-
探索 ArrayList 原理 - 第三节ArrayList 常用方法源码分析
探索 ArrayList 原理
jdk1.8 API
黑马教学视频: java进阶教程丨全面深入解析ArrayList原理(源码分析+面试讲解)4. ArrayList 常用方法源码分析
4.1 构造方法

-
执行这段代码
ArrayList看一下无参构造干了些什么事- 无参构造
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //默认空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 空参构造 public ArrayList() { //初始化赋值一个空数组 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
执行这段代码
ArrayList看一下有一个整型参构造干了些什么事- 有参构造: [指定容量参数]
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 有参构造 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { //接入参值 ,初始化数据 if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { //接入参值为0 ,初始化数据 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { //其它就抛出异常 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
执行下面这段代码
- 看一下有一个集合作为参数的构造干了些什么事
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add("aaa"); arrayList.add("bbb"); arrayList.add("ccc"); ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(arrayList); for (String s:list ) { System.out.println(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
有参构造: [指定合集参数]
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //长度为 0的空数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 集合长度 private int size; // 有参构造 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { // 将构造方法中的参数转为数组 elementData = c.toArray(); //将新数组长度赋值给size if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // 再次进行判断 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) //数组的创建和拷贝 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // 就把空数组的地址赋值给集合存元素的数组 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } //将集合转为数组的请求 public Object[] toArray() { //调用工具类的方法 elementData 源数据, size 是源数组长度 return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } //工具类 class Arrays { // public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { //再次调用方法得到一个数组 return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); } public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") //不管三元运算符结果如何,都会创建一个新的数组; //新的数组的长度一定是和集合的size 一样 T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) //此处比较地址-->详解看第7节Arrays.copyOf() ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); //新数组的拷贝 :把源数组拷贝到新创建的数组中 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); //返回新数组 return copy; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
4.2 案例演示
4.3 添加方法
-
Api 文档如下

-
1、指定的元素追加到此列表末尾 源码分析
- 模拟添加数据,分析添加方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>(); strList.add("1"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 根据如上代码进行分析添加一个元素
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //默认空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //长度为 0的空数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //默认 初始化数组容量为 10 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //2 The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). [ArrayList的大小(它包含的元素数)] private int size; //初始化数组的修改次数 protected transient int modCount = 0; //1 Appends the specified element to the end of this list. [在list 末尾追加一个指定元素] public boolean add(E e) { // 确保内部容量,size是添加前数组内元素的数量 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // size 默认0 //添加数据 elementData[size++] = e; return true; } // 3 确保内部容量可用,size是添加前数组内元素的数量 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { //elementData 初始化的存储容器 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } // 4 计算数组长度 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { //判断 集合存元素的地址是否为默认空容量数组元素 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { //当执行new ArrayList() 时会初始化引用 //返回最大的值 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } //明确的数组容量 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 - 初始化数组元素容量大小({}.length = 10) > 0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //扩容 grow(minCapacity); } /** * * @DESC 核心扩容方法 * @param minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 * 扰动 **/ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 初始的时候elementData= {} 所以旧的容量 oldCapacity= {}.length = 0 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 右移:>> 右移几位就相当于除以2的n 次幂 // 左移:<< 左移几位就相当于乘以2的n 次幂 // 新容量 = 旧容量+右移过后的值 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //源容量的1.5倍 // 赋值新容量大小 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 新容量大小 跟 integer 最大容量比较 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: // elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //超大容量方法 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
-
2、在此列表中的指定位置插入指定的元素 源码分析
- 模拟添加数据,分析添加方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>(); strList.add("2"); strList.add("3"); strList.add(1,"1"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 根据如上代码进行分析指定位置插入指定的元素
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //默认空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //长度为 0的空数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //默认 初始化数组容量为 10 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //2 The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). [ArrayList的大小(它包含的元素数)] private int size; //初始化数组的修改次数 protected transient int modCount = 0; // public void add(int index, E element) { // rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! // 将数组元素elementData 从索引位置1 开始 // 还是拷贝到elementData 索引位置为index +1 位置 // 数组元素为 size-index 之后的数组元素 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); // 数组指定位置赋值 elementData[index] = element; size++; } //检查 索引范围 private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 3 确保内部容量可用,size是添加前数组内元素的数量 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } // 4 计算数组长度 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } //5 确保数组容量,然后进行扩容 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 - 数组元素容量大小(elementData.length = 10) < 0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) // 因为已经添加过元素,最后一次是指定索引添加元素,初始值已经有值 // 只有容量不够才去扩容 grow(minCapacity); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
-
指定位置赋值内存地址分析,如下图解



-
3、按指定集合的Iterator 返回顺序将指定集合中的所有元素追加到此列表末尾 源码分析
- 模拟添加数据,分析添加方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>(); strList.add("2"); strList.add("3"); strList.add(1,"1"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 根据如上代码进行分析将指定集合中的所有元素追加到此列表末尾
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //默认空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //长度为 0的空数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //默认 初始化数组容量为 10 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //2 The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). [ArrayList的大小(它包含的元素数)] private int size; //初始化数组的修改次数 protected transient int modCount = 0; public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { //将有数据的集合转换为数组 Object[] a = c.toArray(); //将有数据的集合的长度赋值给numNew int numNew = a.length; //校验 计算数组容量,首次扩容 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount //真正的拷贝:把a元素整体拷呗到elementData中 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); //集合长度进行更改:size 的大小为数据元素a的长度 size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } // 3 确保内部容量可用 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { //elementData 初始化的存储容器 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } // 4 计算数组长度 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { //判断 集合存元素的数据是否等于默认空容量数组元素 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { //返回最大的值 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } //明确的数组容量 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 - 初始化数组元素容量大小({}.length = 10) > 0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //扩容 grow(minCapacity); } /** * * @DESC 核心扩容方法 * @param minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 * 扰动 **/ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 初始的时候elementData= {} 所以旧的容量 oldCapacity= {}.length = 0 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 右移:>> 右移几位就相当于除以2的n 次幂 // 左移:<< 左移几位就相当于乘以2的n 次幂 // 新容量 = 旧容量+右移过后的值 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //源容量的1.5倍 // 赋值新容量大小 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 新容量大小 跟 integer 最大容量比较 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: // elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //超大容量方法 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
-
结论:底层使用了System.arraycopy 的方法进行拷贝;
-
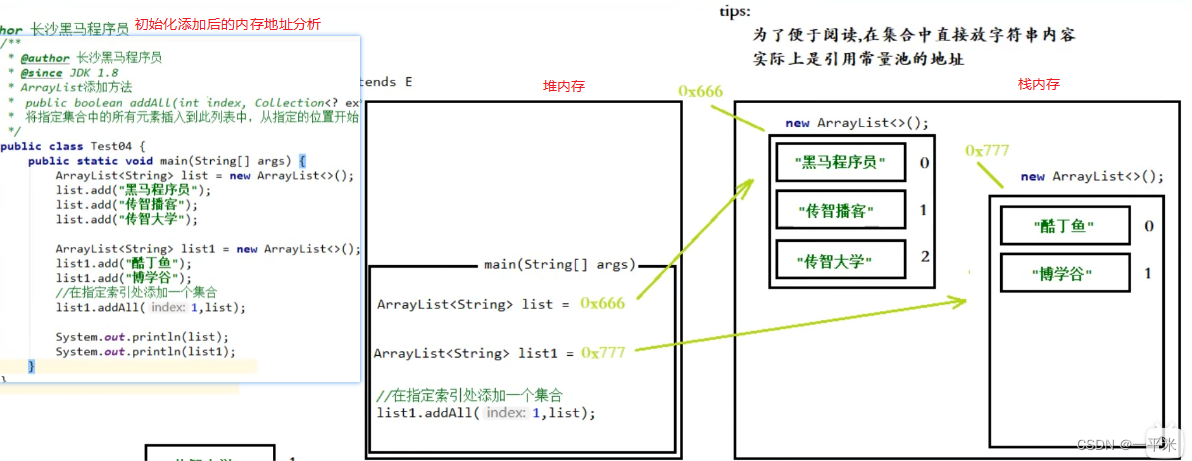
4、 将指定集合的所元素插入到此列表中,从指定的位置开始 源码分析
- 模拟添加数据,分析添加方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); ArrayList<String> listSource = new ArrayList<String>(); listSource.add("醋丁鱼"); listSource.add("博学谷"); listSource.addAll(1,list); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 根据如上代码进行分析指定位置插入指定集合的所元素
//真正存储数据的容器 transient Object[] elementData; //默认空容量的数组,长度为 0 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //长度为 0的空数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //默认 初始化数组容量为 10 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //2 The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). [ArrayList的大小(它包含的元素数)] private int size; //初始化数组的修改次数 protected transient int modCount = 0; public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //检验索引 (index > size || index < 0) rangeCheckForAdd(index); //将有数据的集合转换为数组 Object[] a = c.toArray(); //记录数据源长度 int numNew = a.length; // 目的就是为了给集合存储数据的数组进行扩容 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount //numMoved 要移动的元素的个数 = 数据目的长度-addAll的第一个参数(索引) //size: 数据目的长度(也就是最终添加到的那个元素的长度) //现在需要添加元素,需要后面的元素向后移动留出位置,先计算移动的元素的个数,使用公式size - index即可 int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) //如果移动个数大于0 // 数据目的集合首先自己先做对应拷贝 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); // 真正的将数据源中的所有数据添加到数据目的 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } //检查 索引范围 private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 3 确保内部容量可用 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { //elementData 初始化的存储容器 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } // 4 计算数组长度 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { //判断 集合存元素的数据是否等于默认空容量数组元素 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { //返回最大的值 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } //明确的数组容量 然后扩容 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 - 初始化数组元素容量大小({}.length = 10) > 0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //扩容 grow(minCapacity); } /** * * @DESC 核心扩容方法 * @param minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 * 扰动 **/ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 初始的时候elementData= {} 所以旧的容量 oldCapacity= {}.length = 0 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 右移:>> 右移几位就相当于除以2的n 次幂 // 左移:<< 左移几位就相当于乘以2的n 次幂 // 新容量 = 旧容量+右移过后的值 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //源容量的1.5倍 // 赋值新容量大小 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 新容量大小 跟 integer 最大容量比较 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: // elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //超大容量方法 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
-
指定位置插入集合内存地址分析,如下图解
- 1、 初始化添加后的内存地址分析
- 2、 计算了numMoved 要移动的个数:首次移动之后的内存地址分析

-
3、移动自身元素之后,拷贝源数组元素到目的数组元素中

-
指定位置插入集合移动位置分析,代码模拟添加位置,代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) { String[] array1 = {"黑马程序员","传智播客","传智大学"}; //添加空值模拟初始化集合后的10个空间长度 String[] array2 = {"醋丁鱼","博学谷",null,null,null,null,null,null,null,null}; int numNew = array1.length; //size - index size:目标数组长度 - 索引 int numMoved = 2 - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(array2, 1, array2, 1 + numNew, numMoved); // 复制 array2 元素 从索引位置1开始 目标位置也是array2 开始存储数据的索引位置1+numNew 源数组的数量:要移动的个数numMoved System.out.println("第一次自身拷贝:"+Arrays.toString(array2)); // 1+ numNew 就是要留出array1元素的位置 // {"醋丁鱼","博学谷",null,null,博学谷,null,null,null,null,null}; System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array2, 1, numNew); System.out.println("第二次源数组给目标数据拷贝:"+Arrays.toString(array2)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 输出结果如下
第一次自身拷贝:[醋丁鱼, 博学谷, null, null, 博学谷, null, null, null, null, null] 第二次源数组给目标数据拷贝:[醋丁鱼, 黑马程序员, 传智播客, 传智大学, 博学谷, null, null, null, null, null]- 1
- 2
4.4 删除方法
-
Api jdk1.8

-
1、remove(int index) 删除该列表中指定位置的元素。
- 删除该列表中指定位置的元素。 将任何后续元素移动到左侧(从其索引中减去一个元素)。
- 模拟删除数据,分析删除方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); list.remove(1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 根据如上代码进行分析指定位置删除集合中的元素
- 源码
public E remove(int index) { // 检查索引是否超出范围,如果超出抛出异常:IndexOutOfBoundsException rangeCheck(index); // 标记修改数量统计 modCount++; //取出索引位置处元素,赋值给oldValue E oldValue = elementData(index); //numMoved 要移动的元素的个数 = 数据目的长度-addAll的第一个参数(索引) //size: 数据目的长度(也就是最终添加到的那个元素的长度) int numMoved = size - index - 1; // if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 模拟删除数据索引位置 代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) { String[] array1 = {"黑马程序员","传智播客","传智大学"}; String[] removeIndexElementMoc = removeIndexElementMoc(array1, 1); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(removeIndexElementMoc)); } /** * * @param index 要删除数据的索引位置 */ private static String[] removeIndexElementMoc(String[] array ,int index) { int size = array.length; String oldValue = array[index]; //要移动的个数numMoved int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) // 复制 array 元素 从索引位置index+1开始 array 开始存储数据的索引位置 index 源数组的数量 System.arraycopy(array, index+1, array, index, numMoved); //分析 index + 1 : 数组位置元素为: 传智大学 //分析 numMoved : 要复制的源数组数量 array[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return array; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 输出结果如下
[黑马程序员, 传智大学, null]- 1
-
2、remove(Object o) 从列表中删除指定元素的第一个出现(如果存在)。
- 从列表中删除指定元素的第一个出现(如果存在)。 如果列表不包含该元素,则它不会更改。 更正式地,删除具有最低索引i的元素,使得(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))) (如果存在这样的元素)。 如果此列表包含指定的元素(或等效地,如果此列表作为调用的结果而更改),则返回true 。
- 模拟删除数据,分析删除方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); list.remove("传智大学"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 根据如上代码进行分析指定位置删除集合中的元素
- 源码
public boolean remove(Object o) { // 如果为null ,则删除空元素,否则删除指定元素 if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /** * * 删除指定位置数据 **/ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; //要移动的个数numMoved int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) //拷贝元素elementData 从索引位置 index+1 到目标元素elementData 从第index 位置开始覆盖到 numMoved 结束 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 模拟删除集合数据 代码 参考 remove(int index) 模拟即可;
-
3、removeAll(Collection c) 从此列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。
- 从此列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。
- 模拟删除数据,分析删除方法,如下
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("传智大学"); list.removeAll(list2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 根据如上代码进行分析 从此列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。
- 源码
- 模拟删除数据索引位置 代码如下
- 输出结果如下
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { // 校验集合是否为空 Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } public static <T> T requireNonNull(T obj) { if (obj == null) throw new NullPointerException(); return obj; } /** * @Param c : 被删除的集合列表 * @Param complement: * 批量删除 **/ private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { // 把源数组赋值给 局部elementData 数组 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; //r用来控制循环,w是记录有多少个差集 removeAll 调用记录差集 int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) // 校验c集合元素是否在elementData中:是否为false/true if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) // 若是 complement = true 则将 c中包含elementData中的元素 替换 elementData[w++]位置值 达到元素前移效果 // 若是 complement = false则将 c中不包含elementData中的元素 存入 elementData[w++]位置值 达到元素前移效果 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { //将 自 elementData[w] 到 elementData[size-1]的值全部置为null // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; // 标记elementData数组修改次数 size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; } // 集合是否包含元素O public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; //没有数据则为-1 } public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
-
4、removeIf(Predicate filter) removeIf()的入参是一个过滤条件,用来判断需要移除的元素是否满足条件。
- 方法用于删除所有满足特定条件的数组元素。
- 模拟根据条件删除数据,伊森的根据删除方法
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(); arr.add("a"); arr.add("b"); arr.add("c"); arr.add("d"); arr.add("e"); arr.add("d"); System.out.println(arr); arr.removeIf(item->"d".equals(item)); System.out.println(arr);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 源码
@Override public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); // figure out which elements are to be removed // any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage // will leave the collection unmodified // 用于记录删除数量的局部变量 int removeCount = 0; //removeSet 用来记录被 删除的元素的下标,节省空间且有去重性 final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size); //expectedModCount 线程安全的统计量 final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this.size; //把符合条件的待删除元素的下标设置到BitSet中,即BitSet中对应的下标设为true for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E element = (E) elementData[i]; if (filter.test(element)) { removeSet.set(i); removeCount++; } } // 检测是否有其它线程并发修改这个ArrayList // 这个就是并发是fail-fast机制,可以让当前线程快速失败,而不会产生资源竞争,导致锁之类的现象 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } // shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements // final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0; if (anyToRemove) { final int newSize = size - removeCount; for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) { i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i); elementData[j] = elementData[i]; } for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) { elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work } this.size = newSize; if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } return anyToRemove; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
4.5 修改方法
-
1、set(int index, E element) 用指定的元素替换此列表中指定位置的元素。
- index: 要替换的元素的索引 ;element: 要存储在指定位置的元素
- 模拟修改数据,分析修改方法,如下
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); System.out.println(list); Object set = list.set(0, "安锐捷大学"); System.out.println(set); System.out.println(list);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 根据如上代码进行分析用指定的元素替换此列表中指定位置的元素 返回旧的元素
- 源码
public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
输出结果如下
[黑马程序员, 传智播客, 传智大学] 黑马程序员 [安锐捷大学, 传智播客, 传智大学]- 1
- 2
- 3
4.6 获取方法
- 1、get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置的元素。
- index: 要返回的元素的索引
- 源码,比较简单,直接上源码
public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.7 转换方法
-
1、toString() 返回此集合的字符串表示形式。
- 首先需要明确的是,toString() 方法不是ArrayList 的方法,而是继承的AbstractCollection 的方法
- 模拟修改数据,分析修改方法,如下
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("黑马程序员"); list.add("传智播客"); list.add("传智大学"); String s = list.toString(); System.out.println(list);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 根据如上代码进行分析 返回此集合的字符串表示形式
- 源码
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> { public String toString() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (! it.hasNext()) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append('['); //无限循环 for (;;) { E e = it.next(); sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); if (! it.hasNext()) return sb.append(']').toString(); sb.append(',').append(' '); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
-
输出结果如下
[黑马程序员, 传智播客, 传智大学]- 1
4.8 迭代器
-
1、public Iterator iterator() 普通 迭代器。
-
案例1 已知集合: List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素 hello,java,php 使用迭代器遍历获取集合的每一个元素
-
首先需要明确的是,toString() 方法不是ArrayList 的方法,而是继承的AbstractCollection 的方法
- 模拟示例,分析如下
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); arrayList.add("hello"); arrayList.add("java"); arrayList.add("php"); Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String next = it.next(); System.out.println(next); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 根据如上代码进行分析 返回此集合的字符串表示形式
- 源码
// 获取迭代器的方法 public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(); // 创建了一个对象 } /** * AbstractList.Itr 内部类 迭代器源码 */ private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; //光标索引 下一个光标位置索引 index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; //记录-1 index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; // 将集合实际修改的次数赋值给预期修改的次数 Itr() {} //判断集合是否有元素 public boolean hasNext() { // 光标是否不等于集合的size return cursor != size; } //返回下一个元素 public E next() { //校验: checkForComodification(); // 初始化时 i = 0 int i = cursor; // 判断,如果大于集合的size 就说明没有元素了 if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 把集合存储数据数组的地址赋值给此方法的局部变量 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; //进行判断 ,如果条件满足就会产生并发修改异常 if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); //光标自增 cursor = i + 1; //从数组中取出元素且返回 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } // 校验预期修改集合次数是否和实际修改集合次数一样 final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) // 如果不一样就会产生并发修改异常 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
-
输出结果如下
hello java php- 1
- 2
- 3
-
-
案例2 已知集合: List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素 hello,java,php 使用迭代器遍历获取集合看是否有"php" 这个元素,如果有,就使用集合对象删除该元素
- 首先需要明确的是,toString() 方法不是ArrayList 的方法,而是继承的AbstractCollection 的方法
- 模拟示例,分析如下
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); arrayList.add("hello"); arrayList.add("java"); arrayList.add("php"); Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String next = it.next(); if(next.equals("php")){ arrayList.remove("php"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 根据如上代码进行分析
- 源码
//----------------------------添加数据源码 操作---------------------------- // 添加数据源码 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } // 确保内部容量可用 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { //elementData 初始化的存储容器 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } // 计算数组长度 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { //判断 集合存元素的数据是否等于默认空容量数组元素 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { //返回最大的值 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } //明确的数组容量 然后扩容 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { // 记录添加数据的个数(也就是集合修改的次数) modCount++; // minCapacity 当前真实数组容量大小 - 初始化数组元素容量大小({}.length = 10) > 0 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //扩容 grow(minCapacity); } //----------------------------迭代器源码 操作---------------------------- // 获取迭代器的方法 public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(); // 创建了一个对象,初始化成员变量 } /** * AbstractList.Itr 内部类 迭代器源码 */ private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; //光标索引 下一个光标位置索引 index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; //记录-1 index of last element returned; -1 if no such // 获取迭代器的时候,expectedModCount 的值(也就是集合修改的次数) int expectedModCount = modCount; // 将集合实际修改的次数赋值给预期修改的次数 Itr() {} //判断集合是否有元素 public boolean hasNext() { // 光标是否不等于集合的size return cursor != size; } //返回下一个元素 public E next() { //校验: checkForComodification(); // 初始化时 i = 0 int i = cursor; // 判断,如果大于集合的size 就说明没有元素了 if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 把集合存储数据数组的地址赋值给此方法的局部变量 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; //进行判断 ,如果条件满足就会产生并发修改异常 if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); //光标自增 cursor = i + 1; //从数组中取出元素且返回 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } // 校验预期修改集合次数是否和实际修改集合次数一样 final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) //如果不一样,就会产生并发修改异常 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } //集合删除元素的方法 public boolean remove(Object o) { // 判断要删除的元素是否为null , if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } // 内部快速删除数据实现方式:真正的删除元素的方法 private void fastRemove(int index) { // 在删除的方法中集合实际修改次数会自增 // 集合实际修改次数为:4 但是预期修改次数为 3 modCount++; //计算集合要移动元素的个数 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) // 移动的核心代码 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved); //就是让删除的元素置为null ,目的就是为了尽快被 垃圾回收掉 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 结论如下
1、集合每次调用add方法的时候,实际 修改次数变量的值都会自增一次(modCount++;)
2、在获取迭代器的时候,集合只会执行一次,将实际 修改集合赋值给预期修改集合的次数,就是在初始化迭代器成员变量的时候(int expectedModCount = modCount)
3、集合在删除元素的时候也会针对 实际修改次数的变量进行自增的操作
fastRemove()方法的modCount++; - 报错如下:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:909) at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:859) at source.Iterator_Analyse.main(Iterator_Analyse.java:22)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 首先需要明确的是,toString() 方法不是ArrayList 的方法,而是继承的AbstractCollection 的方法
-
案例3 已知集合: List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素 hello,php,java 使用迭代器遍历获取集合看是否有"php" 这个元素,如果有,就使用集合对象删除该元素
- 注意:此次 php 元素位置第1索引位置
- 模拟示例,分析如下
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); arrayList.add("hello"); arrayList.add("php"); arrayList.add("java"); Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String next = it.next(); if(next.equals("php")){ arrayList.remove("php"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 注意:此次 php 元素位置第1索引位置
-
结论:
- 当要删除的元素在集合的倒数第二个位置的时候,不会产生并发修改异常;
-
原因:
- 是因为在调用hasNext方法的时候,删除数据之后,光标的值 和集合的长度一样,那么就会返回false;因此就不侍调用next() 方法获取集合的元素,那么底层就不会产生并发修改的异常了; 注意,这只是一个巧合,巧合;
-
迭代器默认方法源码分析
- default void remove() 从底层集合中删除此迭代器返回的最后一个元素(可选操作)。
- 模拟分析示例
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(); arrayList.add("hello"); arrayList.add("php"); arrayList.add("java"); Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String next = it.next(); if(next.equals("php")){ // 迭代器删除 it.remove(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 源码分析
//------------------迭代器自带删除方法-------------------------- public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { //内部类调用外部类删除方法 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; //把实际修改集合次数赋值给预期修改次数 expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } //-----------------集合删除的方法 ---------------------------- public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
-
结论:
- 迭代器调用 remove 方法删除元素,其实底层真正还是调用集合自己的删除方法来删除元素;
- 在调用remove 方法中每次都会给预期修改次数的变量赋值;
4.9 清空方法
- void clear() 从列表中删除所有元素。
- 源码 clear() 比较简单,直接上源码
public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4.10 包含方法
- boolean contains(Object o) 如果此列表包含指定的元素,则返回 true
- 源码比较简单,直接上源码
// 集合是否包含元素O public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; //没有数据则为-1 } public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { //判断 元素是否为null for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else {// 取集合中的每一个元素和要找的元素进行比较内容 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4.11 判断集合是否为空方法
-
boolean isEmpty() 如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 true 。
-
源码
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
-
-
相关阅读:
Linux启动流程分析
支付系统 — 支付路由
【日志分析】Android 运营商名称显示优先级(AlphaTag/SPN)
Java基础-并发篇
java计算机毕业设计衣依服装销售平台源码+系统+数据库+lw文档
漫谈:C语言 C++ static究竟是什么
高频面试八股文用法篇(六) 说说反射及其作用
七大排序算法(插排,希尔,选择排序,堆排,冒泡,快排,归并)--图文详解
破解MySQL的神秘感
Zookeeper集群 + Kafka集群
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/pymxb1991/article/details/126558911
