-
<迷宫问题及最短路径问题(使用DFS与回溯法求解)>——《算法》
目录
后记:●由于作者水平有限,文章难免存在谬误之处,敬请读者斧正,俚语成篇,恳望指教!
一、迷宫问题:
1.迷宫问题链接:(牛客网)迷宫问题
1.1 问题描述:

1.2 问题分析:
以上迷宫OJ题曾经是百度某一年的其中一个笔试题,迷宫问题本质就是一个图的遍历问题,从起点开始不断四个方向探索,直到走到出口,走的过程中我们借助栈记录走过路径的坐标,栈记录坐标有两方面的作用,一方面是记录走过的路径,一方面方便走到死路时进行回溯找其他的通路。这里涉及到四路递归。(上、下、左、右四个方向的递归)我们在这里借助深度优先遍历(DFS)与回溯法进行分析、求解。根据题目要求,分析后确定实现方式,模块化实现各部分功能,然后依据“高内聚,低耦合”的方式进行组织!
1.3 功能函数实现:
(1)首先定义迷宫坐标位置的结构体: (2)写出调用逻辑(主函数):
(2)写出调用逻辑(主函数): (3)判断路径坐标进行可以进行遍历:
(3)判断路径坐标进行可以进行遍历:

(4)判断该坐标是否为有效可遍历的坐标

(5) 输出栈里面的坐标路径:
由于栈的“FIFO”性质,又题目要求按照从最开始打印,则需要进行顺序调整。
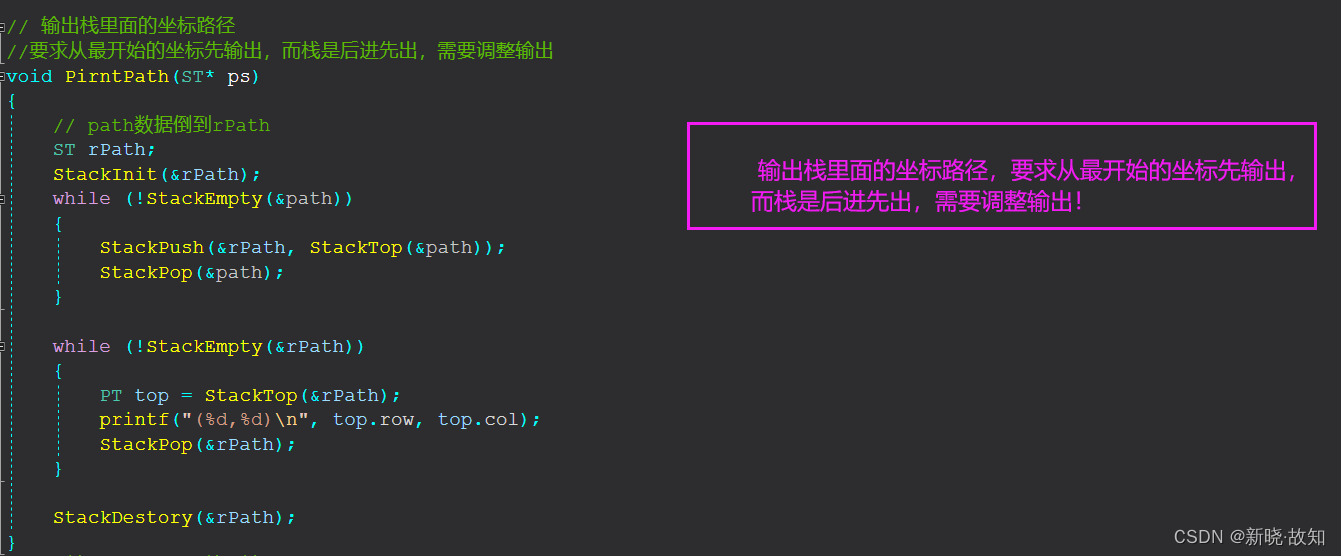
(6)打印遍历的路径坐标:

1.4 栈的模拟实现:
(这里借助栈的“FIFO”性质,借用栈存储递归遍历的数据存储,不符合的坐标就出栈,再进行回溯遍历)
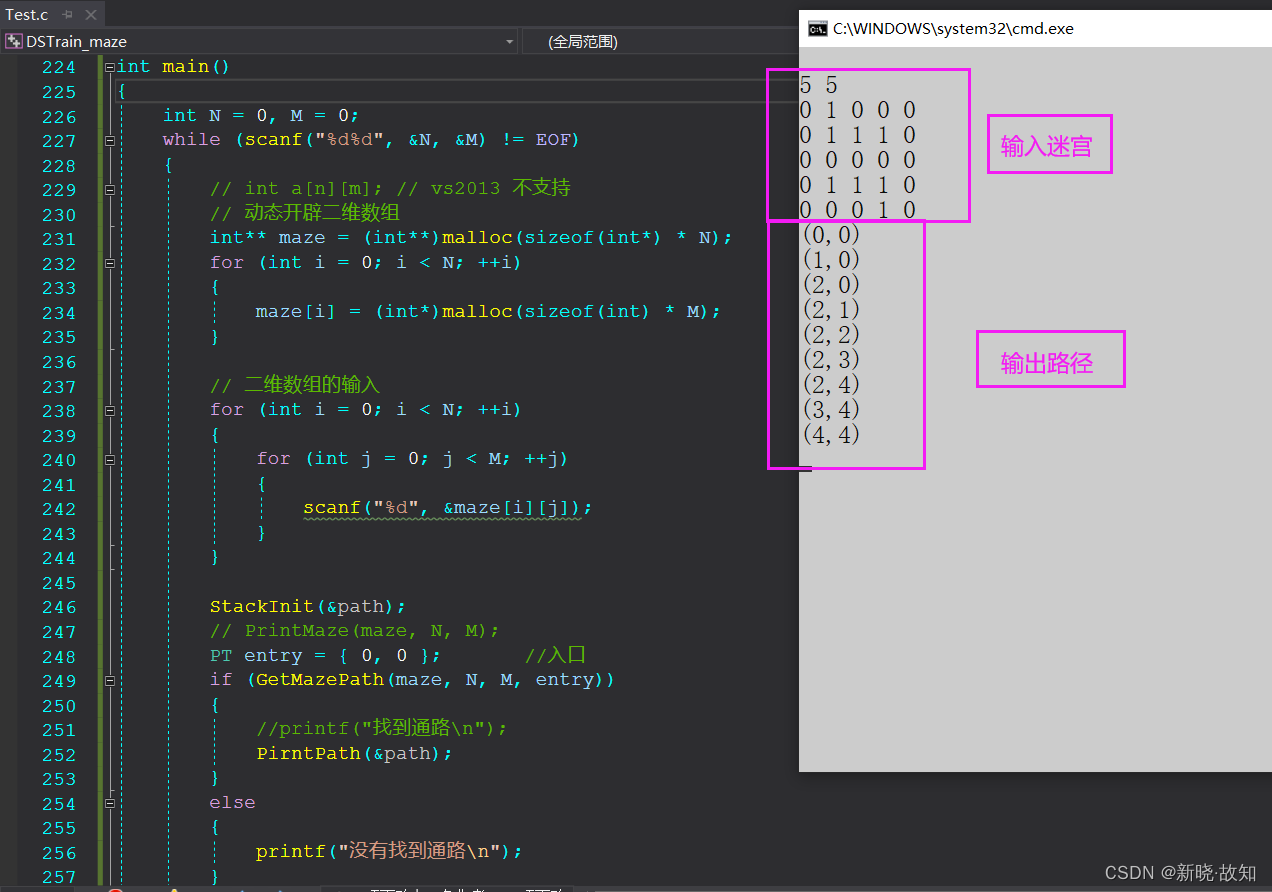
1.5测试用例及演示:
示例1:
- 5 5
- 0 1 0 0 0
- 0 1 1 1 0
- 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 1 1 1 0
- 0 0 0 1 0

示例2:
- 5 5
- 0 1 0 0 0
- 0 1 0 1 0
- 0 0 0 0 1
- 0 1 1 1 0
- 0 0 0 0 0
 测试打印:
测试打印:
1.6 完整源码:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- //定义位置结构体
- typedef struct Postion
- {
- int row;
- int col;
- }PT;
- /
- //栈的实现
- typedef PT STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* a; //通过数组实现栈的结构
- int top;
- int capacity;
- }ST;
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- //释放内存、销毁空间
- void StackDestory(ST* ps);
- // 入栈
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
- // 出栈
- void StackPop(ST* ps);
- //取栈顶数据
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- //栈的大小
- int StackSize(ST* ps);
- //判空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
- if (ps->a == NULL)
- {
- printf("malloc fail!\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->capacity = 4;
- ps->top = 0; //这使得top最终指向的是栈顶的后一个位置。若top=-1,则最终指向的是栈顶。
- }
- //释放内存、销毁空间
- void StackDestory(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- // 入栈
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 满了->增容
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- printf("realloc fail!\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- else
- {
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capacity *= 2;
- }
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- // 出栈
- void StackPop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 栈空了,再调用Pop,就会直接中止程序报错
- assert(ps->top > 0);
- //ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0; //置为0只考虑了int型等,若为char、double等就不适用了。
- ps->top--;
- }
- //取栈顶数据
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 栈空了,再调用Top,就会直接中止程序报错
- assert(ps->top > 0);
- return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
- }
- //求栈大小
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }
- //判空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- //maze实现
- ST path; //定义全局变量
- //打印
- void PrintMaze(int** maze, int N, int M)
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j)
- {
- printf("%d ", maze[i][j]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- // 输出栈里面的坐标路径
- //要求从最开始的坐标先输出,而栈是后进先出,需要调整输出
- void PirntPath(ST* ps)
- {
- // path数据倒到rPath
- ST rPath;
- StackInit(&rPath);
- while (!StackEmpty(&path))
- {
- StackPush(&rPath, StackTop(&path));
- StackPop(&path);
- }
- while (!StackEmpty(&rPath))
- {
- PT top = StackTop(&rPath);
- printf("(%d,%d)\n", top.row, top.col);
- StackPop(&rPath);
- }
- StackDestory(&rPath);
- }
- //判断该坐标是否为有效可遍历的坐标
- bool IsPass(int** maze, int N, int M, PT pos)
- {
- if (pos.row >= 0 && pos.row < N
- && pos.col >= 0 && pos.col < M
- && maze[pos.row][pos.col] == 0)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- //判断路径坐标进行可以进行遍历
- bool GetMazePath(int** maze, int N, int M, PT cur)
- {
- StackPush(&path, cur);
- // 如果走到出口
- if (cur.row == N - 1 && cur.col == M - 1)
- return true;
- // 探测cur位置得上、下、左、右四个方向
- PT next;
- maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2; //已经遍历过的(包括当前)位置,标记为2
- //向上遍历
- next = cur;
- next.row -= 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))
- return true;
- }
- //向下遍历
- next = cur;
- next.row += 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))
- return true;
- }
- //向左遍历
- next = cur;
- next.col -= 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))
- return true;
- }
- //向右遍历
- next = cur;
- next.col += 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next))
- return true;
- }
- StackPop(&path); //不通,这个坐标不能使用,就出栈
- return false; //四个方向都不通,就返回false,递归会回溯,探索其他通路
- }
- int main()
- {
- int N = 0, M = 0;
- while (scanf("%d%d", &N, &M) != EOF)
- {
- // int a[n][m]; // vs2013 不支持
- // 动态开辟二维数组
- int** maze = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- maze[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * M);
- }
- // 二维数组的输入
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j)
- {
- scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);
- }
- }
- StackInit(&path);
- // PrintMaze(maze, N, M);
- PT entry = { 0, 0 }; //入口
- if (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, entry))
- {
- //printf("找到通路\n");
- PirntPath(&path);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("没有找到通路\n");
- }
- StackDestory(&path);
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- free(maze[i]);
- }
- free(maze);
- maze = NULL;
- }
- return 0;
- }
二、迷宫最短路径问题:
1. 迷宫最短路径问题链接:(牛客网)地下迷宫
1.1 问题描述:

1.2 问题分析:
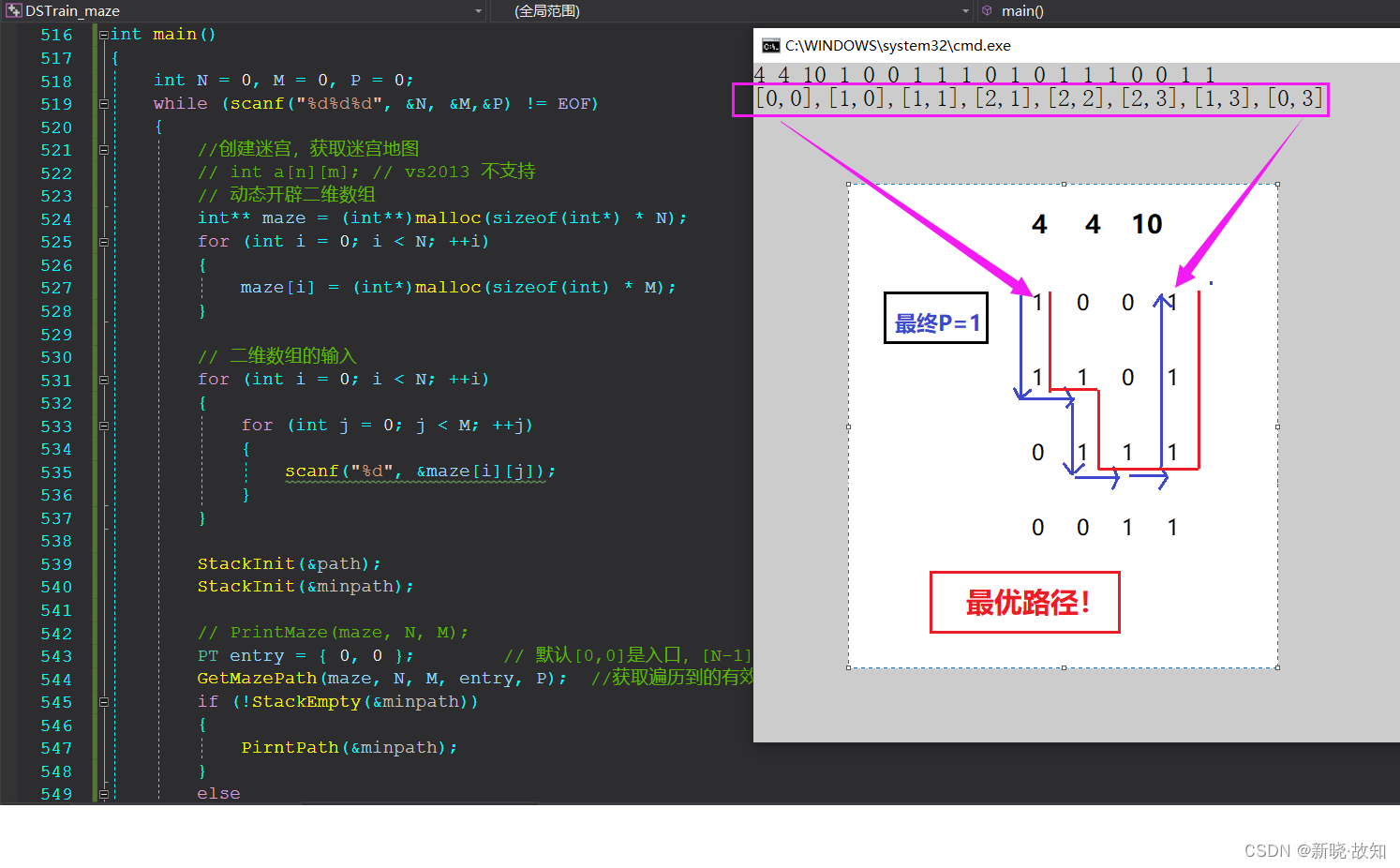
本题在曾经是美团某一年的笔试题,本题在上一个题的基础上计入了体力值的概念,但是本题还有一个隐藏条件,就是要找出迷宫的最短路径,如下图的两个测试用例,需要找出最短路径,才能通过全部测试用例。本题依旧借助深度优先遍历(DFS)和回溯法解决。这里涉及到四路递归,(上、下、左、右四个方向的递归)。分析问题,确定求解方法:根据题目可知:相比于“迷宫问题”,这题在上题的基础上进行了“变种”,即引入了“体力值”和最短路径,而且路径也从“只有一条”变为了“多条路径”,因此,要进行分析,将各个功能模块封装后,依据“高内聚,低耦合”的设计原则进行组织。
1.3 功能函数实现:
(1)定义迷宫坐标的结构体:
(2)写出调用逻辑(主函数):

(3)获取有效遍历的有效路径坐标:

(4)解决浅拷贝的两次释放空间会报错问题:


(5)判断该坐标是否为有效可遍历的坐标:

(6)输出栈里存储的路径坐标:
由于栈的“FIFO”性质,又题目要求按照从最开始打印,则需要进行顺序调整。

(7)打印遍历的有效路径坐标:

1.4 栈的模拟实现:
(这里借助栈的“FIFO”性质,借用栈存储递归遍历的数据存储,不符合的坐标就出栈,再进行回溯遍历)

1.5测试用例及演示:
示例1:
1.6 完整源码:
- //2.迷宫最短路径问题
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- //定义迷宫坐标的结构体
- typedef struct Postion
- {
- int row;
- int col;
- }PT;
- /
- //栈的实现
- typedef PT STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* a; //通过数组实现栈的结构
- int top;
- int capacity;
- }ST;
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- //释放内存、销毁空间
- void StackDestory(ST* ps);
- // 入栈
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
- // 出栈
- void StackPop(ST* ps);
- //取栈顶数据
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- //栈的大小
- int StackSize(ST* ps);
- //判空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
- if (ps->a == NULL)
- {
- printf("malloc fail!\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->capacity = 4;
- ps->top = 0; //这使得top最终指向的是栈顶的后一个位置。若top=-1,则最终指向的是栈顶。
- }
- //释放内存、销毁空间
- void StackDestory(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- // 入栈
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 满了->增容
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- printf("realloc fail!\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- else
- {
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capacity *= 2;
- }
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- // 出栈
- void StackPop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 栈空了,再调用Pop,就会直接中止程序报错
- assert(ps->top > 0);
- //ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0; //置为0只考虑了int型等,若为char、double等就不适用了。
- ps->top--;
- }
- //取栈顶数据
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- // 栈空了,再调用Top,就会直接中止程序报错
- assert(ps->top > 0);
- return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
- }
- //求栈大小
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }
- //判空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- //maze实现
- ST path; //定义全局变量
- ST minpath; //定义最短路径
- //打印
- void PrintMaze(int** maze, int N, int M)
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j)
- {
- printf("%d ", maze[i][j]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- // 输出栈里面的坐标路径
- //要求从最开始的坐标先输出,而栈是后进先出,需要调整输出
- void PirntPath(ST* ps)
- {
- // path数据倒到rPath
- ST rPath;
- StackInit(&rPath);
- while (!StackEmpty(ps))
- {
- StackPush(&rPath, StackTop(ps));
- StackPop(ps);
- }
- //输出分为两种,仅因为题目要求,这里没有什么特定含义
- while (StackSize(&rPath)>1)
- {
- PT top = StackTop(&rPath);
- printf("[%d,%d],", top.row, top.col);
- StackPop(&rPath);
- }
- PT top = StackTop(&rPath);
- printf("[%d,%d]", top.row, top.col);
- StackPop(&rPath);
- StackDestory(&rPath);
- }
- //判断该坐标是否为有效可遍历的坐标
- bool IsPass(int** maze, int N, int M, PT pos)
- {
- if (pos.row >= 0 && pos.row < N
- && pos.col >= 0 && pos.col < M
- && maze[pos.row][pos.col] == 1)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- //解决浅拷贝的两次释放空间报错问题
- void StackCopy(ST* ppath, ST* pcopy)
- {
- pcopy->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType*) * ppath->capacity);
- memcpy(pcopy->a, ppath->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ppath->top);
- pcopy->top = ppath->top;
- pcopy->capacity = ppath->capacity;
- }
- //获取可有效遍历的路径坐标
- void GetMazePath(int** maze, int N, int M, PT cur,int P)
- {
- StackPush(&path, cur);
- // 如果走到出口
- if (cur.row == 0 && cur.col == M - 1)
- {
- // 找到了更短的路径,更新minpath; //P是题目要求的体力值,要求在有效范围内
- if (P >= 0 && StackEmpty(&minpath)
- || StackSize(&path) < StackSize(&minpath))
- {
- StackDestory(&minpath);
- StackCopy(&path, &minpath);
- }
- }
- // 探测cur位置得上下左右四个方向
- PT next;
- maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2; //已经走过得,标记为2
- //向上遍历
- next = cur;
- next.row -= 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 3));
- }
- //向下遍历
- next = cur;
- next.row += 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P));
- }
- //向左遍历
- next = cur;
- next.col -= 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 1));
- }
- //向右遍历
- next = cur;
- next.col += 1;
- if (IsPass(maze, N, M, next))
- {
- (GetMazePath(maze, N, M, next, P - 1));
- }
- //递归会回溯,探索其他通路
- //需要恢复
- maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 1;
- StackPop(&path);
- }
- int main()
- {
- int N = 0, M = 0, P = 0;
- while (scanf("%d%d%d", &N, &M,&P) != EOF)
- {
- //创建迷宫,获取迷宫地图
- // int a[n][m]; // vs2013 不支持
- // 动态开辟二维数组
- int** maze = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- maze[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * M);
- }
- // 二维数组的输入
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j)
- {
- scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);
- }
- }
- StackInit(&path);
- StackInit(&minpath);
- // PrintMaze(maze, N, M);
- PT entry = { 0, 0 }; // 默认[0,0]是入口,[N-1][M-1]是出口
- GetMazePath(maze, N, M, entry, P); //获取遍历到的有效路径
- if (!StackEmpty(&minpath))
- {
- PirntPath(&minpath);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("Can not escape!\n");
- }
- StackDestory(&path);
- StackDestory(&minpath);
- //销毁迷宫
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- free(maze[i]);
- }
- free(maze);
- maze = NULL;
- }
- return 0;
- }
三、总结:
通过迷宫问题及最短路径问题,借助深度优先遍历(DFS)和回溯法求解,这里涉及到四路递归(上、下、左、右四个方向的递归),然而解决方法是一方面,解决工具也是另一方面。这里采用C语言实现求解,借助数据结构中栈的性质,实现深度遍历过程中的数据存储,然后回溯。使用C语言,涉及到二维数组的操作,这里使用了二级指针和指针数组,而在最短路径的比较更新中,涉及到了深浅拷贝问题,这里也需要注意,否则程序将会崩溃!
解决这些题的方法还有很多,解决的工具也有很多,这里不再一一列举!
最后,向前人的智慧结晶致敬!学者,亦有敬畏之心!亦当珍惜学习的机会与时光!
后记:
●由于作者水平有限,文章难免存在谬误之处,敬请读者斧正,俚语成篇,恳望指教!——By 作者:新晓·故知
-
相关阅读:
关于面试,95%会问到的Java面试题(高级部分)
SSH安全外壳协议
mp4视频太大怎么压缩变小?
【嵌入式开源库】EasyLogger的使用, 一款轻量级且高性能的日志库
用于构建用户界面的JavaScript库--->React
三台linux服务器部署ceph集群
皕杰报表之调整css样式
擎创技术流 | ckman教程(3)CKman源码分析部署集群的主要步骤
为什么数据集中的mask是彩色的?
安装GPT 学术优化 (GPT Academic)@FreeBSD
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57859086/article/details/126665880
