-
【数据结构与算法】| 链表练习
题目一
题目:移除链表元素
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
解题思路
首先我们先确定链表走到哪里,所以我定义一个变量cur,当cur的数值等于要删除的数值,那么就动手!
图文讲解

具体的演示可自行根据上图来演示。
具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if(head == null) return null; ListNode cur = head.next; ListNode prev = head; while(cur != null) { if(cur.val == val) { prev.next = cur.next; cur = cur.next; } else { prev = cur; cur = cur.next; } } if(head.val == val) { head = head.next; } return head; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
代码截图:

题目二
题目:反转链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
解题思路
反转链表就是让头结点变成尾结点,然后把每一个结点都插入到尾结点的前面。
图文讲解

具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if(head == null) { return null; } ListNode cur = head.next; head.next = null; while(cur != null) { ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.next = head; head = cur; cur = curNext; } return head; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
代码截图

题目三
题目:链表的中间节点
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
解题思路
这一题用到的是快慢指针的解法,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,当快指针走完的时候,慢指针所指向的节点就是中间节点。运用的思想是慢指针走过的路程是快指针的一半。
图文讲解

具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
代码截图

题目四
题目:链表中倒数第K个节点
解题思路
使用快慢指针的思想,先让快指针走k-1步,然后再让快慢指针一起走,走到快指针结束的时候,慢指针所指向的节点就是倒数第k个节点
图文讲解
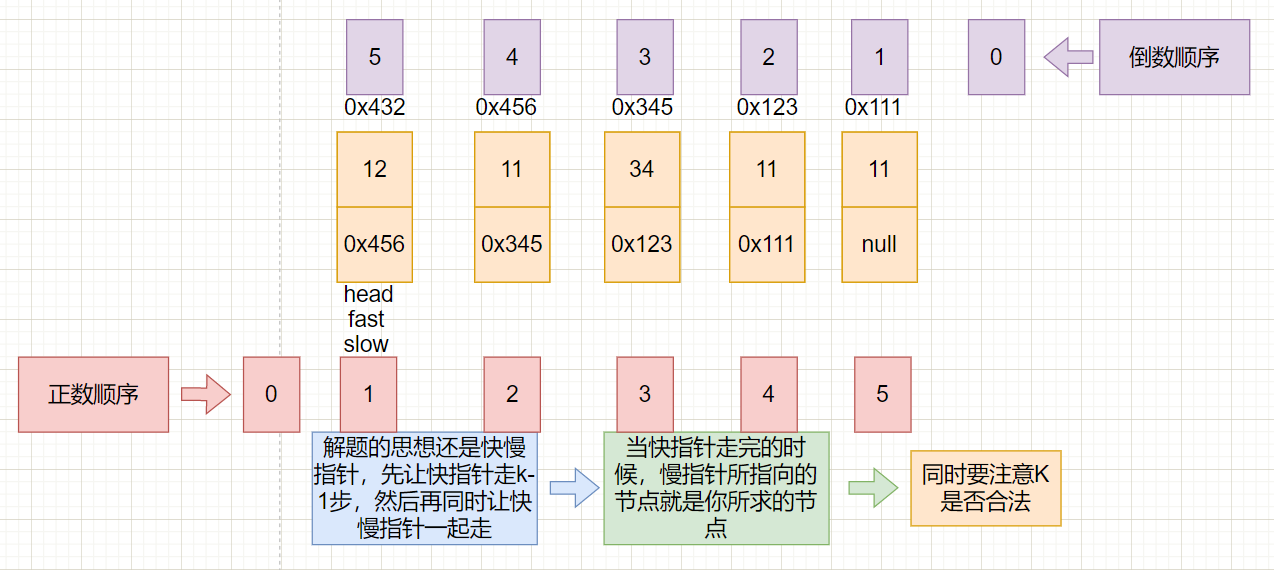
具体代码
import java.util.*; /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class Solution { public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) { if(head == null) { return null; } if(k < 0) { return null; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while(k != 1) { fast = fast.next; if(fast == null) { return null; } k --; } while(fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
代码截图

题目五
题目:合并两个有序链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
解题思路
首先明确一点,两个链表是有序的,然后合并之后还是有序的。我们可以通过创建一个虚拟节点来解决这个问题
图文讲解
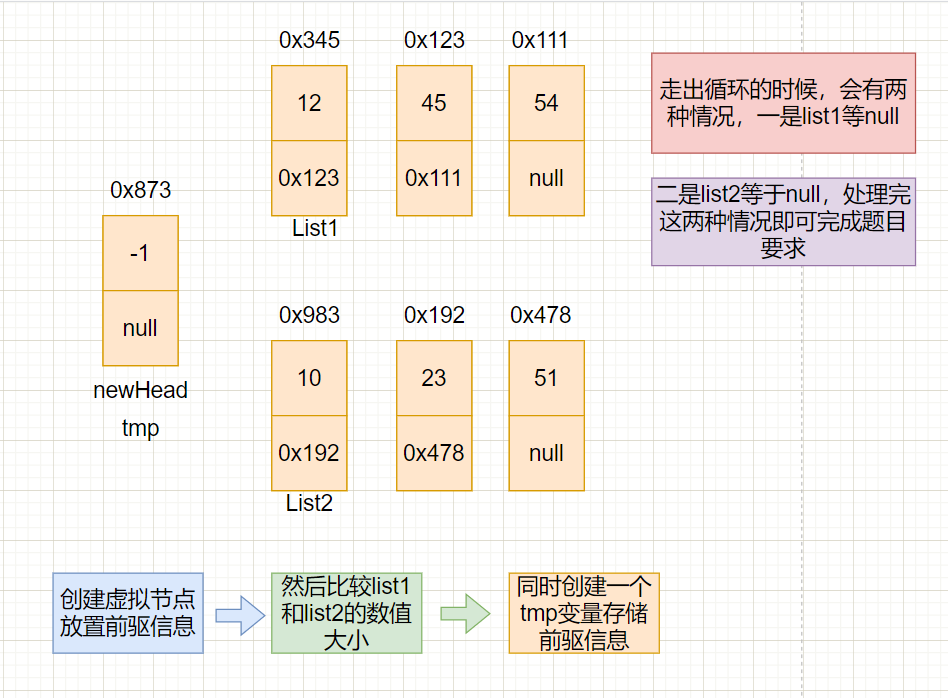
具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode newHead = new ListNode(); ListNode tmp = newHead; while(list1 != null && list2 != null) { if(list1.val > list2.val) { tmp.next = list2; tmp = list2; list2 = list2.next; } else { tmp.next = list1; tmp = list1; list1 = list1.next; } } if(list1 == null) { tmp.next = list2; } if(list2 == null) { tmp.next = list1; } return newHead.next; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
代码截图

题目六
题目:链表分割
解题思路
重新创建两个空链表,一个用来存放大于X的节点,一段用来存放小于X的节点。同时要注意几种情况,一是没有大于X的情况,二是没有小于X的情况,还有一种特殊情况就是有一段链表的最后一个节点的next域不为空。
图文讲解


具体代码
import java.util.*; /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class Partition { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { // write code here if(head == null) { return null; } ListNode bs = null; ListNode be = null; ListNode as = null; ListNode ae = null; ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null) { if(cur.val < x) { //第一次插入 if(bs == null) { bs = cur; be = cur; } //不是第一次插入 else { be.next = cur; be = be.next; } } else { //第一次插入 if(as == null) { as = cur; ae = cur; } //不是第一次插入 else { ae.next = cur; ae = ae.next; } } cur = cur.next; } //存在没有小于X的情况 if(bs == null) { return as; } //存在有小于X的情况 else { be.next = as; } //存在没有大于X的情况 if(as != null) { ae.next = null; } return bs; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
解释都写在了注释里,可自行根据代码模拟运行。
题目七
题目:链表的回文结构
解题思路
首先我们先考虑链表长度为基数的问题,第一步要做的就是找出中间节点,然后反转后半段链表,两边同时判断数值是否相等来确定是否为回文结构
图文讲解
1、找到中间节点

2、反转链表
找到中间节点后,开始反转

3、开始头尾遍历,如果是偶数个数的链表,那么就判断两个节点互相指向。

就类似这种情况
具体代码
import java.util.*; /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class PalindromeList { public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) { // write code here if(head == null || head.next == null) { return false; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode cur = slow.next; while(cur != null) { ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.next = slow; slow = cur; cur = curNext; } fast = head; while(slow != fast) { if(slow.val != fast.val) { return false; } if(fast.next == slow){ return true; } slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
题目八
题目:相交链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
解题思路
首先明确一点是,两个链表相交是Y型的链表,因为不可能一个节点指向一个节点,又指向另一个节点。
先求出两段链表的长度的差值,然后让较长的链表先走差值那么多步,然后再同时开始寻找相交的节点。
图文讲解

具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { int lenA = 0; int lenB = 0; ListNode curA = headA; ListNode curB = headB; //统计链表A的长度 while(curA != null) { lenA ++; curA = curA.next; } while(curB != null) { lenB ++; curB = curB.next; } //求出两链表的差值 int len = lenA - lenB; //重置两个节点 curA = headA; curB = headB; //判断两个链表哪个长 //A链表长 if(len > 0) { while(len != 0) { curA = curA.next; len --; } } //B链表长 else { len = -len; while(len != 0) { curB = curB.next; len --; } } while(curA != null) { if(curA == curB) { return curA; } curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
解题过程都写在了代码注释上了。
题目九
题目:环形链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
解题思路
利用快慢指针直接遍历链表,即可判断链表是否有环。当快慢指针遇到环的时候,就相当于两个人在操场跑步,一个跑得慢,一个跑得快,快的总会撵上慢的。
图文讲解

具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if(fast == slow) { return true; } } return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
题目十
题目:寻找环的入口点
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
解题思路
首先先判定有没有环。有环的情况下,我们假设相遇点和入口的的距离为x,链表的起点和入口的距离为y,环的长度为z。其次我们还有一个已知条件,那就是快指针的路程是慢指针的2倍,所以就有以下的图文讲解。
图文讲解

具体代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; //找环 while(fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if(fast == slow) { break; } } //没有环就返回空 if(fast == null || fast.next == null) { return null; } //从起点开始走 fast = head; //相遇点和起点一起走,然后碰头 while(fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
解释都写在了注释上。
总结
数据结构是一门单独的学科,与编程语言无关,在我看来学好数据结构,一是要多做题,二是仔细,做一个细节狂魔,三是多画图。以上就是我对链表一些练习的个人见解,希望对大家的学习有所帮助!
-
相关阅读:
树莓派Raspberry Pico RP2040 开发环境配置完全缝合终极版C-SDK
一个终端工具竟然有AI功能?使用了1天我立马把其他终端全卸载了!太香了!
matplotlib的默认字体
基于树莓派的安保巡逻机器人--(一、快速人脸录入与精准人脸识别)
自动驾驶升级、开发模式生变,如何实现SOA软件架构快速落地?
YGG 联合创始人 Gabby Dizon 在 Neckerverse 峰会上分享边玩边赚的故事
你好,法语!A2知识点总结(2)
Linux内存地址映射-8086分段分页与缺页异常
wustctf2020_name_your_cat
NLP 04(GRU)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71259890/article/details/126457102
