Morris 遍历实现二叉树的遍历
作者:Grey
原文地址:
说明#
Morris 遍历可以实现二叉树的先,中,后序遍历,且时间复杂度O(N), 空间复杂度可以做到O(1)。
Morris 遍历流程#
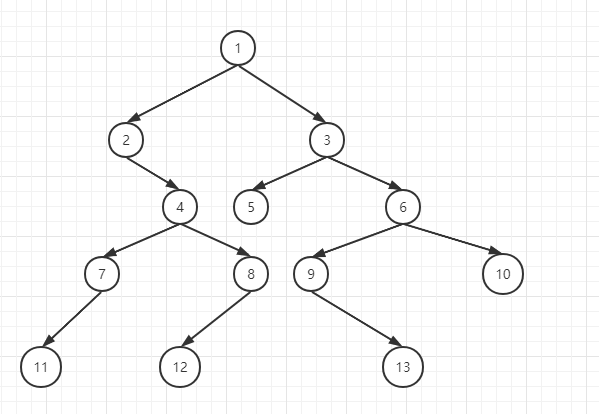
假设有一棵如下的二叉树
Morris遍历的流程主要分如下几个步骤:
第一步,从头节点开始遍历。
第二步,假设当前遍历的节点是cur。
第三步,如果cur无左树, cur来到其右树上,即:cur = cur.right
第四步,如果cur有左树,找到cur左树最右节点,假设叫mostRight,则有如下两种小情况:
情况1,如果mostRight的右指针指向空, 则将mostRight的右指针指向cur,即:mostRight.right = cur, 然后将cur向左移动,即:cur = cur.left,
情况2,如果mostRight的右指针指向当前节点cur,则将mostRight的右指针指向空,即:mostRight.right = null,然后将cur向右移动,即:cur = cur.right。
第五步:当cur = null,遍历结束。
根据如上流程,示例二叉树的Morris遍历序列为:
1-->2-->4-->7-->11-->7-->4-->8-->12-->8-->1-->3-->5-->3-->6-->9-->13-->6-->10
Morris遍历可以实现在O(N)时间复杂度内,用O(1)的空间复杂度实现对树的遍历,而且,只要某个节点有右树,则这个节点一定会被遍历两次,我们可以通过Morris遍历来实现二叉树的先,中,后序遍历,做到时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(1)。
代码实现如下:
public class Code_Morris {
//当前是cur
//1. cur无左树,cur = cur.right
//2. cur有左树,找到左树最右节点mostRight
// a. mostRight的右指针指向null, mostRight.right = cur, cur = cur.right
// b. mostRight的右指针指向当前节点cur,mostRight.right = null, cur = cur.right
//3. cur = null 停
public static void morrisPrint(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("....morris order....");
TreeNode cur = head;
System.out.print(cur.val + "-->");
TreeNode mostRight;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
System.out.print(cur.val + "-->");
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
}
}
cur = cur.right;
if (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + "-->");
}
}
}
}
Morris遍历实现先序遍历#
根据Morris的遍历结果,没有右树的点只会遍历一次,有右树的点会遍历两次,针对遍历一次的点,遍历到就收集,针对遍历两次的点,第一次遍历到就收集,第二次遍历到不收集,整个流程跑完,则得到了先序遍历的结果。
代码如下:
public static List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode mostRight;
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
// 有右树,第一次来到自己就收集
ans.add(cur.val);
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
// mostRight.right = cur;
mostRight.right = null;
}
} else {
// 没有右树的,来到就收集
ans.add(cur.val);
}
cur = cur.right;
}
return ans;
}
测评链接:LeetCode 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Morris遍历实现中序遍历#
针对遍历一次的点,遍历到就收集,针对遍历两次的点,第一次遍历到不收集,第二次遍历才收集,整个流程跑完,则得到了中序遍历的结果。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode mostRight;
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
// 来到自己两次的点,第二次来到才收集
ans.add(cur.val);
mostRight.right = null;
}
} else {
// 只来到自己一次的点,来到就收集
ans.add(cur.val);
}
cur = cur.right;
}
return ans;
}
}
测评链接:LeetCode 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Morris遍历实现后序遍历#
Morris遍历实现后序遍历相对比较麻烦,处理时机只放在能回到自己两次的点,能回到自己两次的点在第二次回到自己的时刻,不打印它自己,而是逆序打印他左树的右边界, 整个遍历结束后,单独逆序打印整棵树的右边界,即得到了后序遍历的结果。
代码如下:
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode mostRight;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
// 第二次来到自己的时候,收集自己的左树的右边界
collect(cur.left, ans);
}
}
cur = cur.right;
}
collect(root, ans);
return ans;
}
private void collect(TreeNode root, List ans) {
TreeNode node = reverse(root);
TreeNode c = node;
while (c != null) {
ans.add(c.val);
c = c.right;
}
reverse(node);
}
private TreeNode reverse(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
TreeNode t = cur.right;
cur.right = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = t;
}
return pre;
}
需要注意两点:
第一点,collect方法即逆序收集左树的有边界,由于每个节点没有指向父的指针,所以,要实现逆序,需要针对右边界采用反转链表的方式。即reverse函数的逻辑。
第二点,在collect方法调用完反转链表操作后,还要还原整个右边界。否则整棵树的指针就指乱了。
测评链接:LeetCode 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal