-
第1章 强化学习基础
1.1 强化学习基础(上)- Overview
What is reinforcement learning

a computational approach to learning whereby an agent tries to maximize the total amount of reward it receives while interacting with a complex and uncertain environment. -Sutton and Barto
Supervised Learning: Image Classification
- Annotated images, data follows i.i.d distribution.
- Learners are told what the labels are.

Reinforcement learning: Playing Breakout
- Data are not i,i,d. Instead, a correlated times series data
- No instant feedback or label for correct action
Action: Move LEFT or Right



Difference between Reinforcement learning and Supervised Learning
- Sequential data as input (not i.i.d)
- The learner is not told which actions to take, but instead must discover which actions yield the most reward by trying them.
- Trial-and-error exploration (balance between exploration and exploitation)
- There is no supervisor, only a reward signal, which is also delayed
Features of Reinforcement learning
- Trial-and-error exploration
- Delayed reward
- Time matters (sequential data, non i.i.d data)
- Agent’s actions affect the subsequent data it receives (agent’s action changes the environment)
Big deal: Able to Achieve Superhuman Performance
- Upper bound for Supervised Learning is human-performance.
- Upper bound for reinforcement learning?

https://www/youtube.com/watch?v=WXuK6gekU1Y
Examples of reinforcement learning
-
A chess player makes a move: the choice is informed both by planning-anticipating possible replies and counterreplies.

-
A gazelle calf struggles to stand, 30 min later it runs 36 kilometers per hour.

-
Portfolio management.

-
Playing Atari game

RL example: Pong
Action: move UP or Down
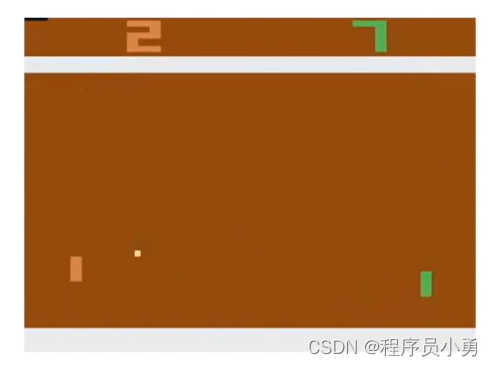
From Andrej Karpathy blog: http://karpathy.github.io/2016/05/31/rl/





Deep Reinforcement Learning: Deep Learning + Reinforcement Learning
- Analogy to traditional CV and deep CV


- Standard RL and deep RL


Why RL works now?
- Computation power: many GPUs to do rial-and-error exploration
- Acquire the degree of proficiency in domains governed by simple, known rules
- End-to-end training, features and policy are jointly optimized toward the end goal.

More Examples on RL

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gn4nRCC9TwQ

https://ai.googleblog.com/2016/03/deep-learning-for-robots-learning-from.html

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jwSbzNHGflM

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ixmE5nt2o88
1.2 强化学习基础(下)- Introduction to Sequential Decision Making
The agent learns to interact with the environment

Rewards
- A reward is a scalar feedback signal
- Indicate how well agent is doing at step t
- Reinforcement Learning is based on maximization of rewards:
All goals of agent can be described by the maximization of expected cumulative reward.
Examples of Rewards
- Chess player play to win:
+/- reward for winning or losing a game
- Gazelle calf struggles to stand:
+/- reward for running with its mom or being eaten
- Manage stock investment
+/- reward for each profit or loss in $
- Play Atari games
+/- reward for increasing or decreasing scores
Sequential Decision Making
-
Objective of the agent: select a series of actions to maximize total future rewards
-
Actions may have long term consequences
-
Reward may be delayed
-
Trade-off between immediate reward and long-term reward
-
The history is sequence of observation, actions, rewards.
H t = O 1 , R 1 , A 1 , . . . , A t − 1 , O t , R t H_{t} = O_{1}, R_{1}, A_{1}, ..., A_{t - 1}, O_{t}, R_{t} Ht=O1,R1,A1,...,At−1,Ot,Rt -
What happens next depends on the history
-
State is the function used to determine what happens next
S t = f ( H t ) S_{t} = f(H_{t}) St=f(Ht)

-
Environment state and agent state
S t e = f e ( H t ) S t a = f a ( H t ) S_{t}^{e} = f^{e}(H_{t}) \,S_{t}^{a} = f^{a}(H_{t}) Ste=fe(Ht)Sta=fa(Ht) -
Full observability: agent directly observe the environment state, formally as Markov decision process (MDP)
O t = S t e = S t a O_{t} = S_{t}^{e} = S_{t}^{a} Ot=Ste=Sta -
Partial observability: agent indirectly observe the environment, formally as partial observable Markov decision process (POMDP)
- Black jack (only see public cards), Atari game with pixel observation
Major Components of an RL Agent
An RL agent may include one or more of these components:
- Policy: agent’s behavior function
- Value function: how good is each state or action
- Model: agent’s state representation of the environment
Policy
- A policy is the agent’s behavior model
- It is a map function state/observation to action.
- Stochastic policy: Probabilistic sample π ( a ∣ s ) = P [ A t = a ∣ S t = s ] \pi (a | s) = P[A_{t} = a | S_{t} = s] π(a∣s)=P[At=a∣St=s]
- Deterministic policy: a ∗ = a r g m a x a π ( a ∣ s ) a* = arg \, \underset{a}{max} \, \pi (a | s) a∗=argamaxπ(a∣s)

Value function
-
Value function: expected discounted sum of future rewards under a particular policy π \pi π
-
Discount factor weights immediate vs future rewards
-
Used to quantify goodness/badness of states and actions
v π ( s ) ≐ E π [ G t ∣ S t = s ] = E π [ ∑ k = 0 ∞ γ k R t + k + 1 ∣ S t = s ] , f o r a l l s ∈ S v_{\pi}(s) \doteq E_{\pi}[G_{t} | S_{t} = s] = E_{\pi}[\sum_{k = 0}^{∞}γ^{k}R_{t + k + 1} | S_{t} = s], for \, all \, s ∈ S vπ(s)≐Eπ[Gt∣St=s]=Eπ[k=0∑∞γkRt+k+1∣St=s],foralls∈S -
Q-function (could be used to select among actions)
q π ( s , a ) ≐ E π [ G t ∣ S t = s , A t = a ] = E π [ ∑ k = 0 ∞ γ k R t + k + 1 ∣ S t = s , A t = a ] . q_{\pi}(s, a) \doteq E_{\pi}[G_{t} | S_{t} = s, A_{t} = a] = E_{\pi}[\sum_{k = 0}^{∞}γ^{k}R_{t + k + 1} | S_{t} = s, A_{t} = a]. qπ(s,a)≐Eπ[Gt∣St=s,At=a]=Eπ[k=0∑∞γkRt+k+1∣St=s,At=a].
Model
A model predict what the environment will do next
predict the next state: P S S ′ a = P [ S t + 1 = s ′ ∣ S t = s ] , A t = a P_{SS'}^{a} = \mathbb{P}[S_{t + 1} = s' | S_{t} = s], A_{t} = a PSS′a=P[St+1=s′∣St=s],At=a
Markov Decision Processes (MDPs)
Definition of MDP
-
P a P^{a} Pa is dynamics/transition model for each action
P ( S t + 1 = s ′ ∣ S t = s , A t = a ) P(S_{t + 1} = s' | S_{t} = s, A_{t} = a) P(St+1=s′∣St=s,At=a) -
R is reward function R ( S t = s , A t = a ) = E [ R t ∣ S t = s , A t = a ] R(S_{t} = s, A_{t} = a) = \mathbb{E}[R_{t} | S_{t} = s, A_{t} = a] R(St=s,At=a)=E[Rt∣St=s,At=a]
-
Discount factor γ ∈ [0, 1]

Maze Example

- Rewards: -1 per time-step
- Actions: N, E, S, W
- States: Agent’s location
From David Silver Slide
Maze Example: Result from Policy-based RL

- Arrows represent policy π ( s ) \pi(s) π(s) for each state s
Maze Example: Result from Values-based RL

- Numbers represent value v π ( s ) v_{\pi(s)} vπ(s) for each state s
Types of RL Agents based on What the Agent Learns
- Values-based agent:
- Explicit: Value function
- Implicit: Policy (can derive a policy from value function)
- Policy-based agent:
- Explicit: policy
- No value function
- Actor-Critic agent:
- Explicit: policy and value function
Types of RL Agents on if there is model
- Model-based
- Explicit: model
- May or may not have policy and/or value function
- Model-free
- Explicit: value function and/or policy function
- No model.
Types of RL Agents

Credit: David Silver’s slide
Exploration and Exploitation
-
Agent only experiences what happens for the actions it tries!
-
How should an RL agent balance its actions?
- Exploration: trying new things that might enable the agent to make better decisions in the future
- Exploitation: choosing actions that are expected to yield good reward given the past experience
-
Often there may be an exploration-exploitation trade-off
- May have to sacrifice reward in order to explore & learn about potentially better policy
-
Restaurant Selection
- Exploitation: Go to your favourite restaurant
- Exploration: Try a new restaurant
-
Online Banner Advertisements
- Exploitation: Show the most successful advert
- Exploration: Show a different advert
-
Oil Drilling
- Exploitation: Drill at the best-known location
- Exploration: Drill at a new location
-
Game Playing
- Exploitation: Play the move you believe is
- Exploration: play an experimental move
Coding
https://github.com/metalbubble/RLexample
OpenAI: specialized in Reinforcement Learning
- https://openai.com/
- OpenAI is a non-profit AI research company, discovering and enacting the path to safe artificial general intelligence (AGI).

OpenAI gym library

https://github.com/openai/retro

Algorithmic interface of reinforcement learning

import gym env = gym.make("Taxi-v2") observation = env.reset() agent = load_agent() for step in range(100): action = agent(observation) observation, reward, done, info = env.step(action)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Classic Control Problems

https://gym.openai.com/envs/#classic_control
Example of CartPole_v0

https://github.com/openai/gym/blob/master/gym/envs/classic_control/cartpole.py
Example code
import gym env = gym.make("CartPole-v0") env.reset() env.render() # display the rendered scene action = env.action_space.sample() observation, reward, done, info = env.step(action)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Cross Entropy method(CEM)
https://gist.github.com/kashif/5dfa12d80402c559e060d567ea352c06
Deep Reinforcement Learning Example
- Pong example
import gym env = gym.make("Pong-v0") env.reset() env.render() # display the rendered scene python my_random_agent.py Pong-v0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

python pg-pong.py- 1
Loading weight: pong_bolei.p(model trained over night)
- Look deeper into the code
observation = env.reset() cur_x = prepro(observation) x = cur_x - pre_x pre_x = cur_x aprob, h = policy_forward(x) Randomized action: action = 2 if np.random.uniform() < aprob else 3 # roll the dice!- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
h = np.dot(W1, x) h[h<0] = 0 # ReLU nonlinearity: threshold at zero logp = np.dot(W2,h) # compute log probability of going up p = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-logp)) #sigmoid function (gives probability of going up)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
How to optimize the W1 and W2?
Policy Gradient!(To be introduced in future lecture)

http://karpathy.github.io/2016/05/31/rl
Homework and What’s Next
- Play with OpenAI gym and the example code
https://github.com/cuhkrlcourse/RLexample
- Go through this blog in detail to understand pg-pong.py
-
相关阅读:
开发微信公众号本地调试【内网穿透】
【C++】C++11新特性
基于高斯混合模型的视频背景提取和人员跟踪算法matlab仿真
C++实现查询本机信息并且上报
力扣 (LeetCode) LeetCode HOT 100
eshop(商城管理系统)MySQL源码
java-net-php-python-springboot家政服务平台计算机毕业设计程序
深入认识Linux
论文投稿指南——收藏|SCI论文投稿注意事项
flink技术总结待续
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43909650/article/details/128028885