-
TCP粘包和拆包
TCP粘包和拆包
(1)TCP是面向连接的,面向流的,提供可靠性服务。收发两端(客户端和服务端)都要有一一成对的socket,因此,发送端为了将多个发给接收端的包,更有效的发给对方,使用了优化方法(Nagle算法),将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据,合并成一个大的数据块,然后进行封包。这样做虽然提高了效率,但是接收端难于分辨出完整的数据包,因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的。
(2)由于TCP无消息保护边界,需要在接收端处理消息边界问题,也就是我们所说的粘包和拆包问题。
(3)TCP粘包、拆包图解

下面我们通过Netty实验还原场景:
我们通过这样的方法来还原粘包和拆包场景,客户端循环想服务端发送10条消息,服务端每次接收到消息即想客户端返回一个UUID,我们可以通过观察,这10条消息服务端接收过程中并不是一次性接收的,并且每次发送接收结果不一,说明部分消息发生了粘包现象(拆包现象)服务端:
MyServerpackage com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import com.sgg.Netty.simple.NettyServerhandler; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //创建BossGroup和WorkerGroup //说明 //1、创建两个线程组BossGroup和WorkerGroup //2、BossGroup只负责处理请求,真正和客户端的业务处理会交给WorkerGroup //3、两个都是无限循环 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //创建服务端的启动对象,配置启动参数 ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //使用链式变成来进行设置 bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) //设置两个线程组 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用NioServerSocketChannel作为服务器的通道实现 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128) //设置线程队列的连接个数 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true) //设置保持活动连接状态 .childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); System.out.println(".....服务器准备好了"); // Future-Listener机制 //绑定一个端口并且同步,生成一个ChannelFuture对象 ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync(); //给cf注册监听器,监控我们关心的事件 cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception { if(cf.isSuccess()){ System.out.println("监听端口成功"); }else{ System.out.println("监听端口失败"); } } }); //对关闭通道进行监听 cf.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
MyServerInitializer
package com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyServerhandler()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
MyServerhandler
package com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.UUID; public class MyServerhandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception { // byte[] buffer = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()]; byteBuf.readBytes(buffer); //将buffer转成字符串 String message = new String(buffer, Charset.forName("utf-8")); System.out.println("服务器接收到数据"+ message); System.out.println("服务器端接收到消息="+ (++this.count)); //服务端回送数据给客户端,回送 一个随机的ID ByteBuf responseByteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(UUID.randomUUID().toString()+" ",Charset.forName("utf-8")); channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(responseByteBuf); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
MyClient
package com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import com.sgg.Netty.http.TestServerInitializer; import com.sgg.Netty.simple.NettyClienthandler; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; public class MyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //客户端需要一个事件循环组 NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //创建客户端启动对象 //注意客户端不是ServerBootstrap,是Bootstrap Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); //设置相关参数 bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new MyClientInitializer()); System.out.println("客户端OK"); //启动客户端 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6668).sync(); //给关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { //关闭 eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
MyClientInitializer
package com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyClienthandler()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
MyClienthandler
package com.sgg.Netty.TCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class MyClienthandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception { byte[] buffer = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes()]; byteBuf.readBytes(buffer); String message = new String(buffer,Charset.forName("utf-8")); System.out.println("客户端接收到消息="+message); System.out.println("客户端接收消息数量="+(++this.count)); } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //使用客户端发送10条数据 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,server"+i, Charset.forName("utf-8")); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
最终我们可以看到:
服务端入下,同样客户端返回的随机数个数与接收次数统一
 那么我们怎么解决TCP的粘包和拆包呢??
那么我们怎么解决TCP的粘包和拆包呢??TCP粘包和拆包解决方案
(1)使用自定义协议+编解码器 来解决
(2)关键就是要解决 服务器每次读取数据长度的问题,这个问题解决,就不会出现服务器多读或少读数据的问题,从而避免TCP粘包和拆包具体实例:
(1)要求客户端发送5个Message对象,客户端每次发送一个Message对象
(2)服务端每次接收一个Message,分5次进行解码,每读到一个Message,会回复一个Message对象给客户端。下面我们来讲解一下我们的思路:
(1)首先我们需要定义一个协议包的对象,也就是定义协议传输的格式
(2)我们需要根据这个协议包的格式来编写编码解码器的handler:MyMessageEncoder、MyMessageDecoder
(3)我们编写具体的消息发送和消息响应的自定义handler

下面我们来看具体实现:
MessageProtocal (协议包类)package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; //协议包 public class MessageProtocal { private int len;// 关键 private byte[] content; public int getLen() { return len; } public void setLen(int len) { this.len = len; } public byte[] getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(byte[] content) { this.content = content; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
MyMessageEncoder (编码器类:将消息转换成协议包对象)
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder; public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<MessageProtocal> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, MessageProtocal messageProtocal, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyMessageEncoder encode 方法调用"); byteBuf.writeInt(messageProtocal.getLen()); byteBuf.writeBytes(messageProtocal.getContent()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
MyMessageDecoder (解码器类:将协议包对象解码为消息)
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder; import java.util.List; public class MyMessageDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> { @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyMessageDecoder decode方法被调用"); //获取length、content int length= byteBuf.readInt(); byte[] content = new byte[length]; byteBuf.readBytes(content); //封装成MessageProtlcol对象,放入byteBuf,传递到下一个handler MessageProtocal messageProtocal = new MessageProtocal(); messageProtocal.setLen(length); messageProtocal.setContent(content); //将封装的messageProtocal对象放入list list.add(messageProtocal); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
服务端类:MyServer、MyServerInitializer、MyServerhandler
MyServerpackage com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //创建BossGroup和WorkerGroup //说明 //1、创建两个线程组BossGroup和WorkerGroup //2、BossGroup只负责处理请求,真正和客户端的业务处理会交给WorkerGroup //3、两个都是无限循环 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //创建服务端的启动对象,配置启动参数 ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //使用链式变成来进行设置 bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) //设置两个线程组 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用NioServerSocketChannel作为服务器的通道实现 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128) //设置线程队列的连接个数 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true) //设置保持活动连接状态 .childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); System.out.println(".....服务器准备好了"); // Future-Listener机制 //绑定一个端口并且同步,生成一个ChannelFuture对象 ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync(); //给cf注册监听器,监控我们关心的事件 cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception { if(cf.isSuccess()){ System.out.println("监听端口成功"); }else{ System.out.println("监听端口失败"); } } }); //对关闭通道进行监听 cf.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
MyServerInitializer
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder()); //添加加码器handler到pipeline pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder()); //添加解码器handler到pipeline pipeline.addLast(new MyServerhandler()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
MyServerhandler
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.UUID; public class MyServerhandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocal> { private int count; @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, MessageProtocal messageProtocal) throws Exception { //接收到数据,并处理 int len = messageProtocal.getLen(); byte[] content = messageProtocal.getContent(); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("服务器收到消息如下:"); System.out.println("长度="+len); System.out.println("内容="+new String(content,Charset.forName("utf-8"))); System.out.println("服务器接收到消息包数量:"+(++this.count)); //回复消息 //定义一个字符串 String responseContent = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); //将字符串转为byte数组 byte[] rescontent = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8"); //得到数据长度 int reslength = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8").length; //封装成messageProtocal1对象 MessageProtocal messageProtocal1 = new MessageProtocal(); messageProtocal1.setLen(reslength); messageProtocal1.setContent(rescontent); channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(messageProtocal1); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
客户端类:MyClient、MyClientInitializer、MyClienthandler
MyClientpackage com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; public class MyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //客户端需要一个事件循环组 NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //创建客户端启动对象 //注意客户端不是ServerBootstrap,是Bootstrap Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); //设置相关参数 bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new MyClientInitializer()); System.out.println("客户端OK"); //启动客户端 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6668).sync(); //给关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { //关闭 eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
MyClientInitializer
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new MyClienthandler()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
MyClienthandler
package com.sgg.Netty.protocolTCP; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class MyClienthandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocal> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, MessageProtocal messageProtocal) throws Exception { int len = messageProtocal.getLen(); byte[] content = messageProtocal.getContent(); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("客户端接收消息如下:"); System.out.println("长度:"+len); System.out.println("内容:"+new String(content,Charset.forName("utf-8"))); System.out.println("客户端接收消息数量"+(++this.count)); } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //使用客户端发送10条数据 for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ String mes = "今天天气冷"; byte[] content = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")); int length = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")).length; //创建协议包对象 MessageProtocal messageProtocal = new MessageProtocal(); messageProtocal.setLen(length); messageProtocal.setContent(content); ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocal); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { System.out.println("异常信息="+cause.getMessage()); ctx.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
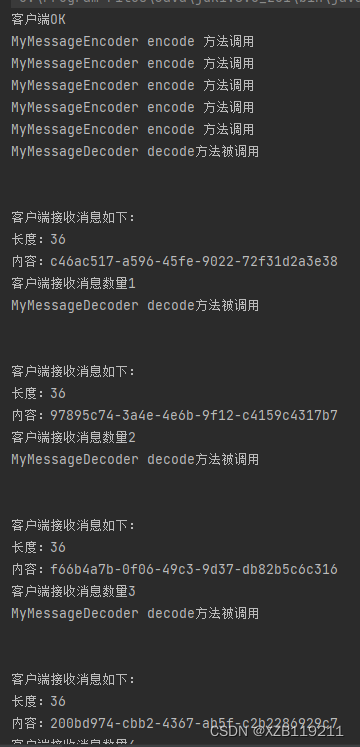
如上我们可以得到结果如下,不论怎么发送,消息永远不会发生粘包和拆包的现象:

-
相关阅读:
docker下载镜像慢
SpringBoot + Vue 实现侧边栏目录动态展示
MySQL常用函数大全(面试篇)
111.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇9]—[Windows 2008 R2内核溢出提权]
[Work Summary] Python将PDF转换成Word文档
基于驾驶训练优化算法的函数寻优算法
一文细谈SNN的基本数学原理,LIF模型,STDP与STBP学习方法
go 语言爬虫库goQuery 的详细使用(知乎日报详情页解析示例)
springboot+skywalking初体检
【AGC】云托管新建站点时间过长的问题排查方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/XZB119211/article/details/127891217
