-
算法刷题-链表
算法刷题-链表
203. 移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。示例 1:
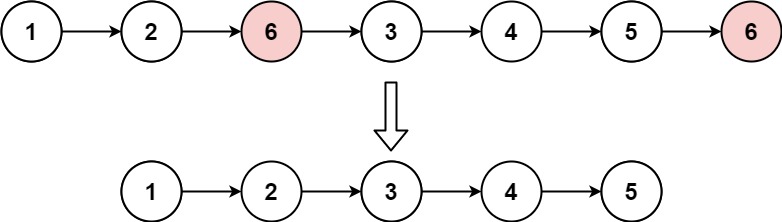
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]- 1
- 2
思路
建立一个虚拟头节点,指向链表的头节点,然后再遍历链表删除值为val的节点,这样比较好方便删除头节点
代码
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { ListNode* head2 =new ListNode(0); head2->next=head; ListNode* cur=head2; while(cur->next!=NULL){ if(cur->next->val==val){ ListNode* tmp=cur->next; cur->next=tmp->next; delete tmp; }else{ cur=cur->next; } } head=head2->next; delete head2; return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
707. 设计链表
你可以选择使用单链表或者双链表,设计并实现自己的链表。
单链表中的节点应该具备两个属性:
val和next。val是当前节点的值,next是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果是双向链表,则还需要属性
prev以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点下标从 0 开始。实现
MyLinkedList类:MyLinkedList()初始化MyLinkedList对象。int get(int index)获取链表中下标为index的节点的值。如果下标无效,则返回-1。void addAtHead(int val)将一个值为val的节点插入到链表中第一个元素之前。在插入完成后,新节点会成为链表的第一个节点。void addAtTail(int val)将一个值为val的节点追加到链表中作为链表的最后一个元素。void addAtIndex(int index, int val)将一个值为val的节点插入到链表中下标为index的节点之前。如果index等于链表的长度,那么该节点会被追加到链表的末尾。如果index比长度更大,该节点将 不会插入 到链表中。void deleteAtIndex(int index)如果下标有效,则删除链表中下标为index的节点。
思路
注意野指针
代码
class MyLinkedList { public: struct node { int val; node *next; node(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} }; MyLinkedList() { sz = 0; head = new node(0); } int get(int index) { node *cur = head->next; if (index < 0 || index >= sz) return -1; while (index--) cur = cur->next; return cur->val; } void addAtHead(int val) { addAtIndex(0, val); } void addAtTail(int val) { addAtIndex(sz, val); } void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { if (index > sz)return; if (index < 0) index = 0; node *cur = head; while (index-- > 0) cur = cur->next; node *tmp = new node(val); tmp->next = cur->next; cur->next = tmp; sz++; } void deleteAtIndex(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= sz)return; node *cur = head; while (index--) cur = cur->next; node *tmp = cur->next; cur->next = tmp->next; delete tmp; tmp = nullptr;//防止野指针 sz--; } private: int sz; node *head; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]- 1
- 2
思路
让每个节点指向前面的节点即可
代码
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* right; ListNode* cur=head; ListNode* pre=nullptr; while(cur){ right=cur->next; cur->next=pre; pre=cur; cur=right; } return pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]- 1
- 2
思路
参考代码随想录中的反转步骤,还是用到虚拟头节点:

代码
ListNode *swapPairs(ListNode *head) { ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head; ListNode *cur = dummyHead; while (cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) { ListNode *node1 = cur->next; ListNode *node2 = node1->next; ListNode *node3 = node2->next; cur->next = node2; node2->next = node1; node1->next = node3; cur = node1; } return dummyHead->next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]- 1
- 2
思路
双指针,让快指针先走n+1步,然后慢指针从头节点开始和快指针一起走,
当快指针走到最后的时候,此时慢指针的下一个节点就是倒数第N个节点,删除即可
代码
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) { ListNode* dummy =new ListNode(0); dummy->next=head; ListNode* fast= dummy; ListNode* slow =dummy; n++; while(n--) fast=fast->next; while(fast!=nullptr) fast=fast->next,slow=slow->next; ListNode* tmp=slow->next; slow->next=tmp->next; delete tmp; return dummy->next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点
headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回null。图示两个链表在节点
c1开始相交**:**题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
思路
因为相交肯定是从最后一个开始香蕉
先计算两个链表的长度,然后让链表长度长的先把多出来的部分走完,再一起往前走,知道相同为止
代码
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { int n=0,m=0; ListNode *dummy=headA; while(dummy!=nullptr) n++,dummy=dummy->next; dummy=headB; while(dummy!=nullptr) m++,dummy=dummy->next; ListNode* curA=headA; ListNode* curB=headB; if(m>n) swap(curA,curB),swap(n,m); while(n>m) curA=curA->next,n--; while(curA!=nullptr){ if(curA==curB) return curA; curA=curA->next,curB=curB->next; } return nullptr; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪
next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果pos是-1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
思路
代码随想录:
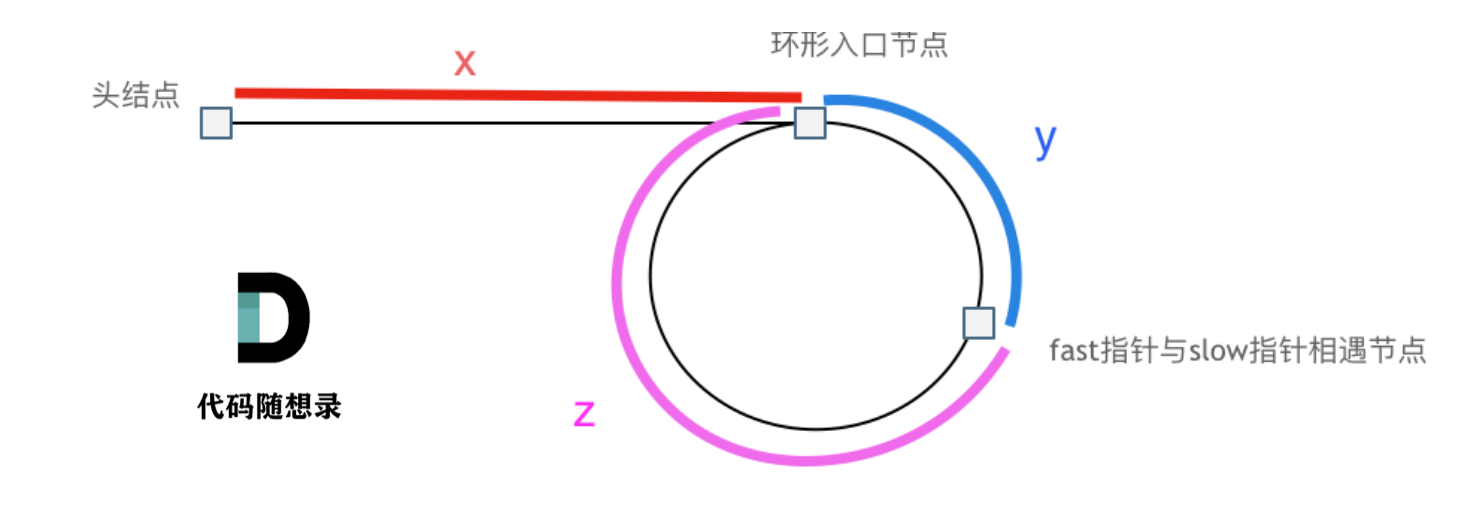
相遇时:
slow指针走了 x + y x+y x+y
fast指针走了 x + y + n ( y + z ) x+y+n(y+z) x+y+n(y+z)
因此: 2 ( x + y ) = x + y + n ( y + z ) 2(x+y)=x+y+n(y+z) 2(x+y)=x+y+n(y+z)
化简得: x = n ( y + z ) − y x=n(y+z)-y x=n(y+z)−y
整理得: x = ( n − 1 ) ( y − z ) + z x=(n-1)(y-z)+z x=(n−1)(y−z)+z
当 n = 1 n=1 n=1的时候, x = z x=z x=z
也就是说:从相遇点和头节点开始同时走,他们第一次相遇的时候就是环形的入口。
代码
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { ListNode *fast=head; ListNode *slow=head; while(fast!=nullptr &&fast->next!=nullptr){ slow=slow->next; fast=fast->next->next; if(slow==fast){ ListNode *a=head; ListNode *b=fast; while(a!=b) a=a->next,b=b->next; return a; } } return nullptr; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
-
相关阅读:
【数据结构与算法】之深入解析“解出数学表达式的学生分数”的求解思路与算法示例
小程序map组件二——[蓝色波浪篇]引入并配置Vant Weapp(详细)+腾讯地图地点搜索插件获取实时位置实战
微信小程序简单输入框界面(实现选择标签功能)
Redis 主从搭建
34、Java——一个案例学会Dom4j解析技术对XML文件的增删改查
使用Vscode创建一个C_Hello程序
openstack计算节点的虚机部署安装
FineReport数据图表制作-标签控件
Educational Codeforces Round 119 (Rated for Div. 2)
10个Reduce函数的使用小技巧
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74085417/article/details/133976502
