-
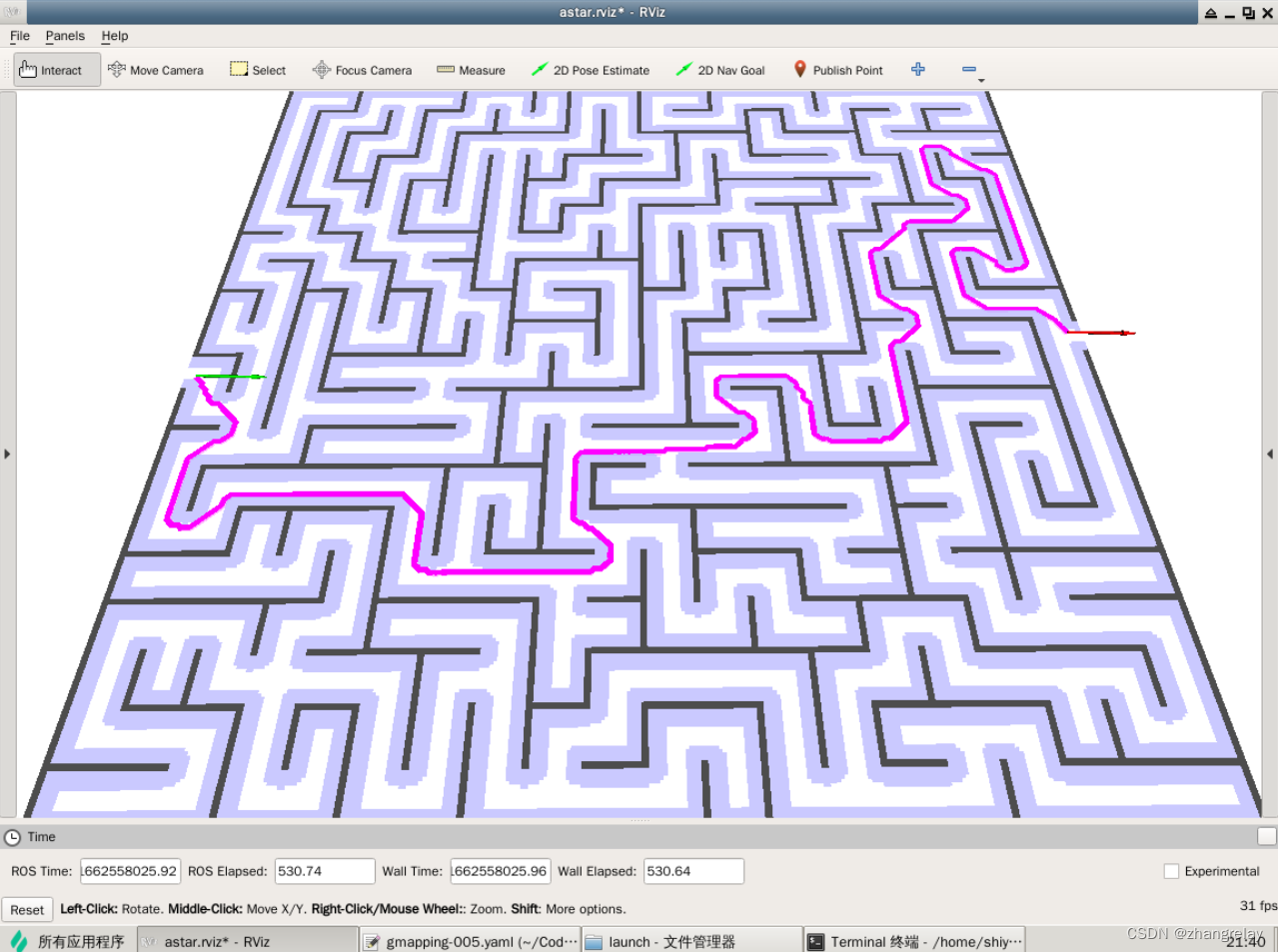
ROS1云课→21可视化工具rviz中的A*
ROS1云课→20迷宫不惑之A*大法(一种虽古老但实用全局路径规划算法)
20中有一幅图:
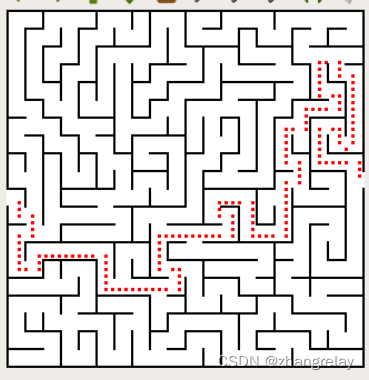
如何实现如下:
障碍物膨胀系数0.1

障碍物膨胀系数0.25

障碍物膨胀系数0.5


掌握了如上内容,最基础的全局路径规划算法A*,基本原理和ROS中使用就ok了。
差异性:


Note that a lot less of the potential has been calculated (indicated by the colored areas). This is indeed faster than using Dijkstra's, but has the effect of not necessarily producing the same paths. Another thing to note is that in this implementation of A*, the potentials are computed using 4-connected grid squares, while the path found by tracing the potential gradient from the goal back to the start uses the same grid in an 8-connected fashion. Thus, the actual path found may not be fully optimal in an 8-connected sense. (Also, no visited-state set is tracked while computing potentials, as in a more typical A* implementation, because such is unnecessary for 4-connected grids). To see the differences between the behavior of Dijkstra's and the behavior of A*, consider the following example.
(机器翻译)
请注意,计算的潜力要少得多(由彩色区域表示)。 这确实比使用 Dijkstra 更快,但效果不一定是产生相同的路径。 需要注意的另一件事是,在 A* 的这个实现中,使用 4 连接网格正方形计算电位,而通过追踪从目标回到起点的电位梯度找到的路径以 8 连接方式使用相同的网格 . 因此,找到的实际路径在 8 连接的意义上可能不是完全最优的。 (此外,在计算势能时没有跟踪访问状态集,就像在更典型的 A* 实现中一样,因为这对于 4 连接网格来说是不必要的)。 要查看 Dijkstra 的行为和 A* 的行为之间的差异,请考虑以下示例。
Dijkstra's

A*


- /*********************************************************************
- *
- * Software License Agreement (BSD License)
- *
- * Copyright (c) 2008, 2013, Willow Garage, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
- * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
- * are met:
- *
- * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
- * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
- * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
- * disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
- * with the distribution.
- * * Neither the name of Willow Garage, Inc. nor the names of its
- * contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
- * from this software without specific prior written permission.
- *
- * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
- * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
- * FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
- * COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
- * INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
- * BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
- * LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
- * CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
- * LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
- * ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
- * POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
- *
- * Author: Eitan Marder-Eppstein
- * David V. Lu!!
- *********************************************************************/
- #include
- #include
- namespace global_planner {
- AStarExpansion::AStarExpansion(PotentialCalculator* p_calc, int xs, int ys) :
- Expander(p_calc, xs, ys) {
- }
- bool AStarExpansion::calculatePotentials(unsigned char* costs, double start_x, double start_y, double end_x, double end_y,
- int cycles, float* potential) {
- queue_.clear();
- int start_i = toIndex(start_x, start_y);
- queue_.push_back(Index(start_i, 0));
- std::fill(potential, potential + ns_, POT_HIGH);
- potential[start_i] = 0;
- int goal_i = toIndex(end_x, end_y);
- int cycle = 0;
- while (queue_.size() > 0 && cycle < cycles) {
- Index top = queue_[0];
- std::pop_heap(queue_.begin(), queue_.end(), greater1());
- queue_.pop_back();
- int i = top.i;
- if (i == goal_i)
- return true;
- add(costs, potential, potential[i], i + 1, end_x, end_y);
- add(costs, potential, potential[i], i - 1, end_x, end_y);
- add(costs, potential, potential[i], i + nx_, end_x, end_y);
- add(costs, potential, potential[i], i - nx_, end_x, end_y);
- cycle++;
- }
- return false;
- }
- void AStarExpansion::add(unsigned char* costs, float* potential, float prev_potential, int next_i, int end_x,
- int end_y) {
- if (next_i < 0 || next_i >= ns_)
- return;
- if (potential[next_i] < POT_HIGH)
- return;
- if(costs[next_i]>=lethal_cost_ && !(unknown_ && costs[next_i]==costmap_2d::NO_INFORMATION))
- return;
- potential[next_i] = p_calc_->calculatePotential(potential, costs[next_i] + neutral_cost_, next_i, prev_potential);
- int x = next_i % nx_, y = next_i / nx_;
- float distance = abs(end_x - x) + abs(end_y - y);
- queue_.push_back(Index(next_i, potential[next_i] + distance * neutral_cost_));
- std::push_heap(queue_.begin(), queue_.end(), greater1());
- }
- } //end namespace global_planner
后续回归到ROS导航视角:
- 介绍导航功能包集和它们的强大功能——这是ROS中最重要的软件包之一。
- 介绍tf,说明一个物理量如何从一个坐标系变换到另一坐标系。例如,一个传感器采集的数据或一个执行器收到期望位置的命令。tf是一个保持坐标系跟踪的库。
- 创建一个激光雷达的驱动或对其进行仿真。
- 计算并发布里程计(odometry)数据,以及stdr是如何提供结果的。
- 基础控制器,包括如何在机器人上创建。
- 用ROS执行同步定位与地图构建(Simultaneous Localization And Mapping,SLAM)。使用自己的机器人在环境中移动时,为此环境构建一个地图。使用导航包集里的自适应蒙特卡罗定位(adaptive Monte Carlo localization,AMCL)算法为机器人在此地图中进行定位。AMCL是用于2D机器人运动的概率定位系统。它采用了自适应蒙特卡罗定位方法,此方法使用了一个粒子滤波器在一个已知地图中跟踪机器人的位姿。
-
相关阅读:
Java虚拟机(JVM)面试题(总结最全面的面试题!!!)
图数据库的初步介绍
算法练习13——跳跃游戏II
单目标应用:基于螳螂搜索算法(Mantis Search Algorithm,MSA)的微电网优化调度MATLAB
【ASM】字节码操作 MethodWriter
SQL做流水号
【vr】【unity】白马VR课堂系列-VR开发核心基础05-主体设置-手柄对象的引入和设置
JavaScript学习Day005(操作节点)
pyqt6 vscode
Sun Solaris 修改IP地址或者主机名
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ZhangRelay/article/details/126754439
