.has(currentObject)) { newObject[key] = currentObject } else { set.add(currentObject) newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) } break case "symbol": newObject[key] = Symbol(currentObject.description) break; case "array": newObject[key] = _deepClone(currentObject) break default: newObject[key] = currentObject break } } return newObject } newObject = _deepClone(originObject) const symbols = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(originObject) for (const symbol of symbols) { newObject[symbol] = _deepClone(originObject[symbol]) } return newObject }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
测试代码
const object = { 1: 1, 3: "1", 4: true, 5: Symbol("123"), 6: null, 7: undefined, 8: { }, 9: function () { }, 10: [1, 2, { name: "a" }], [Symbol()]: 11 } object[11] = object const cloneObject = deepClone(object) console.log(cloneObject[10][2] === object[10][2]) cloneObject[10][2].name = "b" console.log(cloneObject, object) const arr = [1, 3, { name: "a" }] const cloneArr = deepClone(arr) console.log(cloneArr === arr) console.log(cloneArr[2] === arr[2]) console.log(cloneArr[2], arr[2]) cloneArr[2].name = "b"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
结果

structedClone
以上代码虽然能实现深拷贝的功能,但也有不少缺陷,其中最大的问题有两点
- 特殊对象
函数没有处理一些特殊对象,如date,set,map等,这可能会导致一些问题。在JavaScript中这些对象是特殊的引用类型,不能简单地被视为普通对象处理 - 原型链的处理
函数也没有处理对象的原型链,如果原对象从某个原型对象继承了属性,那么新对象将无法访问这些属性
幸运的是在ES2022中推出了一个新APIstructedClone,这个API能很轻松的实现深拷贝
structuredClone(value) structuredClone(value, { transfer })- 1
- 2
此API的兼容性
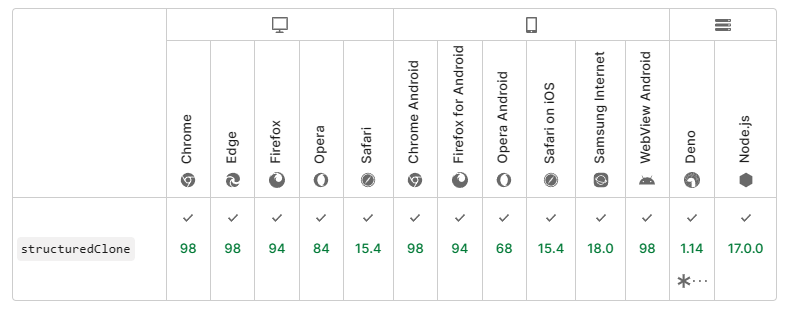
-
相关阅读:
腾讯安全发布《BOT管理白皮书》|解读BOT攻击,探索防护之道
如何修改域名DNS服务器?修改DNS服务器常见问题汇总
自学(网络安全)黑客——高效学习2024
IDEA 2023搭建 SpringMVC +FreeMarker+JDBC
美颜滤镜SDK,企业技术解决方案
神经网络训练防止过拟合和欠拟合的方法
java学习第181天,javaWeb学习第40天,复习第17天;泛型、p228-236(08/03)-6.5h
机器学习算法(一):1. numpy从零实现线性回归
buuctf crypto 【[HDCTF2019]basic rsa】解题记录
VSCode导出markdown为网页时带有目录
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46244470/article/details/132151709
