-
golang入门笔记——nginx
Nginx介绍
Nginx是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,特点是占用内存少,并发能力强,Nginx专为性能优化而开发,能经受高负载的考验,有报告表明能支持高达50000个并发连接数。
正向代理:通过代理服务器访问目标服务器,我们知道目标服务器的链接,但无法直接访问目标服务器,必须通过代理的方式访问。
反向代理:一个请求访问目标服务器时,请求先到达代理服务器,由代理服务器转发给目标服务器,此时反向代理服务器和目标服务器对外就是一个服务器,暴露的是代理服务器地址,隐藏了真实服务器IP地址。
反向代理:

正向代理:

Nginx的优缺点:优点:
1.占用内存小,可实现高并发连接,处理响应快 2.可实现http服务器、虚拟主机、反向代理、负载均衡 3.Nginx配置简单 4.可以不暴露正式的服务器IP地址- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
缺点:
1.动态处理差:Nginx处理静态文件好,耗费内存少,但是处理动态页面则很鸡肋,现在一般前端用 2.Nginx作为反向代理抗住压力- 1
- 2
Nginx性能为啥这么高
1.异步非阻塞处理机制 2.epoll模型 3.提供队列,排队解决- 1
- 2
- 3
Nginx应用场景
1.http服务器。Nginx是一个http服务可以独立提供http服务。可以做网页静态服务器。 2.虚拟主机。可以实现在一台服务器虚拟出多个网站,例如个人网站使用的虚拟机。 3.反向代理,负载均衡。当网站的访问量达到一定程度后,单台服务器不能满足用户的请求时,需要用多台服务器集 群可以使用nginx做反向代理。并且多台服务器可以平均分担负载,不会应为某台服务器负载高宕机而某台服务器闲 置的情况。 4.nginx 中也可以配置安全管理、比如可以使用Nginx搭建API接口网关,对每个接口服务进行拦截。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
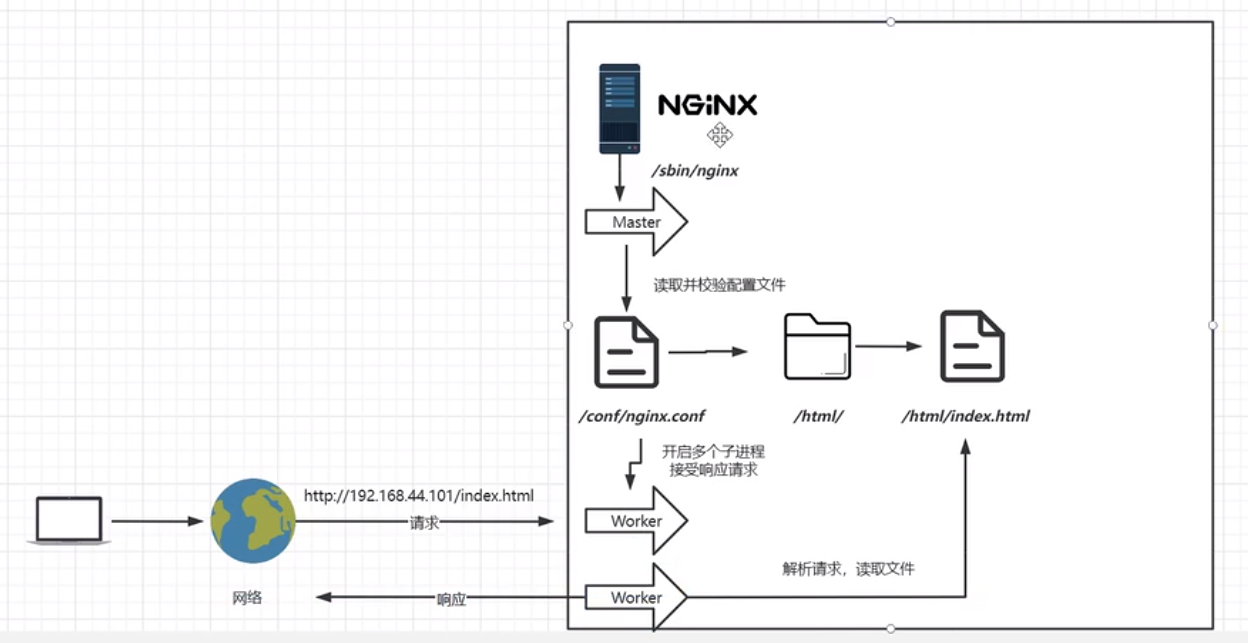
Nginx进程模型:
Nginx的进程分为两种:master进程和worker进程
work进程数量由work_processes决定的
master进程负责接收外界的信号和指令,worker来负责工作,master会监控worker

Nginx模块化体系
Nginx工作原理:1.接收客户端请求:当客户端发起HTTP请求时,Nginx会监听指定的端口并接收请求 2.解析配置文件:Nginx在启动时会加载并解析配置文件,其中包含服务器设置、反向代理规则、缓存配置等 3.处理请求:当收到客户端请求后,Nginx会根据配置文件中的规则进行处理,可根据请求的URL分配给不同的后端 服务,Nginx可对请求进行一系列的处理操作,包括:访问控制、URL重写、gzip压缩、SSL/TLS加密等- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Nginx处理一个HTTP请求的全过程
1.Read Request Headers:解析请求头 2.Identify Configuration Block:识别由哪一个location进行处理,匹配URL 3.Apply Rate Limits:判断是否限速。 4.Perform Authentication:连接控制,验证请求。例如可能根据Referer头部做一些防盗链的设置,或者验证用户的权 限 5.Generate Content:生成返回给用户的响应。为了生成这个响应,做反向代理的时候可能会和上游服务进行通信, 然后这个过程还可能会有些子请求或者重定向,那么还会走一下这个过程。 6.Response Filters:过滤返回给用户的响应。比如压缩响应,或者对图片进行处理 7.记录日志- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Nginx的安装
1.获取nginx安装包:
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.21.6.tar.gz- 1
- 2
2.解压安装包
tar zxvf nginx-1.21.6.tar.gz- 1
3.配置
./configure- 1
4.编译安装
#编译 make #安装 make install- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
5.启动、关闭nginx服务
###启动服务 #需要先进入sbin目录下 cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin #启动nginx服务 ./nginx ###关闭服务 #需要先进入sbin目录下 cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin #关闭nginx服务 ./nginx -s stop #快速停止 ./nginx -s quit #优雅关闭,在退出前完成已经接受的连接请求 ./nginx -s reload #重新加载配置- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
将nginx安装成系统服务
创建服务脚本
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service- 1
服务脚本内容
[Unit] Description=nginx - web server After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid ExecstartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ExecReoad=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload Execstop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop ExecQuit=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit PrivateTmp=true [Insta11] WantedBy=multi-user.target- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
重新加载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload- 1
Nginx文件
主要的文件有三个:conf、html、logs
├── client_body_temp ├── conf │ ├── fastcgi.conf (是fastcgi的配置文件) │ ├── fastcgi.conf.default │ ├── fastcgi_params (是fastcgi的参数文件) │ ├── fastcgi_params.default │ ├── mime.types (记录的是HTTP协议中的Content-Type的值和文件后缀名的对应关系) │ ├── mime.types.default │ ├── nginx.conf (是Nginx的核心配置文件,这个文件非常重要,也是学习的重点) │ ├── nginx.conf.default │ ├── scgi_params (是scgi的参数文件) │ ├── scgi_params.default │ ├── uwsgi_params (是uwsgi的参数文件) │ ├── uwsgi_params.default │ ├── koi-utf (与编码转换映射相关的配置文 件,下面两个也是) │ ├── koi-win │ └── win-utf ├── fastcgi_temp ├── html (存放nginx自带的两个静态的html页面) │ ├── 50x.html (访问失败后的失败页面) │ └── index.html (访问成功的默认首页) ├── logs │ ├── access.log (访问日志) │ ├── error.log (错误日志) │ └── nginx.pid (记录nginx的pid好) ├── proxy_temp ├── sbin (存放执行程序文件nginx) │ └── nginx (用于控制Nginx的启动和停止) ├── scgi_temp └── uwsgi_temp- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
nginx.conf#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #工作的进程个数 #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { #事件驱动模块 worker_connections 1024; #一个work可以创建多少个连接 } http { include mime.types; #引入一个子配置文件,mime.types记录返回的数据是什么类型的文件数据 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件数据类型 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #数据零拷贝 #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #保持连接超时的时间 #gzip on; server { #虚拟主机 vhost listen 80; #监听的端口号 server_name localhost; #主机名,也可以配置域名 #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { #URI,域名之后的路径 root html; #从哪个目录下找这个主机 index index.html index.htm; #默认页 } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # 错误重定向URI location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
ServerName匹配规则:
1.我们可以在同一个ServerName中匹配多个域名,写上面的会优先被匹配 2.完整匹配 3.通配符匹配 4.通配符结束匹配 5.正则匹配,正则开始符~,结束符$,例子:~^[0-9]+\.mmban\.com$- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Nginx常用变量:
$host: 请求的主机头 $remote_addr: 客户端IP地址 $remote_port: 客户端端口号 $remote_user: 已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名 $http_referer: 请求引用地址 $http_user_agent: 客户端代理信息(UA) $http_x_forwarded_for: 相当于网络访问路径 $body_bytes_sent: 页面传送的字节数 $time_local: 服务器时间 $request: 客户端请求 $request_uri: 请求的URI,带参数, 不包含主机名 $request_filename: 请求的文件路径 $request_method: 请求的方法,如GET、POST $args: 客户端请求中的参数 $query_string: 等同于$args, 客户端请求的参数 $nginx_version: 当前nginx版本 $status: 服务器响应状态码 $server_addr: 服务器地址 $server_port: 请求到达的服务器端口号 $server_protocol: 请求的协议版本 $content_type: HTTP请求信息里的Content-Type字段 $content_length: HTTP请求信息里的Content-Length字段 $uri: 请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数,参数位于$args) $document_root: 当前请求在root指令中指定的值 $document_uri: 与$uri相同- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Nginx反向代理
修改conf文件:
worker_processes 1; #工作的进程个数 events { #事件驱动模块 worker_connections 1024; #一个work可以创建多少个连接 } http { include mime.types; #引入一个子配置文件,mime.types记录返回的数据是什么类型的文件数据 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件数据类型 sendfile on; #数据零拷贝 keepalive_timeout 65; #保持连接超时的时间 server { #虚拟主机 vhost listen 80; #监听的端口号 server_name localhost; #主机名,也可以配置域名 location / { #URI,域名之后的路径 proxy_pass http://www.zhangyongjian.top;#代理到这个地址上 } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # 错误重定向URI location = /50x.html { root html; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
proxy_pass 如果配置的是http://zhangyongjian.top,会发生网页的重定向,地址栏会变成www.zhangyongjian.top。proxy_pass不支持https
proxy_pass的不同处理方式:
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080和proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/(多了末尾的/)是不同的的处理方式,而proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/和proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/abc是相同的处理方式。
对于不带URI方式,nginx将会保留location中路径部分
对于带URI方式,nginx将使用诸如alias的替换方式对URL进行替换,并且这种替换只是字面上的替换
location /api2/ { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/; } #当访问 http://localhost/api2/xxx 时,http://localhost/api2/(注意最后的/) #被替换成了http://localhost:8080/,然后再加上剩下的xxx,于是变成http://localhost:8080/xxx。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
server{ listen 80; server_name localhost; location /api1/{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; } #http://localhost/api1/xxx->http://localhost:8080/api1/xxx location /api2{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; } #http://localhost/api2/xxx->http://localhost:8080/api2/xxx location /api3/{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/; } #http://localhost/api3/xxx->http://localhost:8080/xxx location /api4{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/ } #http://localhost/api4/xxx->http://localhost:8080//xxx location /api5/ { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha; } # http://localhost/api5/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/hahaxxx, #请注意这里的haha和xxx之间没有斜杠,分析一下原因。 location /api6/ { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha/; } # http://localhost/api6/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha/xxx location /api7 { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha; } # http://localhost/api7/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha/xxx location /api8 { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/haha/; } # http://localhost/api8/xxx -> http://localhost:8080/haha//xxx,请注意这里的双斜杠。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
负载均衡
在一台主机上该nginx.conf
worker_processes 1; #工作的进程个数 events { #事件驱动模块 worker_connections 1024; #一个work可以创建多少个连接 } http { include mime.types; #引入一个子配置文件,mime.types记录返回的数据是什么类型的文件数据 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件数据类型 sendfile on; #数据零拷贝 keepalive_timeout 65; #保持连接超时的时间 upstream httpds{ #定义一个服务器组 server 192.168.44.102:80 weight=8 down; #weight 访问权重,down是下线,不负载到这台机器 server 192.168.44.103:80 weight=2 backup; #weight 访问权重 backup 没有主机可以用时再负载到这台主机 } server { #虚拟主机 vhost listen 80; #监听的端口号 server_name localhost; #主机名,也可以配置域名 location / { #URI,域名之后的路径 proxy_pass http://httpd;#负载均衡到这个服务器组中 } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # 错误重定向URI location = /50x.html { root html; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34

轮询的方式来进行负责均衡无法保持会话,也就是说登陆之后访问另外一个服务器就获取不到登陆信息
ip_hash:根据来源的ip地址hash计算重定向到一台服务器(不太会用)
upstream myserver{ ip_hash; server 127.0.0.1:8081; server 127.0.0.1:8082; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
least_conn:根据用户访问的url定向访问请求(不太会用)
fair:根据后端服务器响应时间转发请求,响应时间短的优先分配
upstream myserver{ server 127.0.0.1:8081; server 127.0.0.1:8082; fair; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
所谓四层负载均衡指的是OSI七层模型中的传输层,主要是基于IP+PORT的负载均衡
实现四层负载均衡的方式: 硬件:F5、BIG-IP、Radware等 软件:LV2、Nginx、Hayproxy等- 1
- 2
- 3
所谓七层负载均衡指的是在应用层,主要是基于虚拟的URL或主机的负载均衡
实现七层负载均衡的方式: 软件:Nginx、Hayproxy等- 1
- 2
四层和七层负载均衡的区别
1.四层负载均衡数据包是在底层就进行了分发,而七层负载均衡数据包则在最顶端进行分发,所以四层负载均衡的效 率比七层负载均衡的要高 2.四层负载均衡不识别域名,而七层负载均衡识别域名。- 1
- 2
- 3
Nginx七层负载均衡的指令
upstream指令:该指令是用来定义一组服务器,它们可以是监听不同端口的服务器,并且也可以是同时监听TCP和Unix socket的服务器。服务器可以指定不同的权重,默认为1
server指令:该指令用来指定后端服务器的名称和一些参数,可以使用域名、IP、端口或者Unix socket
nginx动静分离

动静分离就是把后端服务需要使用到的静态资源前置放到nginx代理中location /css { root css; index index.html index.htm; } location /js{ root js; index index.html index.htm; } location /img{ root img; index index.html index.htm; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
正则方式:
location ~*/(js|img|css){ alias html; #alias和root的区别 #root的处理结果是:root路径+location路径 #alias的处理结果是:使用alias路径替换location路径 autoindex on; #列出访问目录 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
URLRewrite
location /j{ rewrite ^/([0-9]+).html$ /index.jsp?pageNum=$1 break; #把*.html地址转变为/index。jsp?pageNum=* #flag标记说明: #last 本条规则匹配完成后,继续向下匹配新的location URI规则 #break 本条规则匹配完成即终止,不再匹配后面的任何规则 #redirect 返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址 #permanent 返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址 proxy_pass: http://192.168.44.104:8080; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
防盗链


valid_referers 192.168.44.101; #检测referers if($invalid_referer){ #检测完是无效的引用 return 403; } location ~*/(js|img|css){ root html; index index.html index.htm; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
nginx高可用配置
keepalived:检测对方nginx是否存活

安装keepalived
yum install -y keepalived- 1
vi /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { #全局配置 router id lb111 #标识主机 } vrrp_instance atguigu { #实例名称 state MASTER #当前这台主机是MASTER interface ens33 #网卡名称 virtual_router_id 51 #标识keepalived组 priority 100 #竞选master时的优先级,谁的优先级高,谁是master advert_int 1 #间隔检测的时间 authentication { #nginx组配对认证的相关配置 auth type PASS auth pass 1111 } virtual ipaddress ( #虚拟的ip地址,可以填多个 192.168.200.16 192.168.200.17 192.168.200.18 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
keepalived启动
cd /usr/local/sbin/ ./keepalived- 1
- 2
VRRP (Virtual Route Redundancy Protocol) 协议,翻译过来为虚拟路由冗余协议。VRRP协议将两台或多台路由器设备虚拟成一个设备,对外提供虚拟路由器IP而在路由器组内部,如果实际拥有这个对外IP的路由器如果工作正常的话就是MASTER,MASTER实现针对虚拟路由器IP的各种网络功能。其他设备不拥有该虚拟IP,状态为BACKUP,除了接收MASTER的VRRP状态通告信息以外,不执行对外的网络功能。当主机失效时BACKUP将接管原先MASTER的网络功能。
这个协议是干什么的?
1.选择协议:虚拟一个IP选择节点成为MASTER 2.路由容错协议:Master和Backup路由会有心跳检测,Master会定时告知Backup自己的状态,如果指定时间内, Backup没有接收到这个通知内容,Backup就会替代Master成为新的Master。- 1
- 2
- 3
keepalived之vrrp_script
keepalived只能做到对网络故障和keepalived本身的监控,即当出现网络故障或者keepalived本身出现问题时,进行切换。但是这些还不够,我们还需要监控keepalived所在服务器上的其他业务,比如Nginx,如果Nginx出现异常了,仅仅keepalived保持正常,是无法完成系统的正常工作的,因此需要根据业务进程的运行状态决定是否需要进行主备切换,这个时候,我们可以通过编写脚本对业务进程进行检测监控。
实现步骤:
1.在keepalived配置文件中添加对应的配置项
vrrp_script 脚本名称 { script "脚本位置" interval 3 #执行时间间隔 weight -20 #动态调整vrrp_instance的优先级 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2.编写脚本
ck_nginx.sh

3.为脚本文件设置权限sudo chmod- 1
安全性
https的安全性保障

https升级过程:1.向CA申请证书
2.将证书上传到服务器
3.证书安装
server{ listen 443 ssl; server_name aa.abc.com; ssl_certificate /data/cert/server.crt; ssl_certificate_key /data/cert/server.key; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
4.重启nginx
Nginx限流
Nginx限流就是限制用户请求速度,防止服务器受不了,限流有3种
1.正常限制访问频率(正常变量) 2.突发限制访问频率(突发流量) 3.限制并发连接数- 1
- 2
- 3
Nginx的限流是基于两个模块:
1.漏桶算法:实现的请求限流模块ngx_http_limit_req_module控制速率 2.连接数限流模块:ngx_http_limit_conn_module控制并发数- 1
- 2
1.正常限制访问频率:限制一个用户发送的请求,我Nginx多久接收一个请求。Nginx中使用nginx_limit_req_module模块来限制访问频率,限流的原理实质是基于漏桶算法原理来实现的。在nginx.conf配置文件中可以使用limit_req_zone命令及limit_req命令限制单个IP的请求处理频率
#定义限流维度,一个用户一分钟一个请求进来,多余的全部漏掉 limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/m; #$binary_remote_addr是一种key,表示基于remote_addr(客户端IP)来做限流,binary_的目的是压缩 #内存占用量。 #zone:定义共享内存区来存储访问信息,contentRateLimit:10m表示一个大小为10M,名字为 #contentRateLimit的内存区域。1M能存储16000 IP地址的访问信息,10M可以存储16W IP地址访问信息 #rate:用于设置最大访问速率,rate=10r/s表示每秒最多处理10个请求。Nginx实际上以毫秒为粒度来跟踪 #请求信息,因此10r/s实际上是限制:每100毫秒处理一个请求。这意味着,自上一个请求处理完后,若后续100毫秒内又有请求到达,将拒绝处理该请求。 #所以如果10次请求同时到达,那么只有一个请求能够得到执行,其它的,都会被拒绝 #这不太友好,大部分业务场景下我们希望10个请求都能得到执行 #因此,可以配置burst #绑定限流维度 server{ location /seckill.html{ limit_req zone=one; proxy_pass http://lj_seckill; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
1r/s代表1秒一个请求,1r/m一分钟接收一个请求,如果Nginx这时还有别人的请求没有处理完,Nginx就会拒绝处理该用户请求。
2.突发限制访问频率(突发流量):
限制一个用户发送的请求,我Nginx多久接收一个。
上面的配置一定程度可以限制访问频率,但是也存在着一个问题:如果突发流量超出请求被拒绝处理,无法处理活动时候的突发流量,这时候应该如何进一步处理呢?
Nginx提供burst参数结合nodelay参数可以解决流量突发的问题,可以设置能处理的超过设置的请求数外能额外处理的请求数。我们可以将之前的例子添加burst参数以及nodelay参数:#定义限流维度,一个用户一分钟一个请求进来,多余的全部漏掉 limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/m; #绑定限流维度 server{ location/seckill.html{ limit_req zone=zone burst=5 nodelay; proxy_pass http://lj_seckill; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
burst=5 nodelay代表Nginx对于一个用户的请求会立即处理前五个,多余的就慢慢来落,没有其他用户的请求我就处理你的,有其他的请求的话我Nginx就漏掉不接受你的请求
- 限制并发连接数
Nginx中的ngx_http_limit_conn_module模块提供了限制并发连接数的功能,可以使用limit_conn_zone指令以及limit_conn执行进行配置。
http { limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=myip:10m; limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=myServerName:10m; } server { location / { limit_conn myip 10; limit_conn myServerName 100; rewrite / http://www.lijie.net permanent; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
上面配置了单个IP同时并发连接数最多只能10个连接,并且设置了整个虚拟服务器同时最大并发数最多只能100个链接。当然,只有当请求的header被服务器处理后,虚拟服务器的连接数才会计数。
Nginx缓存集成
Nginx是从0.7.48版开始提供缓存功能。Nginx是基于Proxy Store来实现的,其原理是把URL及相关组合当做Key,在使用MD5算法对Key进行哈希,得到硬盘上对应的哈希目录路径,从而将缓存内容保存在该目录中。它可以支持任意URL连接,同时也支持404/301/302这样的非200状态码。Nginx即可以支持对指定URL或者状态码设置过期时间,也可以使用purge命令来手动清除指定URL的缓存。

Nginx缓存设置的相关指令:Nginx的web缓存服务主要是使用ngx_http_proxy_module模块相关指令集来完成,接下来我们把常用的指令来进行介绍下。
proxy_cache_path:该指定用于设置缓存文件的存放路径。
levels:指定该缓存空间对应的目录层数,最多可以设置3层,每层取值为1|2

keys_zone:用来为这个缓存区设置名称和指定大小

inactive:指定缓存的数据多次时间未被访问就将被删除

max_size:设置最大缓存空间,如果缓存空间存满,默认会覆盖缓存时间最长的资源

http{ proxy_cache_path /usr/local/proxy_cache levels=2:1 keys_zone=itcast:200m inactive=1d max_size=20g; }- 1
- 2
- 3
proxy_cache:该指令用来开启或关闭代理缓存,如果是开启则自定义使用哪个缓存区来进行缓存
zone_name:指定使用缓存区的名称

proxy_cache_key:该指令用来设置web缓存的key值,Nginx会根据key值MD5哈希存缓存

proxy_cache_valid:使用该指令用来对不同状态码的URL设置不同的缓存时间

proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m; proxy_cache_valid 404 1m; #为200和302的响应URL设置10分钟缓存,为404的响应URL设置1分钟缓存 proxy_cache_valid any lm; #对所有响应状态码的URL都设置1分钟缓存- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
proxy_cache_min_uses:该命令用来设置资源被访问多少次后被缓存

proxy_cache_min_uses:该指令用来设置资源被访问多少次后被缓存

proxy_cache_methods:该指令用户设置缓存哪些HTTP方法

默认缓存HTTP的GET和HEAD方法,不缓存POST方法http{ proxy_cache_path /usr/local/proxy_cache levels=2:1 keys_zone=itcast:200m inactive=1d max_size=20g; location /{ proxy_cache $scheme$proxy_hosts$request_uri; proxy_cache_key itheima; proxy_cache_valid 200 5d; proxy_cahche_valid any 1m; proxy_cache_min_uses 5; proxy_pass 127.0.0.1:8080/js/; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
proxy_no_cache:该指令是用来定义不将数据进行缓存的条件

proxy_no_cache $cookie_nocache $arg_nocache $arg_comment;- 1
proxy_cache_bypass:该指令用来设置不从缓存中获取数据的条件

proxy_cache_bypass $cookie_nocache $arg_nocache $arg_comment;- 1
上述两指令都有一个指定的条件,这个条件可以是多个,并且多个条件中至少有一个不为空且不等于"0”,则条件满足成立。上面给的配置实例是从官方网站获取的,里面使用到了三个变量,分别是 c o o k i e n o c a c h e 、 cookie_nocache、 cookienocache、arg_nocache、$arg_comment
$cookie_nocache 指的是当前请求的cookie中键的名称为nocache对应的值 $arg_nocache和$arg_comment 指的是当前请求的参数中属性名为nocache和comment对应的属性值- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
http{ log_format main $schemes$proxy_hosts$request_uri; log_format params $cookie_nocache|$arg_nocache|$arg_comment; upstream backend { server 192.168.200.146:8080; } server { listen 8081; server_name localhost; location / { access_log logs/access_params.log params; #打印的日志文件和日志格式 root html; index index.html; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Lua脚本
lua的安装
1.下载源码压缩包
wget https://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.4.1.tart.gz- 1
2.安装lua
cd lua-5.4.1 make linux test make install- 1
- 2
- 3
Lua的语法:
Lua有两种交互方式:交互式和脚本式
Lua交互式编程模式可以通过命令lua -i或lua来启用
第一个lua脚本
#!/usr/local/bin/lua print("hello world!!!")- 1
- 2
注释符
– 单行注释
–[[
多行注释
–]]lua关键字:

lua的8个数据类型类型字段 类型名称 nil 空,无效值 boolean 布尔值,true/false number 数值 string 字符串 function 函数 table 表 thread 线程 userdata 用户数据 可以通过type函数获取变量类型
字符串的定义中,用[[]]代替··
{}代表表,也可以创建数组
--定义数组 arr={"TOM","JERRY","ROSE"} --数组下标从1开始 arr={} arr["X"]=10 arr["Y"]=20 --arr["X"]和arr.X都能获取到- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
function:函数定义
function functionName(params) end function add(a,b) print(a,b) end function add(...) local a,b,c=... print(a,b,c) end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
Lua控制结构
if条件判断
function testif(a) if a>0 then print("正数") return "正数" elseif a==0 then print("0") return "0" else print("负数") return "负数" end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
while循环
function testwhile() while true do print("hello world!") end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
repeat循环
function testRepeat() local i=10 repeat print(i) i=i-1 until i<1 end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
for循环:数值型for循环和泛型for循环
--数值型for循环 function testfor() for i = 0,100,10 do --从0开始,到100,步长为10,默认步长是1 print(i) end end --泛型for循环 function testfor2(x) for i,v in ipairs(x) do print(i,v) end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
OpenRestry
前面我们提到过,openResty是由淘宝工程师开发的,所以其官方网站(http://openresty.org/)我们读起来是非常的方便。OpenResty是一个基于Nginx与 Lua的高性能 Web平台,其内部集成了大量精良的Lua 库、第三方模块以及大多数的依赖项。用于方便地搭建能够处理超高并发、扩展性极高的动态 Web 应用、Web 服务和动态网关。所以本身OpenResty内部就已经集成了Nginx和Lua,所以我们使用起来会更加方便。
OpenRestry的安装:
(1)下载openResty: https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.15.8.2.tar.gz
(2)使用wget下载: wget https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.15.8.2.tar.gz
(3)解压缩: tar -zxf openresty-1.15.8.2.tar.gz
(4)进入openResty目录: cd openresty-1.15.8.2
(5)执行命令:./configure
(6)执行命令:make && make install
(7)进入openResty的目录,找到nginx:cd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/
(8)在conf目录下的nginx.conf添加如下内容location /lua{ default_type 'text/html' content_by_lua 'ngx.say("HELLO,OpenRestry
")' }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(9)在openresty的sbin目录下启动nginx
(10)通过浏览器访问测试

location /getByGender{ default_type 'text/html'; set_by_lua $param " --获取URL上的参数对应的值 name gender local uri_args=ngx.req.get_uri_args() local name=uri_args['name'] local gender=uri_args['gender'] --条件判断 if gender 1 先生 0 女士 if gender=='1' then return name..'先生' else if gender=='0' then return name..'女士' else return name end "; return 200 $param; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
nginx工作原理
当客户端发起HTTP请求时,Nginx会监听指定的端口(默认是80)并接收请求。Nginx接收到请求后,会根据配置文件中的规则进行处理,它可以将请求的URL分给不同的后端服务器,或者直接提供静态文件。在请求处理阶段,Nginx会对请求进行一系列的处理操作,包括:访问控制、URL重写、gzip压缩、SSL/TLS加密等。Nginx是一个事件驱动的异步服务器,用较少的系统资源,能够处理大量并发连接,并具有良好的性能和可靠性。
-
相关阅读:
ARM pwn 入门 (4)
2022-09-09 Unity InputSystem1——概述
java计算机毕业设计教务管理系统源码+数据库+lw文档+系统
产品经理进阶:产品的起点是发现并理解问题
Flask——基于python完整实现客户端和服务器后端流式请求及响应
Vue/React 项目部署到服务器后,刷新页面出现404报错
BUUCTF 乌镇峰会种图 1
asp.net core 远程调试
Vue前端项目安装及相关问题解决
线性表——顺序表和链表
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43716830/article/details/132555540
