-
第七章:Vue3(上)
第七章:Vue3(上)
7.1:Vue3快速上手
- Vue3简介
- 2020年9月18日,
Vue.js发布3.0版本,代号:One Piece(海贼王) - 耗时两年多、2600+次提交、30+个RFC、600+次PR、99位贡献者
- 2020年9月18日,
- Vue3带来了什么
- 性能的提升
- 打包大小减少41%
- 初次渲染快55%,更新渲染快133%
- 内存减少54%
- 源码的升级
- 使用
proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式 - 重写虚拟DOM的实现和
Tree-Shaking
- 使用
- 拥抱TS
Vue3可以更好的支持TS
- 新的特性
Composition API(组合API)setup配置ref与reactivewatch与watchEffectprovide与inject
- 新的内置组件
FragmentTeleportSuspense
- 其他改变
- 新的生命周期钩子
- data选项应始终被声明为一个函数
- 移除keyCode支持作为v-on的修饰符
- 性能的提升
7.2:常用Composition API
-
拉开序幕的setup
- 理解:Vue3.0中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数。
setup是所有Composition API(组合API)的表演舞台。- 组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在setup中。
setup函数的两种返回值。- 若返回值是一个对象,则对象中的属性、方法,在模板中均可直接使用。(重点关注)
- 若返回一个渲染函数:则可以自定义渲染内容。(了解)
- 注意点:
- 尽量不要与Vue2配置混用
Vue2配置(data、methods、computed…)中可以访问setup的属性、方法- 但
setup中不能访问到Vue2配置的(data、methods、computed…) - 如果有重名,
setup优先。
setup不能是一个async函数,因为返回值不再是return的对象,而是promise,模板看不到return对象中的属性。(后期也可以返回一个promise实例,但需要Suspense和异步组件配合)
- 尽量不要与Vue2配置混用
-
ref函数
- 作用:定义一个响应式的数据
- 语法:
const xxx = ref(initValue)- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference对象)
- JS中操作数据:
xxx.value - 模板中读取数据:不需要
.value,直接:{{ xxx }}
- 备注:
- 接收的数据可以是:基本类型,也可以是对象类型。
- 基本类型的数据:响应式依然是靠
Object.definePeoperty()的get与set完成的。 - 对象类型的数据:内部求助了
Vue3中的一个新函数————reactive函数。
-
reactive函数
- 作用:定义一个对象类型的响应式数据(基本类型不要用它,要用ref函数)
- 语法:
const 代理对象 = reactive(源对象)接收一个对象(或数组),返回一个代理对象(Proxy的实例对象) reactive定义的响应式数据是“深层次的”。- 内部基于
ES6的Proxy实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据进行操作。
-
Vue3的响应式
-
原理实现:
- 通过
Proxy(代理):拦截对象中任意属性的变化,包括:属性值的读写、属性的添加、属性的删除等等。 - 通过
Reflect(反射):对源对象的属性进行操作。
new Proxy(data, { // 拦截读取属性值 get (target, prop) { return Reflect.get(target, prop) }, // 拦截设置属性值或添加新属性 set (target, prop, value) { return Reflect.set(target, prop, value) }, // 拦截删除属性 deleteProperty (target, prop) { return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop) } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 通过
-
-
reactive对比ref
-
从定义数据角度对比:
ref用于定义:基本数据类型reactive用于定义:对象(或数组)类型数据
注意:
ref也可以用来定义对象(或数组)类型数据,它内部会自动通过reactive转为代理对象。 -
从原理调度对比
- ref通过
Object.defineProperty()的get与set来实现响应式(数据劫持) reactive通过使用Proxy来实现响应式(数据劫持),并通过Reflect操作源对象内部的数据。
- ref通过
-
从使用角度对比
ref定义的数据:操作数据需要.value,读取数据时模板中直接读取不需要.value。reactive定义的数据:操作数据与读取数据:均不需要.value
-
-
setup的两个注意点
- setup执行的时机
- 在
beforeCreate之前执行一次,this是undefined
- 在
- setup参数
props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性。context:上下文对象attrs:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在props配置中声明的属性,相当于this.$attrsslots收到的插槽内容,相当于this.$slotsemit:分发自定义事件的函数,相当于this.$emit
- setup执行的时机
-
计算属性与监视
-
- 与Vue2中的computed配置功能一致。
- 写法
import {computed} from 'vue' setup(){ ... //计算属性——简写 let fullName = computed(()=>{ return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName }) //计算属性——完整 let fullName = computed({ get(){ return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName }, set(value){ const nameArr = value.split('-') person.firstName = nameArr[0] person.lastName = nameArr[1] } }) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
-
监视
-
与Vue2中watch配置功能一致
-
两个小坑
- 监视
reactive定义的响应数据时:oldValue无法正确获取、强制开启了深度监视(deep配置失效) - 监视
reactive定义的响应数据中某个属性(属性为对象)时:deep配置有效。
//情况一:监视ref定义的响应式数据 watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('sum变化了',newValue,oldValue) },{immediate:true}) //情况二:监视多个ref定义的响应式数据 watch([sum,msg],(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('sum或msg变化了',newValue,oldValue) }) /* 情况三:监视reactive定义的响应式数据 */ watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('person变化了',newValue,oldValue) },{immediate:true,deep:false}) //此处的deep配置不再奏效 //情况四:监视reactive定义的响应式数据中的某个属性 watch(()=>person.job,(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue) },{immediate:true,deep:true}) //情况五:监视reactive定义的响应式数据中的某些属性 watch([()=>person.job,()=>person.name],(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue) },{immediate:true,deep:true}) //特殊情况 watch(()=>person.job,(newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue) },{deep:true}) //此处由于监视的是reactive素定义的对象中的某个属性,所以deep配置有效- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 监视
-
-
WatchEffect函数
-
watch的套路是:既要指明监视的属性,也要指明监视的回调。 -
watchEffect的套路是:不用指明监视哪个属性,监视的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监视哪个属性。 -
watchEffect有点像computed- 但
computed注重的计算出来的值(回调函数的返回值),所以必须要写返回值。 - 而
watchEffect更注重的是过程(回调函数的函数体),所以不用写返回值。
watchEffect(() => { const x1 = sum.value; const x2 = person.age; console.log('watchEffect配置的回调执行了'); })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 但
-
-
-
vue3声明周期
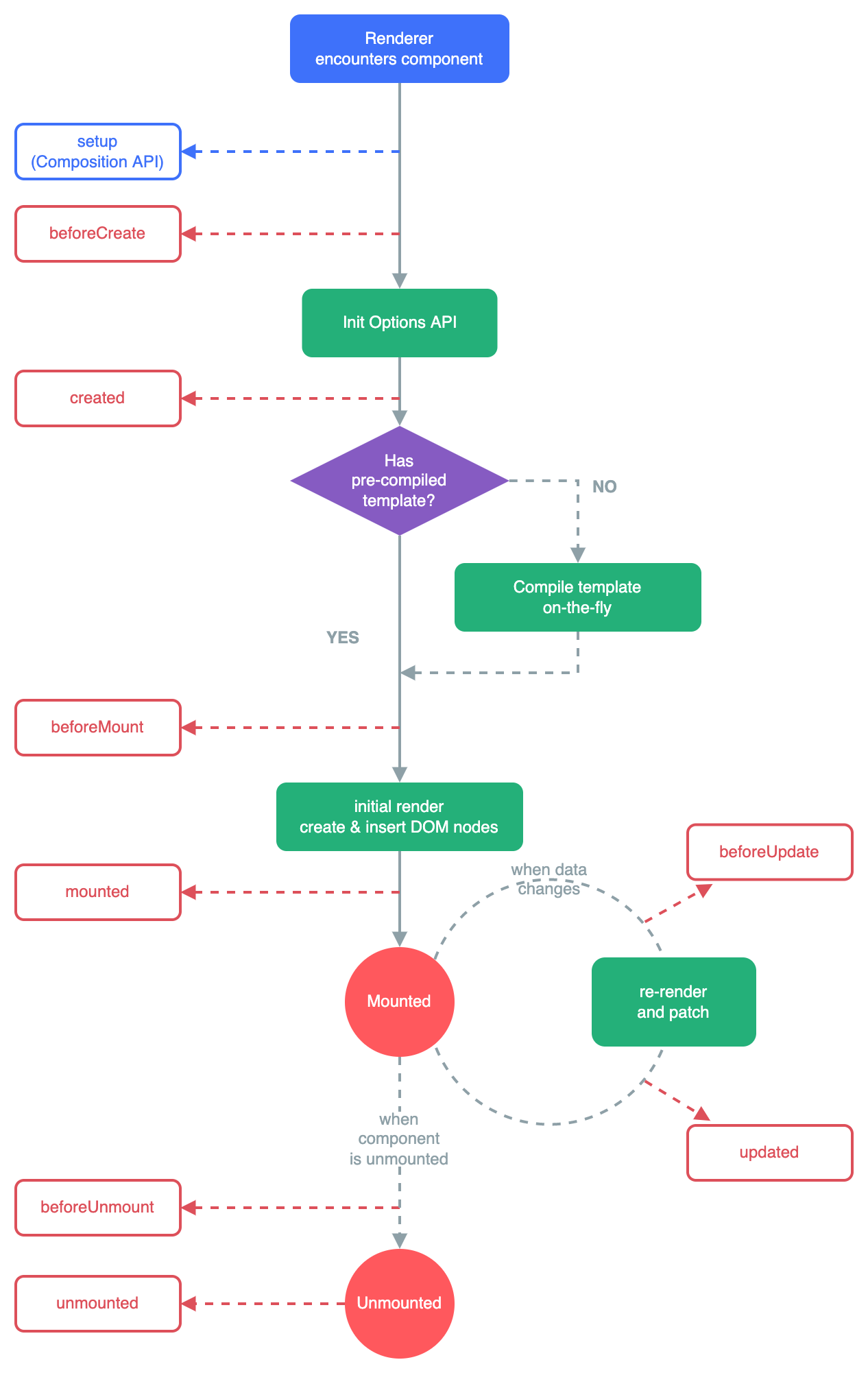
- vue3中可以继续使用Vue2中的生命周期钩子,但有两个被更名
beforeDestroy改名为beforeUnmountdestroyed改名为unmounted
- vue3也提供了
Composition API形式的生命周期钩子,与Vue2中钩子对应关系如下beforeCreate===>setup()created=======>setup()beforeMount===>onBeforeMountmounted=======>onMountedbeforeUpdate===>onBeforeUpdateupdated=======>onUpdatedbeforeUnmount==>onBeforeUnmountunmounted=====>onUnmounted
- vue3中可以继续使用Vue2中的生命周期钩子,但有两个被更名
-
自定义hook函数
- 什么是hook? ————本质是一个函数,把setup函数中使用的
Composittion API进行了封装。 - 类似于vue2中的mixin
- 自定义hook的优势:复用代码,让setup中的逻辑更清楚易懂。
- 什么是hook? ————本质是一个函数,把setup函数中使用的
-
toRef
- 作用:创建一个ref对象,其
value值指向另一个对象中的某个属性。 - 语法:
const name = toRef(person, 'name') - 应用:要将响应式对象中的某个属性单独提供给外部使用时。
- 扩展:
toRefs与toRef功能一致,但可以批量创建多个ref对象。语法:toRefs(person)
- 作用:创建一个ref对象,其
- Vue3简介
-
相关阅读:
vue3使用Swiper实现简单轮播图
java计算机毕业设计药品销售系统源程序+mysql+系统+lw文档+远程调试
Java从入门到精通-数组(一)
叉车数字化安全管理平台,安全管控升级,打造智慧监管新模式
css实现div倾斜效果
MySQL 快速入门之第二章 数据类型、建表以及约束
SpringBoot整合minio分布式文件实操
国内免费好用 Chat GPT推荐
TDengine函数大全-系统函数
芯片设计中的ECO是什么?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wcy_0522/article/details/126577515
