接上回
上一篇我们简单介绍了基于SpringBoot实现简单的Web开发,本节来看Web开发中必不可少的内容——数据持久化
先看项目结构:

1. 创建数据表
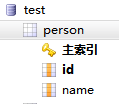
打开mysql,打开数据库 test (没有可以创建一个),创建表格 person
给 person 表创建两个字段 id、name

2. 打开 pom.xml,添加相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.2.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.5.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
mybatis-spring-boot-starter 满足了 mybatis在springboot下的拆箱即用
mybatis-plus-boot-starter 实现了 mybatis-plus 的自动化配置,同样拆箱即用
注意:是mybatis-plus-boot-starter,不是mybatis-plus;前者包含后者的引用,如果只引用后者执行程序会报错!
由于mybatis-plus是基于mybatis的,所以两者引用缺一不可
mysql-connector-java 是基础的mysql驱动接口,这个也是不可或缺的
mybatis是安全、优秀的java持久层框架,基于xml可灵活定制sql语句
mybatis-plus在mybatis的基础上做了更进一步的简化,可免去xml编写
同时,mybatis-plus遵循非侵入式设计的原则,即完全兼容原mybatis的使用习惯,非常方便
3. 给application.properties添加数据库配置
# mysql相关设置 spring.datasource.username=admin spring.datasource.password=admin spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
到这里可能有人会问,咋没看到mybatis.xml的配置?不是一般都会有一句:
#指定Mybatis的Mapper文件 mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*xml
如果我们使用mybatis的原生功能,这一句配置是需要加上的,但是如果我们基于mybatis-plus,可以先不加这一句,因为它是免xml配置的!
4. 新建 model/Person
package com.example.hellospringboot.model; public class Person { private Integer id = 0; private String name = ""; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
注意:类名 Person 要和数据库表名 person 一致(首字母大写是Java的类命名规则,这个没有问题)
id和name两个字段的名称和类型也要和数据库保持一致
5. 新建 mapper/PersonMapper
package com.example.hellospringboot.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.example.hellospringboot.model.Person; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Mapper @Repository public interface PersonMapper extends BaseMapper{ }
这里让PersonMapper继承自mybatis-plus提供的BaseMapper,这是启用mybatis-plus免xml特性的关键!
BaseMapper为我们定制常用的数据库增删改查的方法,直接继承使用即可!
6. 新建 service/PersonService 接口及其实现类 service/impl/PersonServiceImpl
package com.example.hellospringboot.service; import com.example.hellospringboot.model.Person; import java.util.List; public interface PersonService { Integer insert(Person person); Integer update(Person person); Integer delete(int id); Listselect(); }
package com.example.hellospringboot.service.impl; import com.example.hellospringboot.mapper.PersonMapper; import com.example.hellospringboot.model.Person; import com.example.hellospringboot.service.PersonService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService { @Autowired PersonMapper mapper; public Integer insert(Person person){ return mapper.insert(person); } public Integer update(Person person){ return mapper.updateById(person); } public Integer delete(int id){ return mapper.deleteById(id); } public Listselect(){ return mapper.selectList(null); } }
我们给mapper新增了@Repository注解,可以让Service自动装载Mapper不报错
通过代码我们可以看到,继承自BaseMapper
7. 新建 controller/PersonController
package com.example.hellospringboot.controller; import com.example.hellospringboot.model.Person; import com.example.hellospringboot.service.PersonService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.List; @RestController @RequestMapping("/person") public class PersonController { @Autowired PersonService service; @PostMapping("/insert") public Integer insert(Person person){ return service.insert(person); } @PostMapping("/update") public Integer update(Person person){ return service.update(person); } @PostMapping("/delete") public Integer delete(int id){ return service.delete(id); } @GetMapping("/select") public Listselect(){ return service.select(); } }
我们这里使用了@RestController注解,这样可以非常方便的测试我们的业务逻辑
这里可以看到,insert、update、delete三个写方法我们使用了Post协议,select读方法使用了Get协议
其实标准的RestApi风格另外还有Put和Delete协议,这里其实没有严格的规定
由于Get协议的参数是直接暴露在url串里的,所以一般写方法我们不建议使用Get协议
8. 使用Postman测试结果

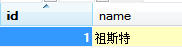

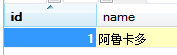


我们在请求参数中分别传入id和name,springboot框架会自动将其拼装成Person对象,真的是非常智能化!
另外,得益于mybatis-plus免xml的特性,我们不用自己手写任何的xml逻辑实现,甚至通篇未出现任何大家常见的mybatis相关配置!
以上。
本节内容我们介绍了数据持久化的相关操作,并且是基础传统的关系型数据库——mysql
下一节我们将共同探讨如何使用SpringBoot整合redis及mongodb,敬请期待!
