-
Spring Boot项目介绍(值得学习,超详细)
目录
2.1 第一种方式, 使用Spring提供的初始化器, 就是向导创建SpringBoot应用
9 ComnandLineRunner 接口 , ApplcationRunner接口
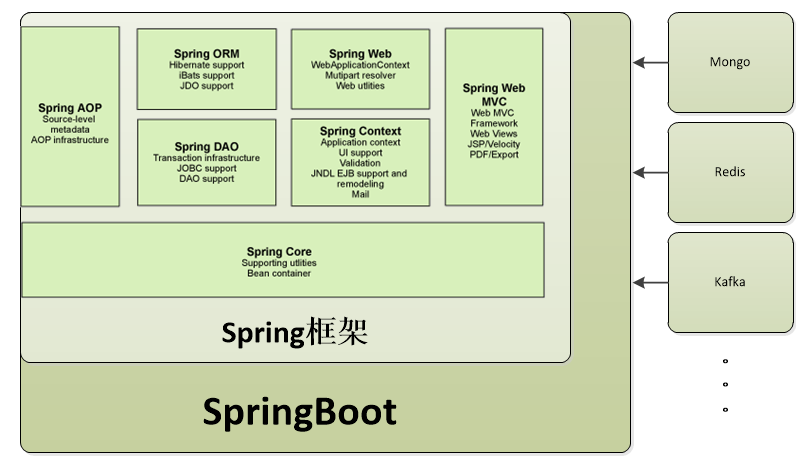
1 Spring Boot介绍
SpringBoot是Spring中的一个成员, 可以简化Spring,SpringMVC的使用。 他的核心还是IOC容器。
特点:
-
Create stand-alone Spring applications
创建spring应用
-
Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
内嵌的tomcat, jetty , Undertow
-
Provide opinionated 'starter' dependencies to simplify your build configuration
提供了starter起步依赖,简化应用的配置。
比如使用MyBatis框架 , 需要在Spring项目中,配置MyBatis的对象 SqlSessionFactory , Dao的代理对象
在SpringBoot项目中,在pom.xml里面, 加入一个 mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖
-
Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible
尽可能去配置spring和第三方库。叫做自动配置(就是把spring中的,第三方库中的对象都创建好,放到容器中, 开发人员可以直接使用)
-
Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration
提供了健康检查, 统计,外部化配置
-
Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration
不用生成代码, 不用使用xml,做配置
2 创建Spring Boot项目
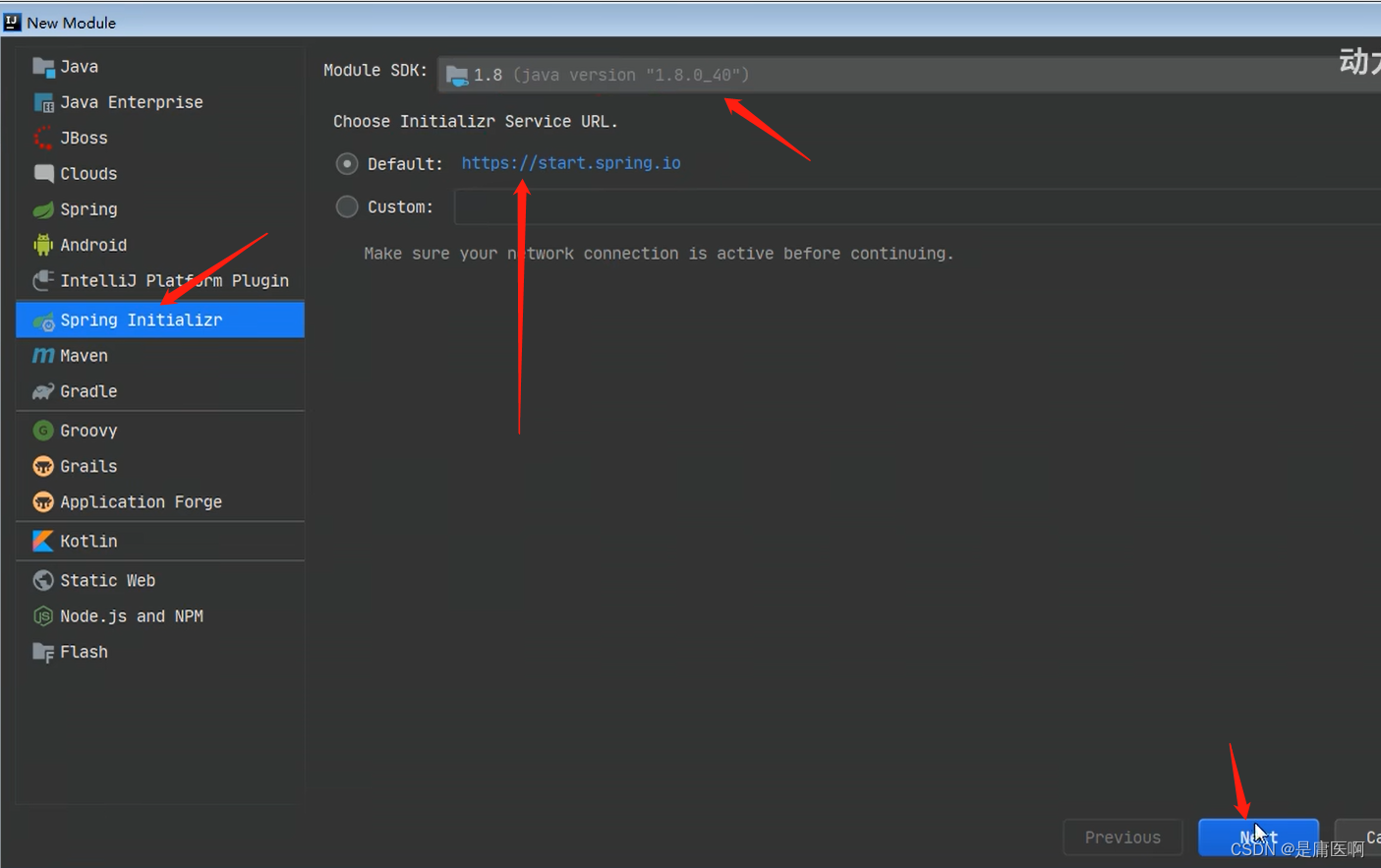
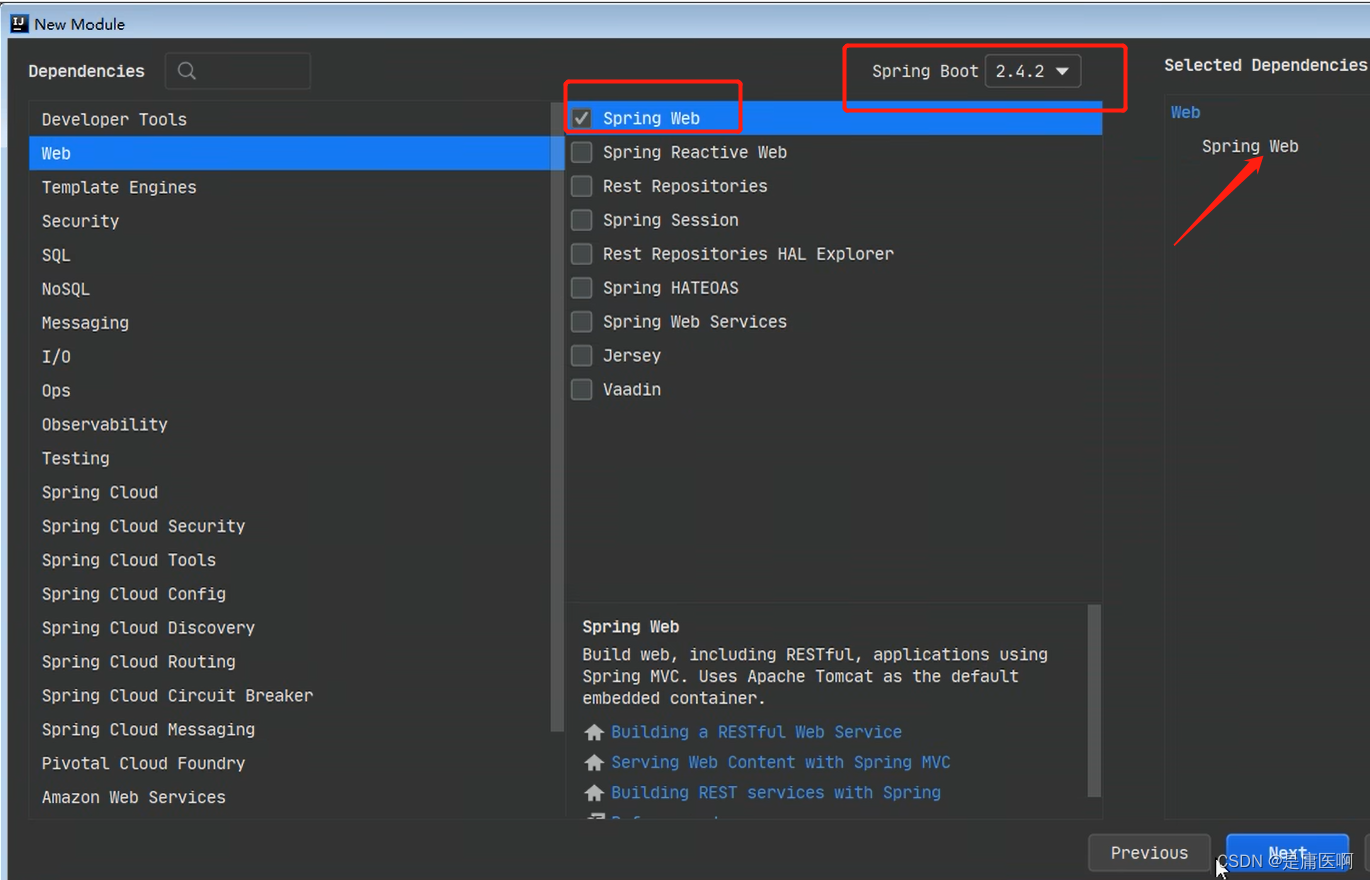
2.1 第一种方式, 使用Spring提供的初始化器, 就是向导创建SpringBoot应用
使用的地址: https://start.spring.io
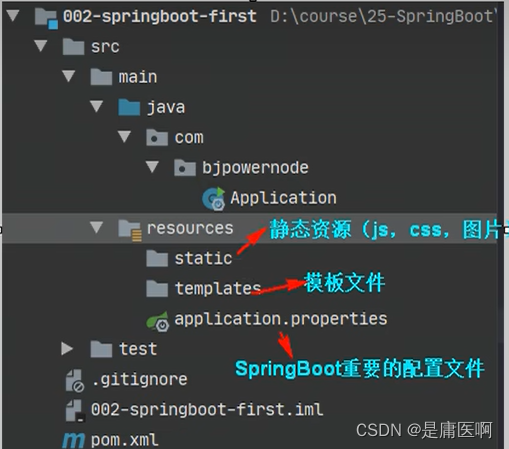
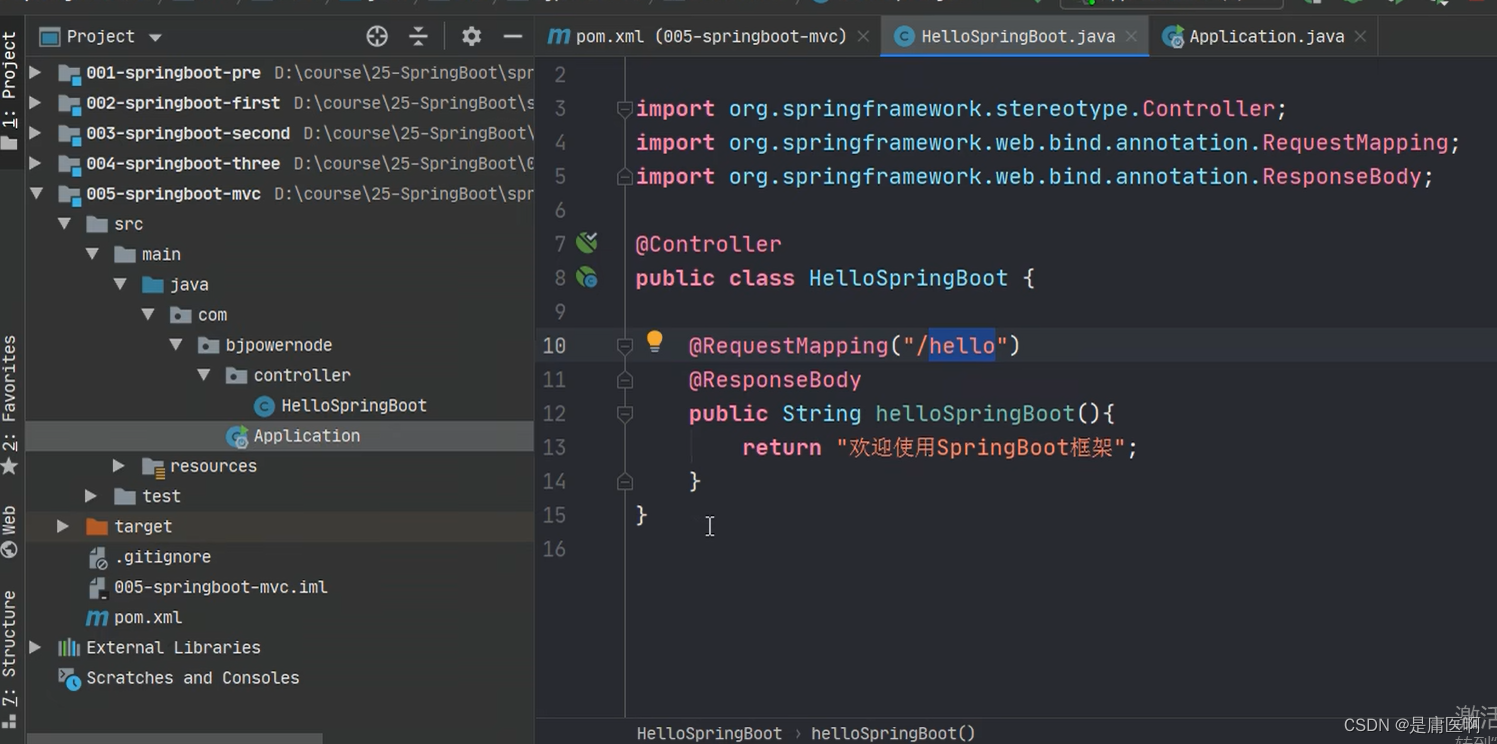
SpringBoot项目的结构:
使用国内的地址

 创建maven项目
创建maven项目 
3 注解的使用
- @SpringBootApplication
- 符合注解:由
- @SpringBootConfiguration
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- @ComponentScan
- 1.@SpringBootConfiguration
- @Configuration
- public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
- @AliasFor(
- annotation = Configuration.class
- )
- boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
- }
- 说明:使用了@SpringBootConfiguration注解标注的类,可以作为配置文件使用的,
- 可以使用Bean声明对象,注入到容器
 2.@EnableAutoConfiguration
2.@EnableAutoConfiguration启用自动配置, 把java对象配置好,注入到spring容器中。例如可以把mybatis的对象创建好,放入到容器中
3.@ComponentScan
- @ComponentScan 扫描器,找到注解,根据注解的功能创建对象,给属性赋值等等。
- 默认扫描的包: @ComponentScan所在的类所在的包和子包。
4 SpringBoot的配置文件
配置文件名称: application
扩展名有: properties( k=v) ; yml ( k: v)
使用application.properties, application.yml
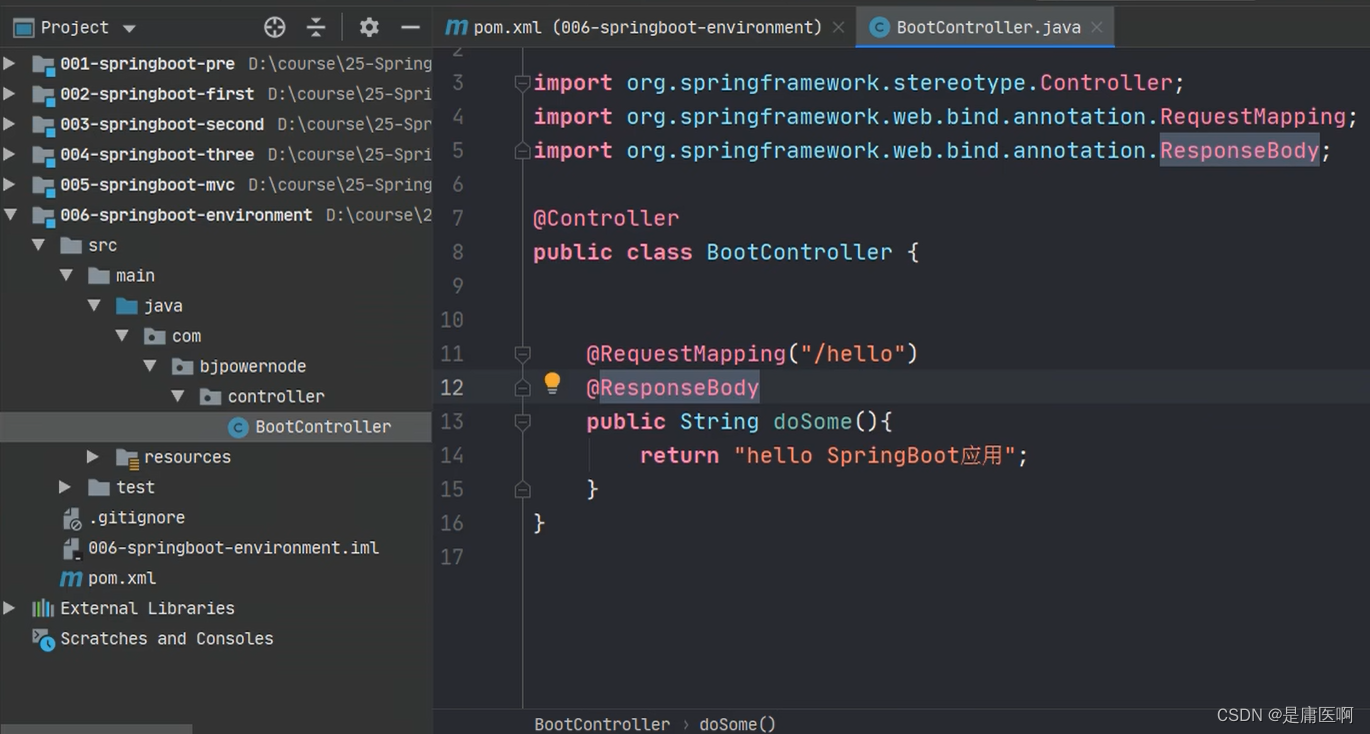
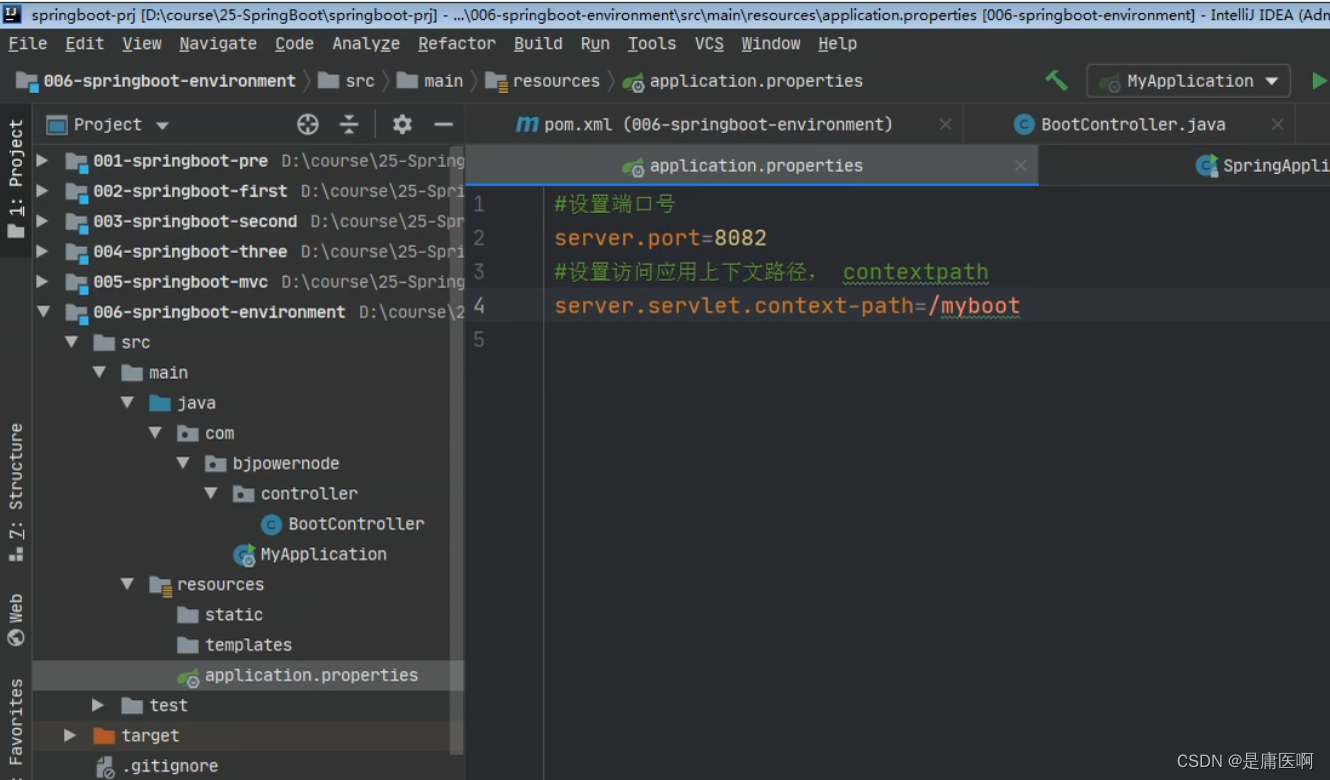
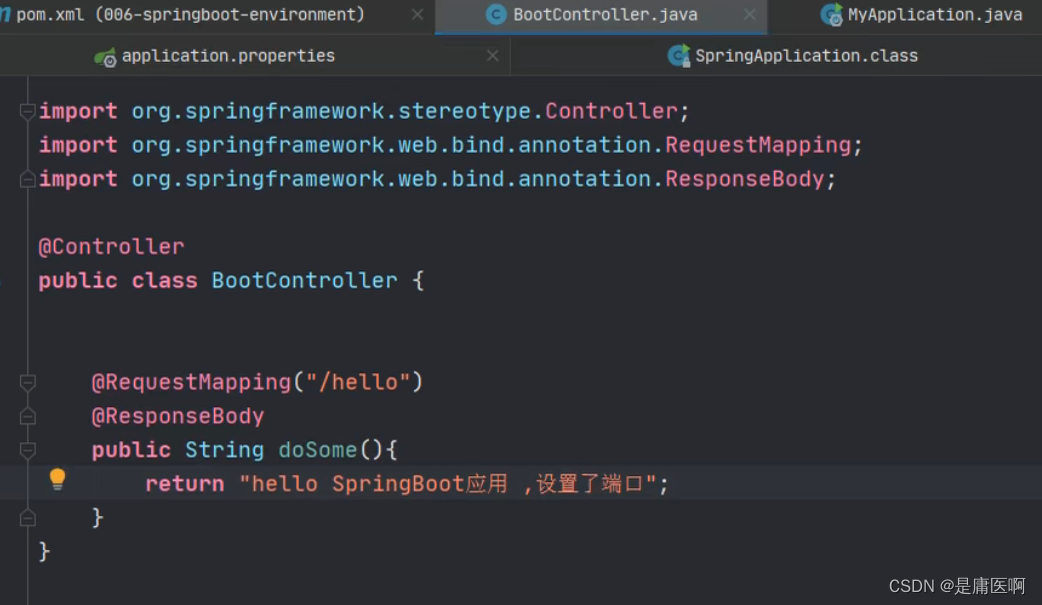
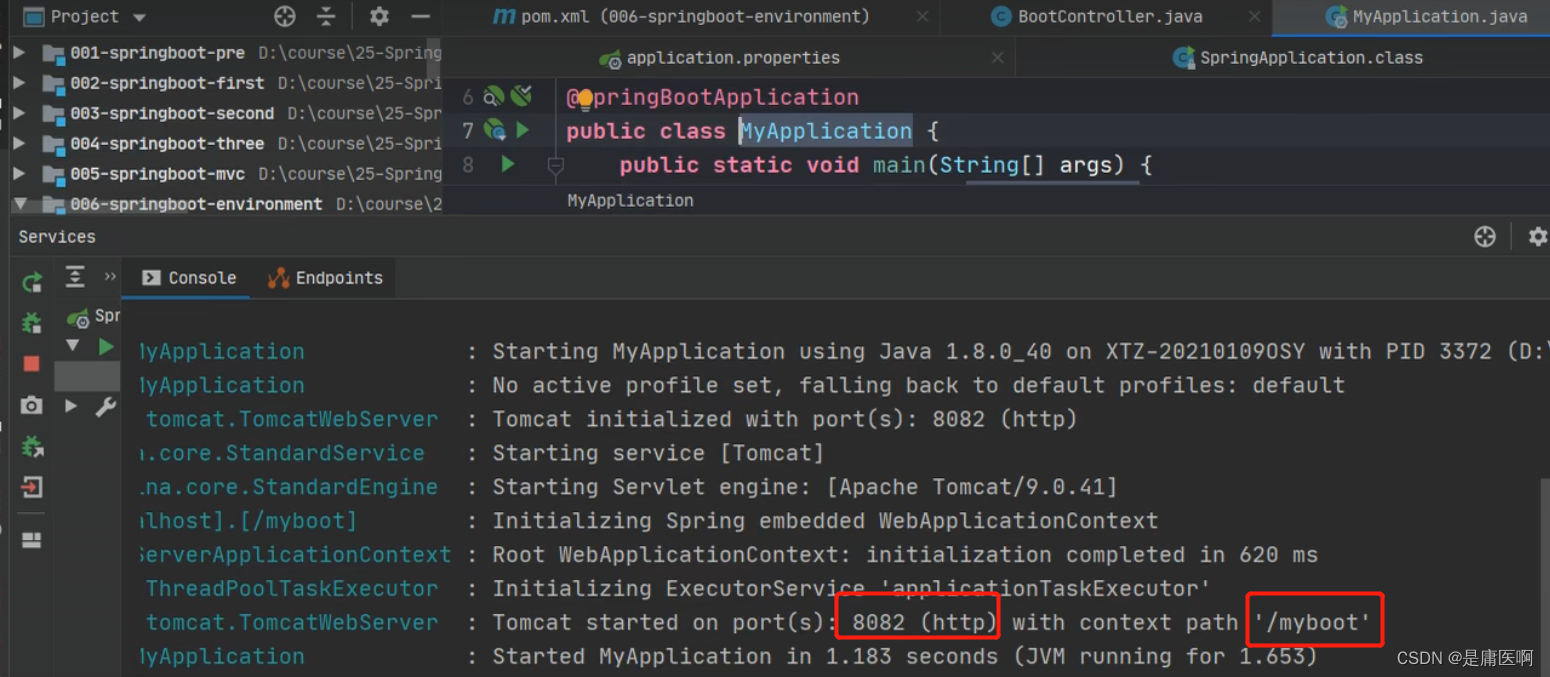
application.properties设置 端口和上下文
- #设置端口号
- server.port=8082
- #设置访问应用上下文路径, contextpath
- server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
-
application.yml
- server:
- port: 8083
- servlet:
- context-path: /myboot2
空格必须要有
5 多环境配置
有开发环境, 测试环境, 上线的环境。
每个环境有不同的配置信息, 例如端口, 上下文件, 数据库url,用户名,密码等等
使用多环境配置文件,可以方便的切换不同的配置。
使用方式: 创建多个配置文件, 名称规则: application-环境名称.properties(yml)
创建开发环境的配置文件: application-dev.properties( application-dev.yml )
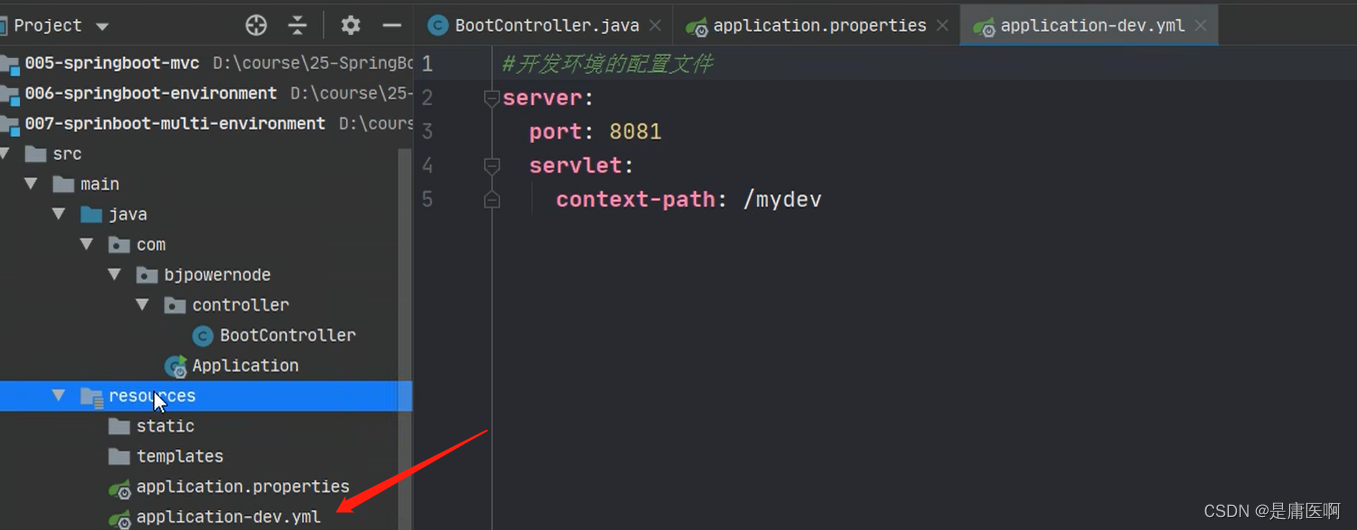
创建测试者使用的配置: application-test.properties
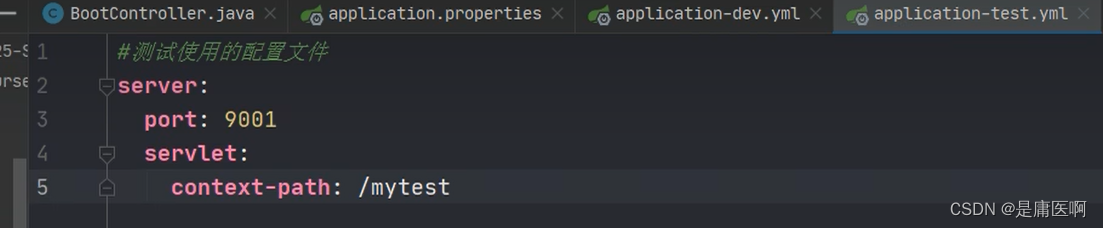
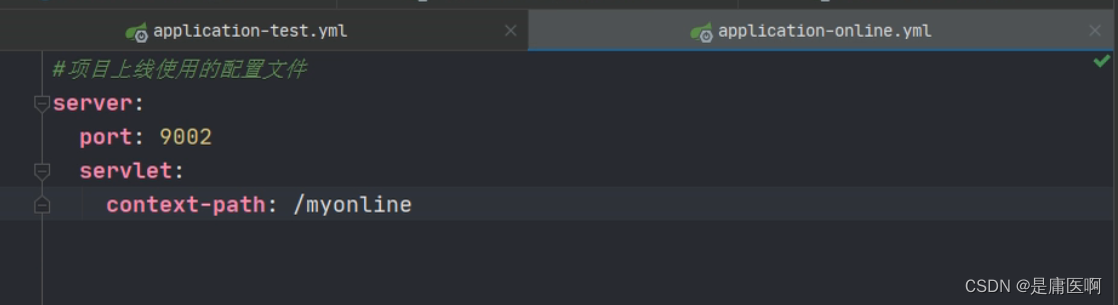 加粗的是我们自定义的名称
加粗的是我们自定义的名称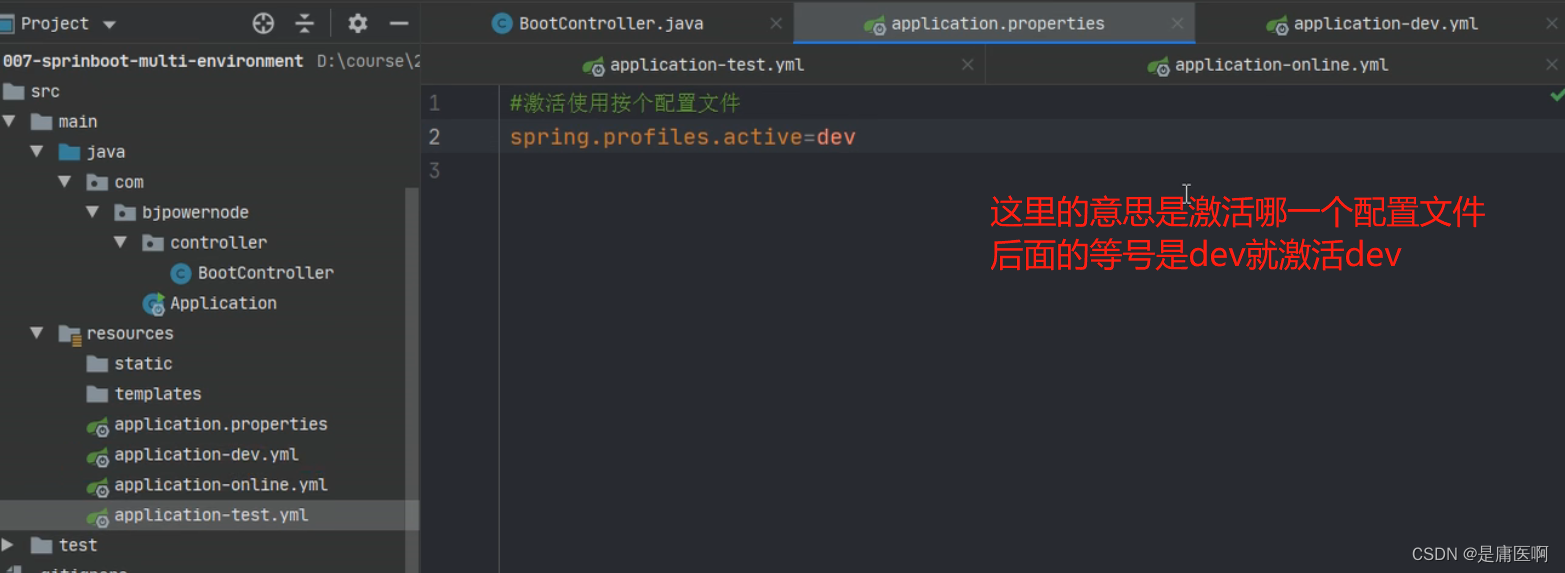
@Value读取数据
@Value("${key}") , key 来自 application.properties(yml)application.properties:添加两个自定义配置项 school.name 和school.website。在 IDEA 中可以看到这两个属性不能被 SpringBoot 识别,背景是桔色的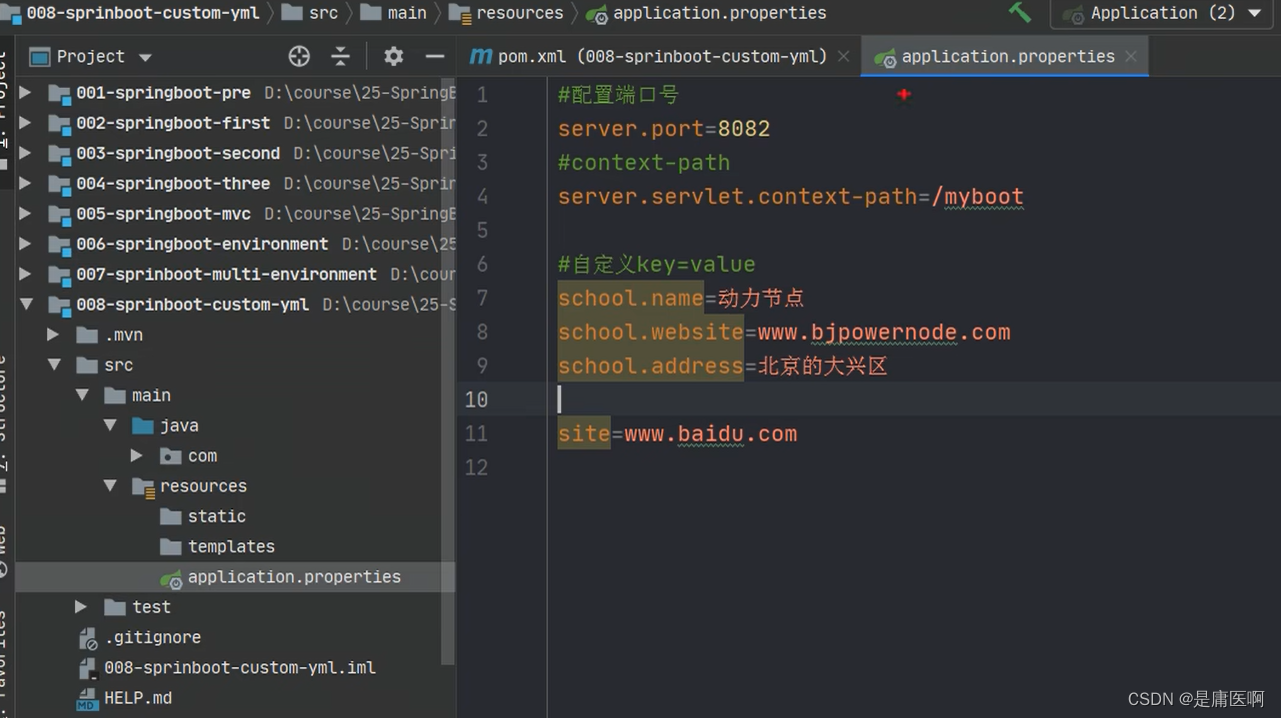
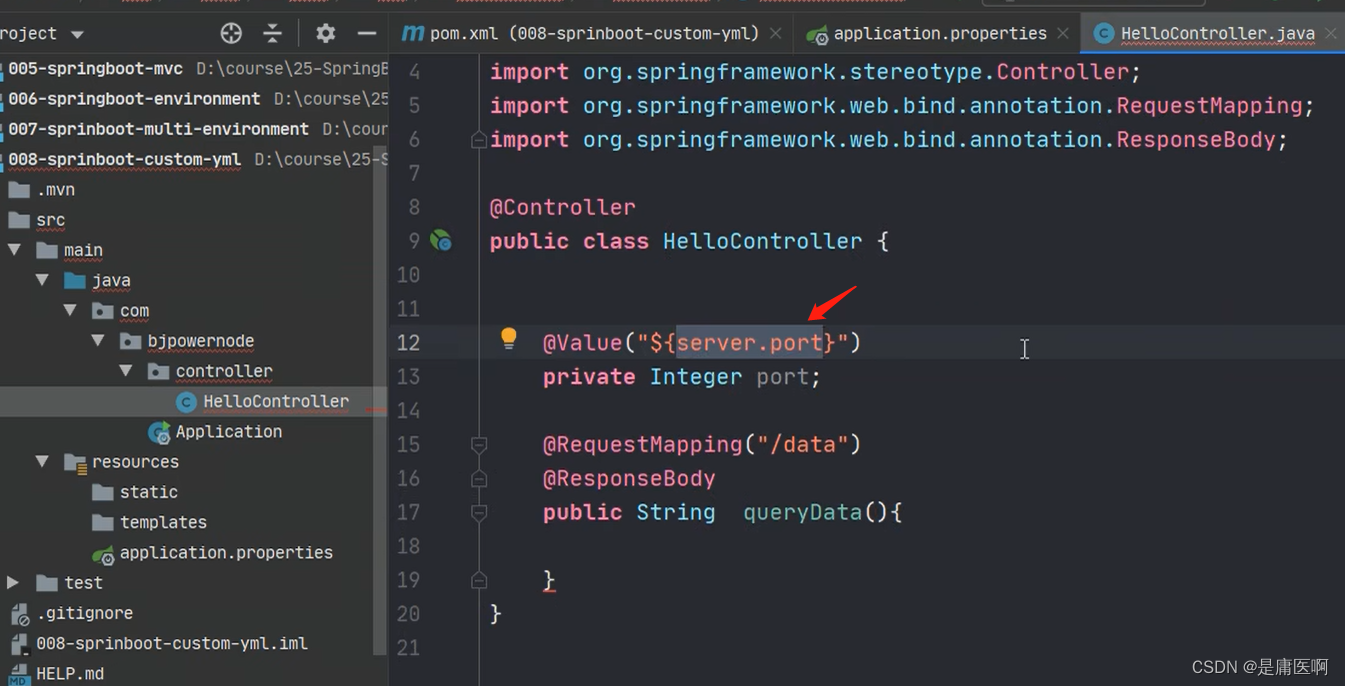
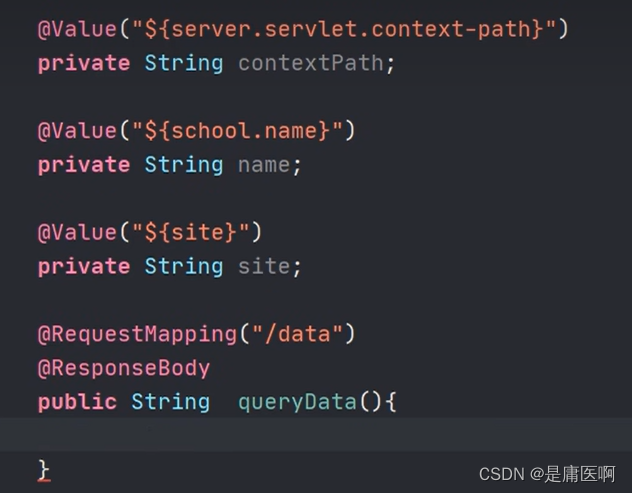
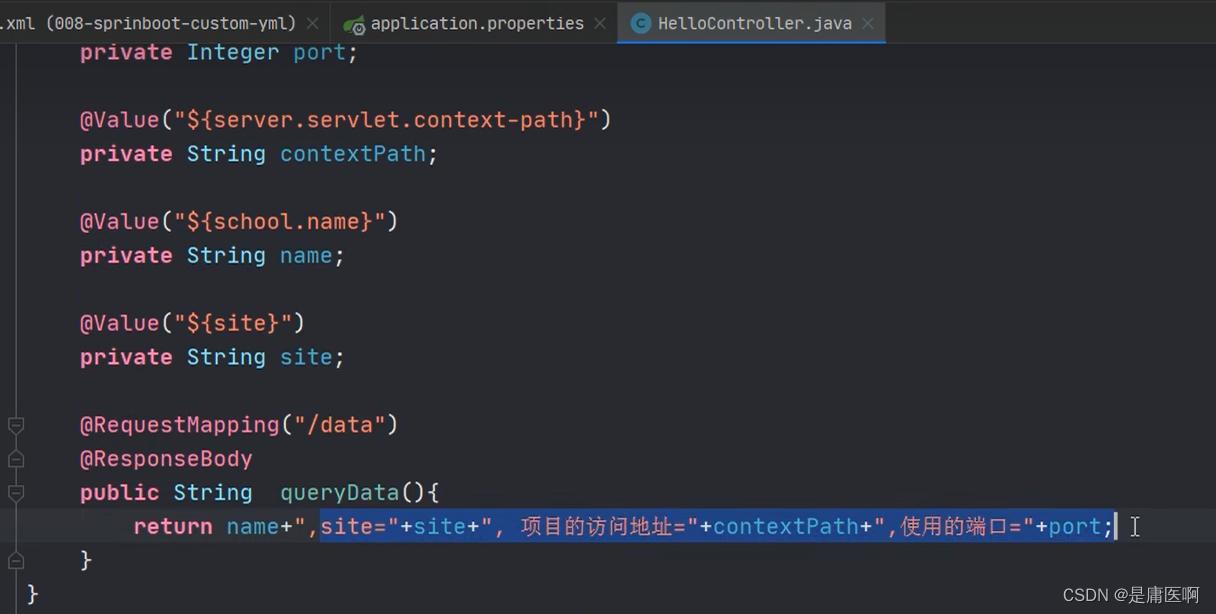

在配置文件中找school(把配置文件中的数据映射为java对象)
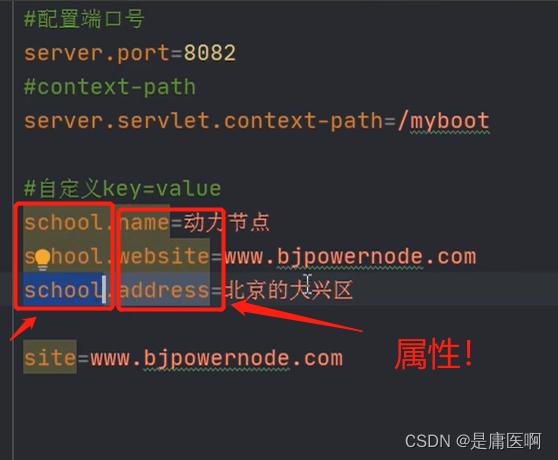
告诉框架在school中找school开头的属性,将这些和对象的属性名去比较,名字是一样的;那就将同样的话,就将文件中的数据赋给同名的属性,然后get set tostring
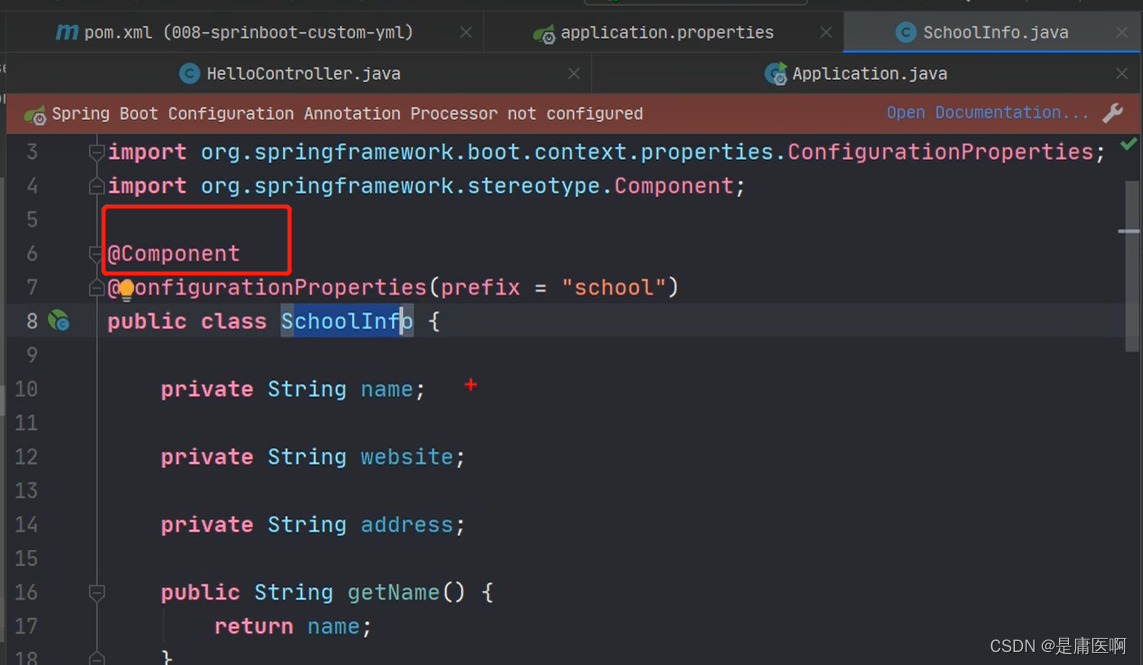
然后加@Component,目的是创建子类的对象
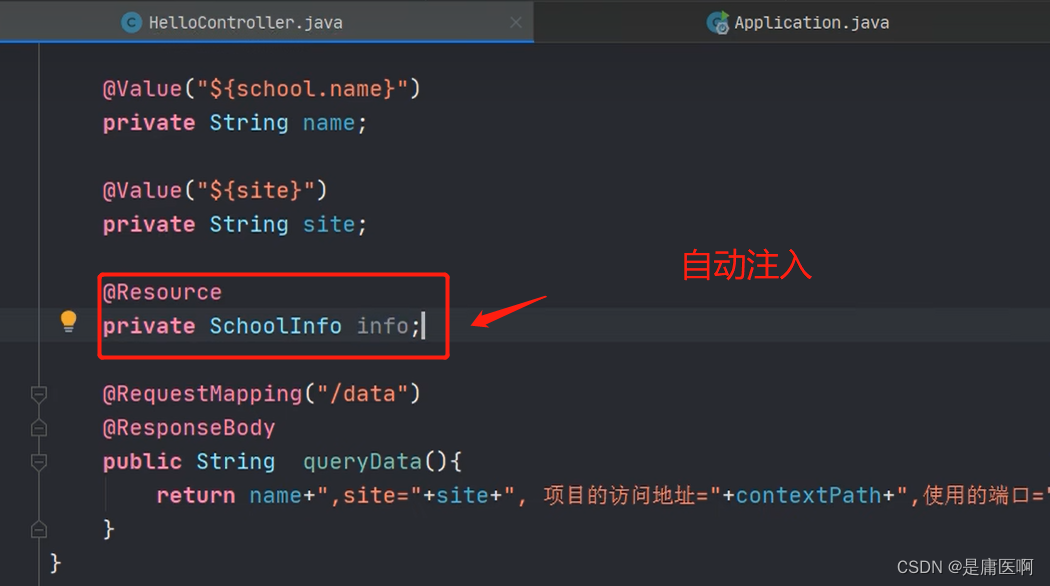 @Resource自动注入 ,从类中拿到SchoolInfo这个号对象,赋给info
@Resource自动注入 ,从类中拿到SchoolInfo这个号对象,赋给info6 @ConfigurationProperties
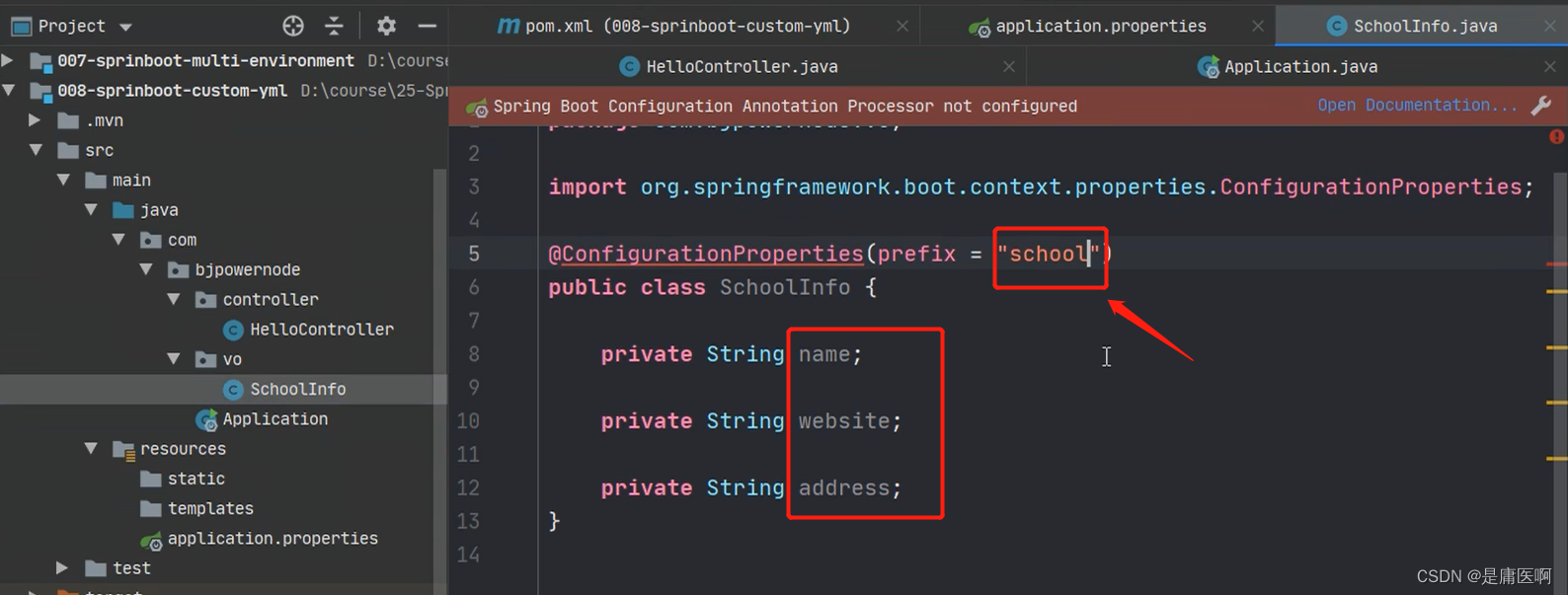
@ConfigurationProperties: 把配置文件的数据映射为java对象。
属性:prefix 配置文件中的某些key的开头的内容。
- @Component
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
- public class SchoolInfo {
- private String name;
- private String website;
- private String address;
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getWebsite() {
- return website;
- }
- public void setWebsite(String website) {
- this.website = website;
- }
- public String getAddress() {
- return address;
- }
- public void setAddress(String address) {
- this.address = address;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "SchoolInfo{" +
- "name='" + name + '\'' +
- ", website='" + website + '\'' +
- ", address='" + address + '\'' +
- '}';
- }
- }
application.properties
- #配置端口号
- server.port=8082
- #context-path
- server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
- #自定义key=value
- school.name=动力节点
- school.website=www.bjpowernode.com
- school.address=北京的大兴区
- site=www.bjpowernode.com
7 使用jsp
SpringBoot不推荐使用jsp ,而是使用模板技术代替jsp
使用jsp需要配置:
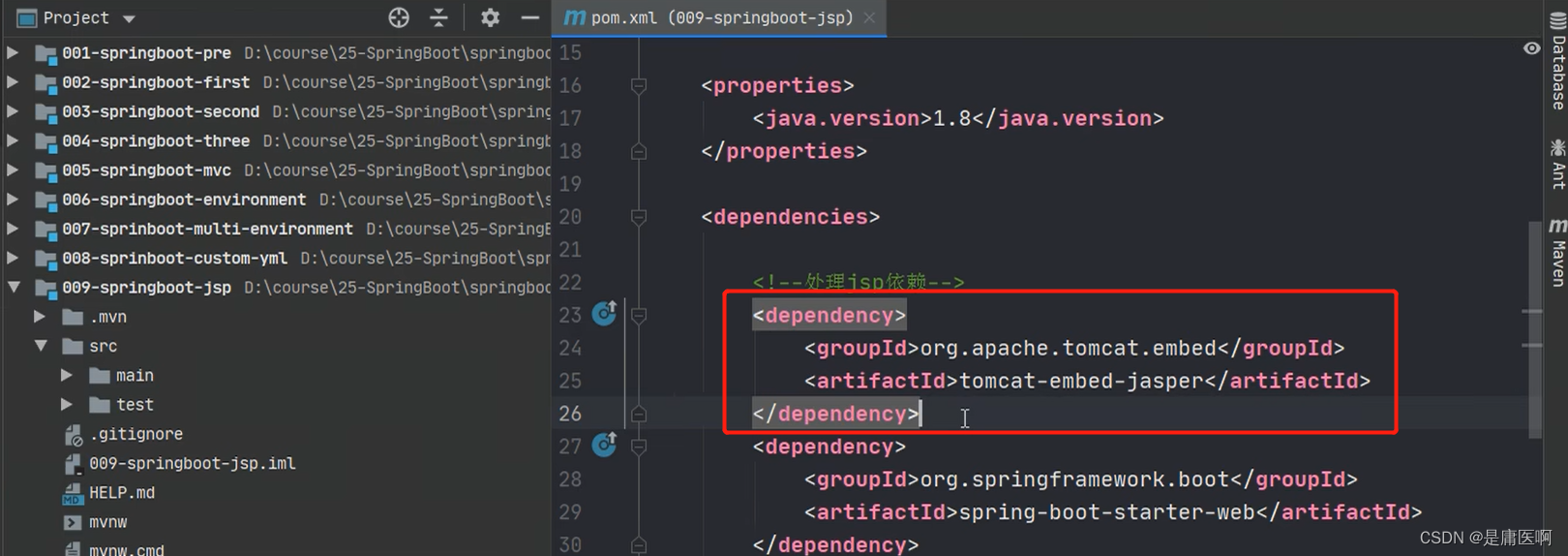
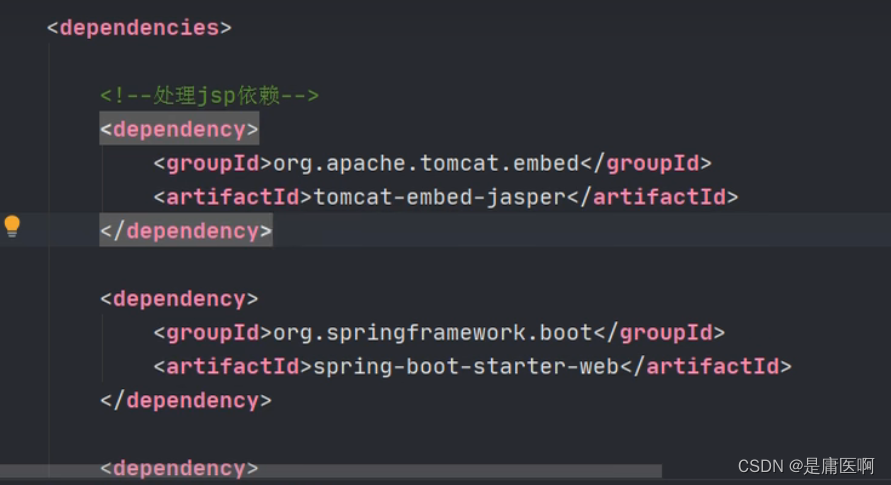
1) 加入一个处理jsp的依赖。 负责编译jsp文件
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
- <artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasperartifactId>
- dependency>

测试
2) 如果需要使用servlet, jsp,jstl的功能
- <dependency>
- <groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
- <artifactId>jstlartifactId>
- dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
- <artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
- dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
- <artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-apiartifactId>
- <version>2.3.1version>
- dependency>
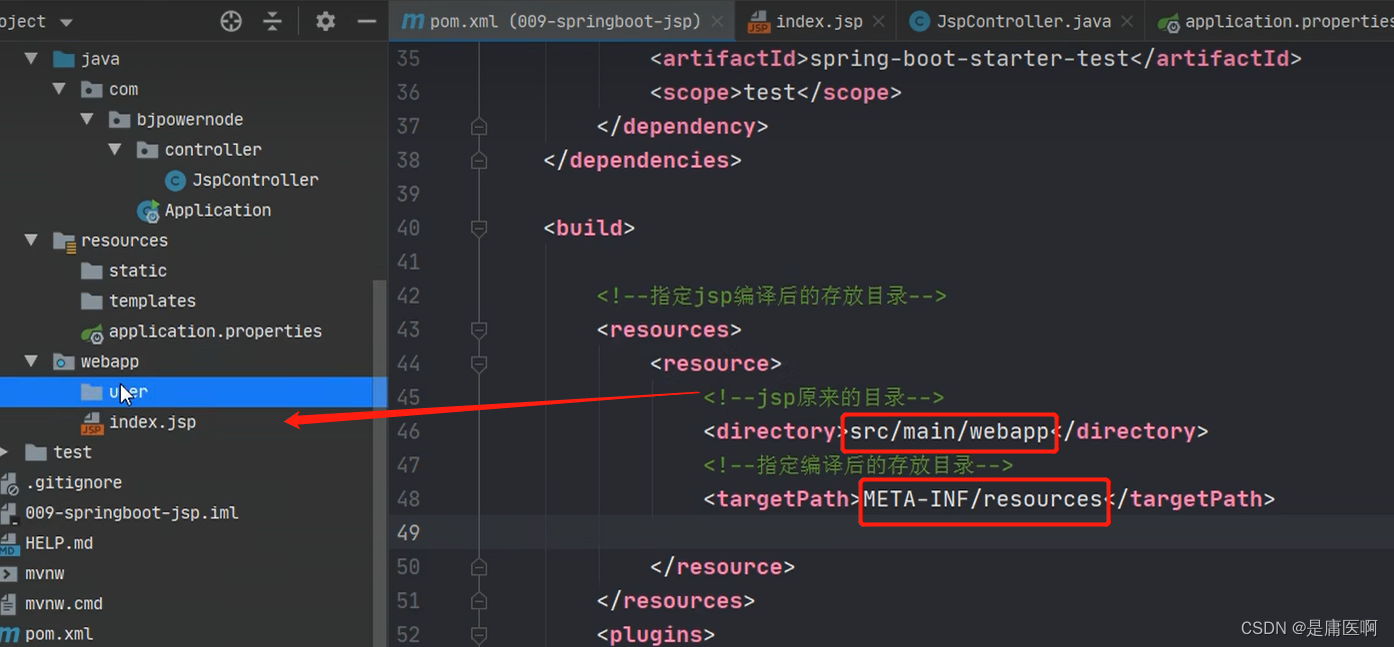
3) 创建一个存放jsp的目录,一般叫做webapp
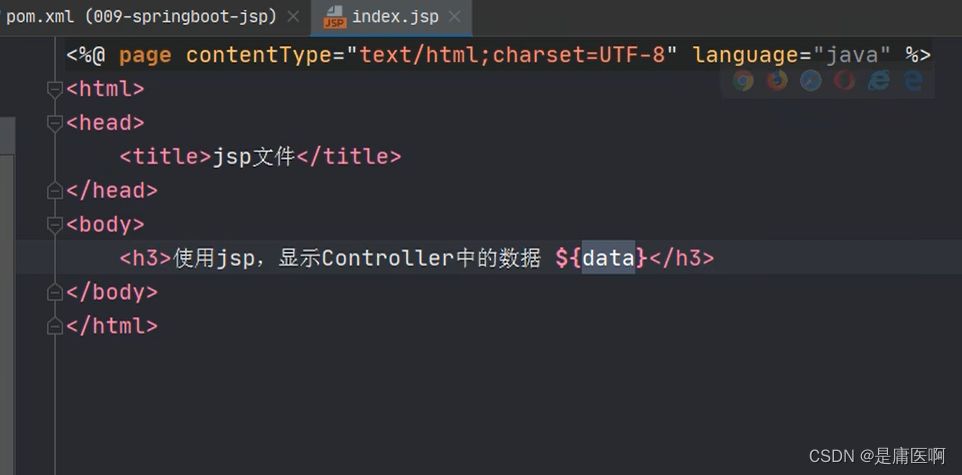
index.jsp
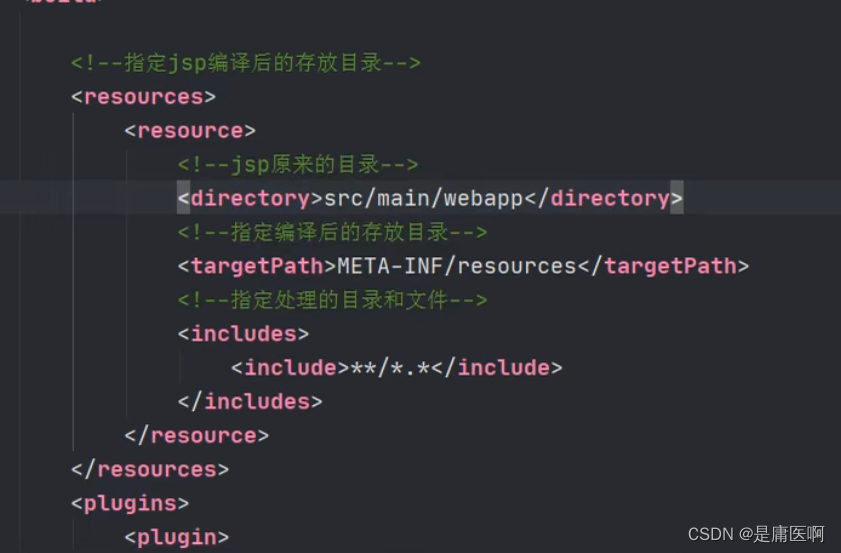
4) 需要在pom.xml指定jsp文件编译后的存放目录。
META-INF/resources
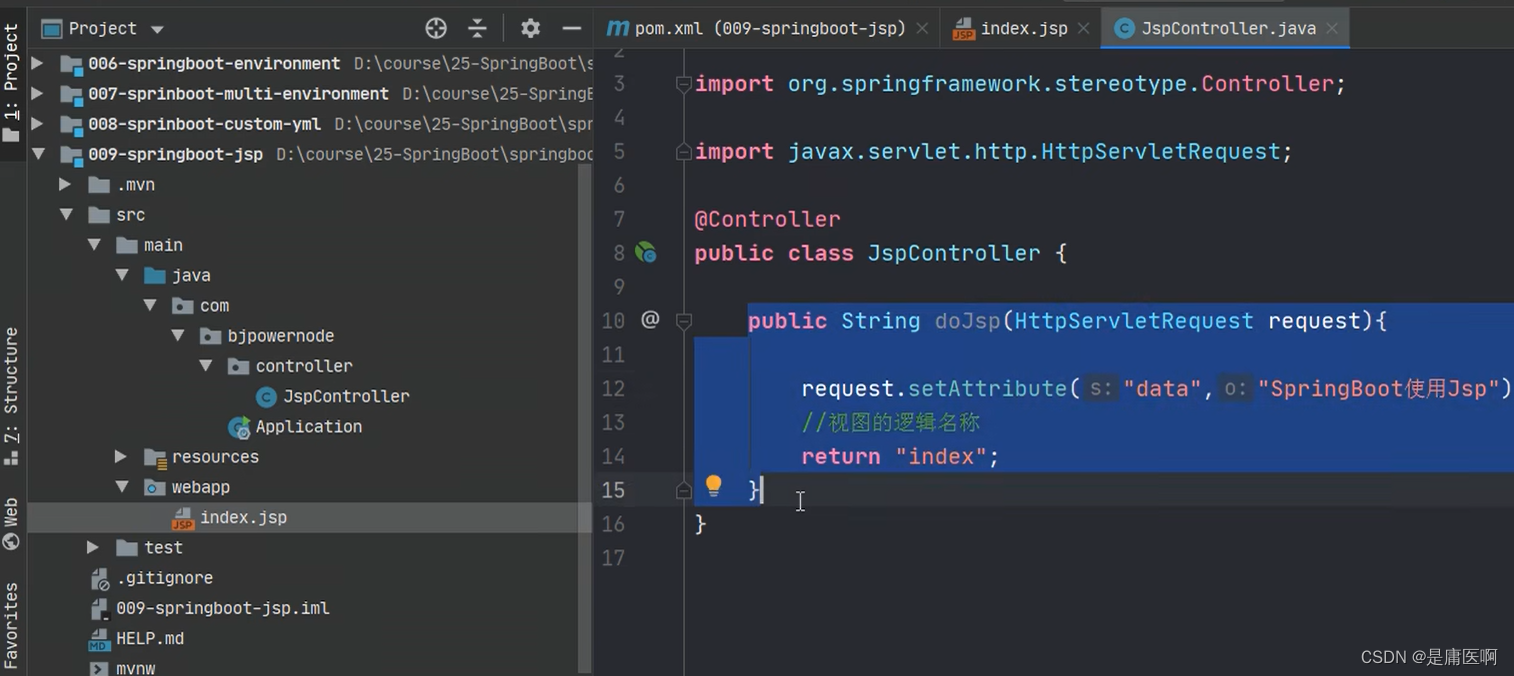
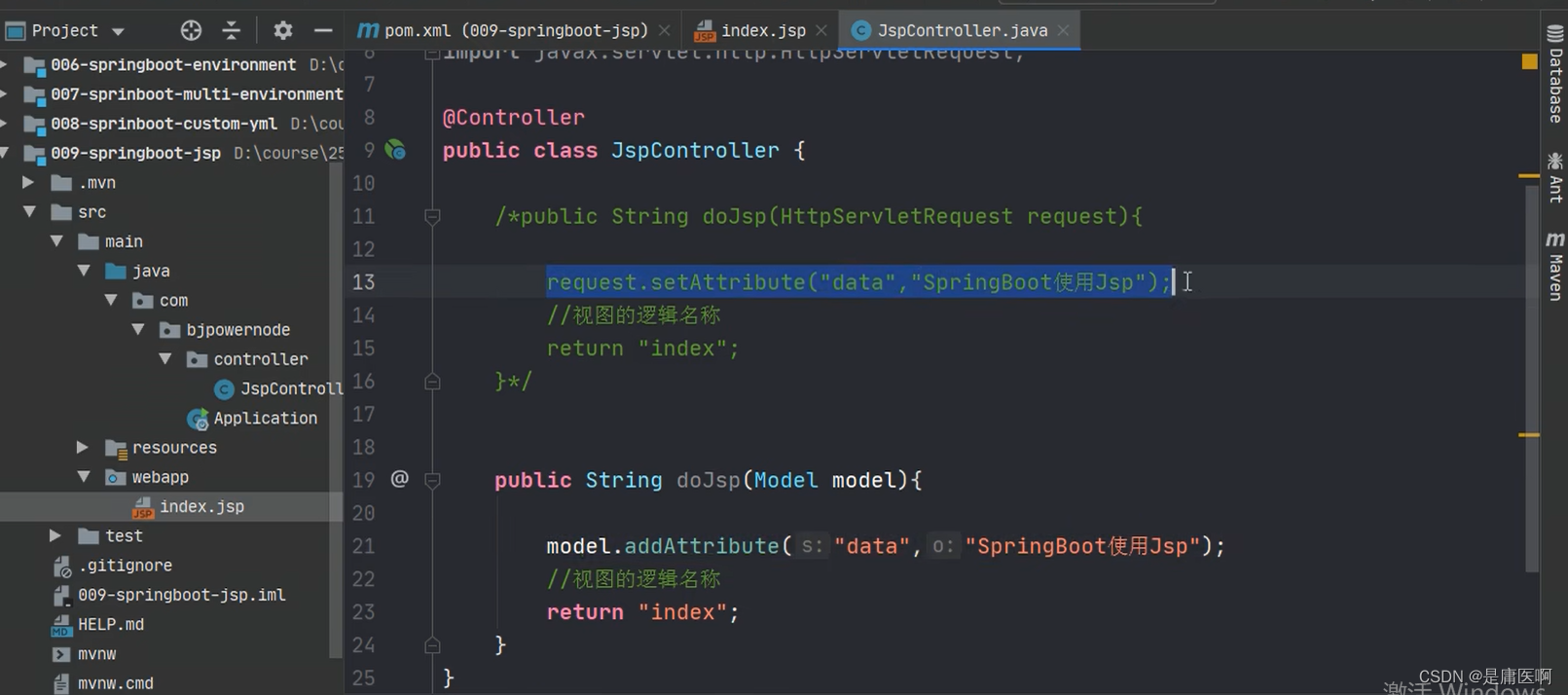
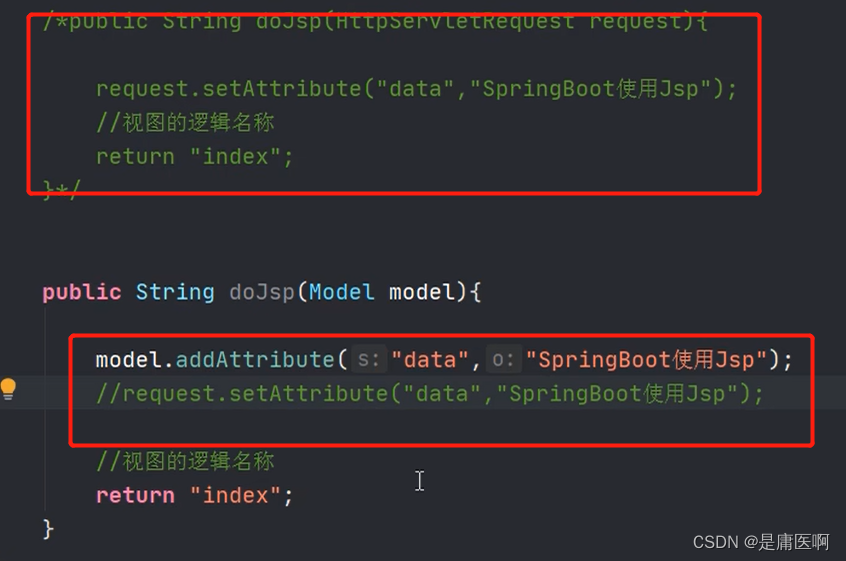
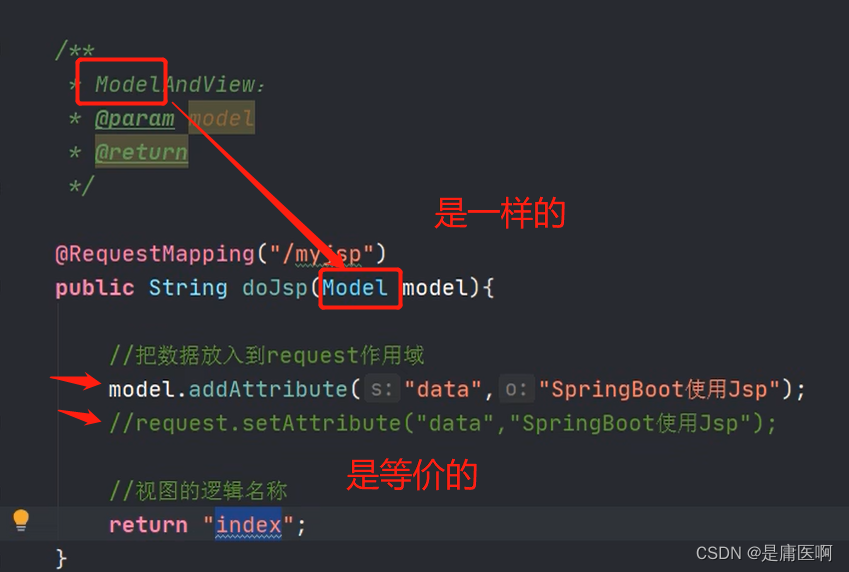
5)创建Controller, 访问jsp
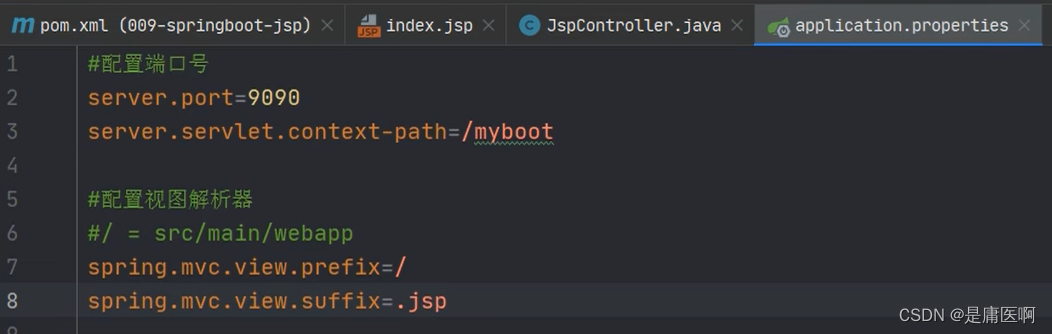
6)在application.propertis文件中配置视图解析器
8 使用容器
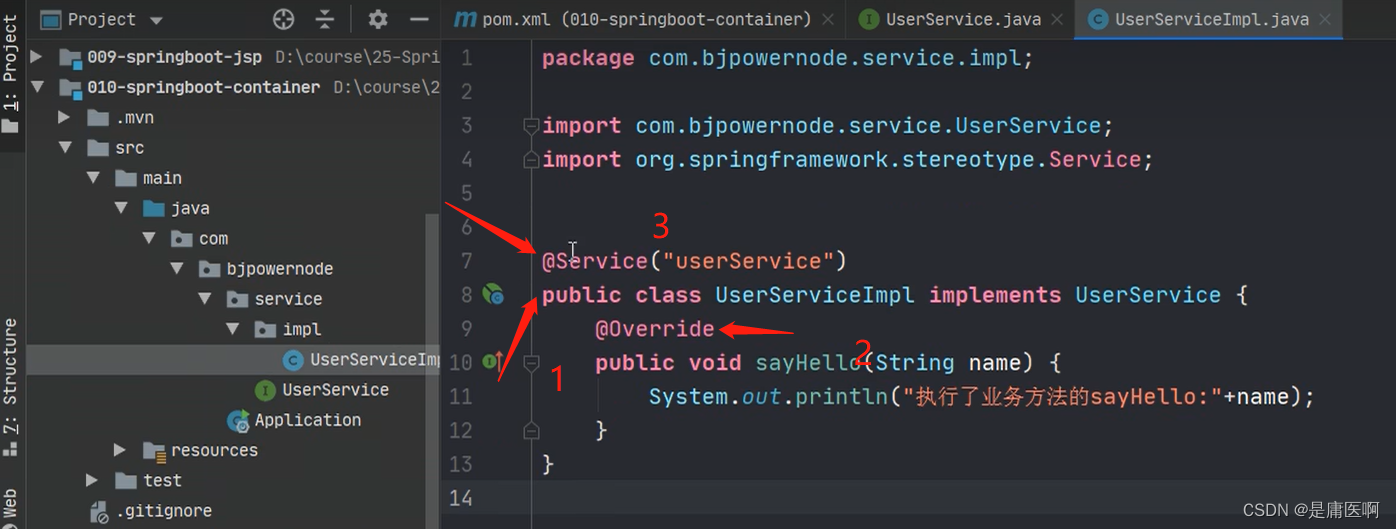
你想通过代码,从容器中获取对象。
通过SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 返回值获取容器。
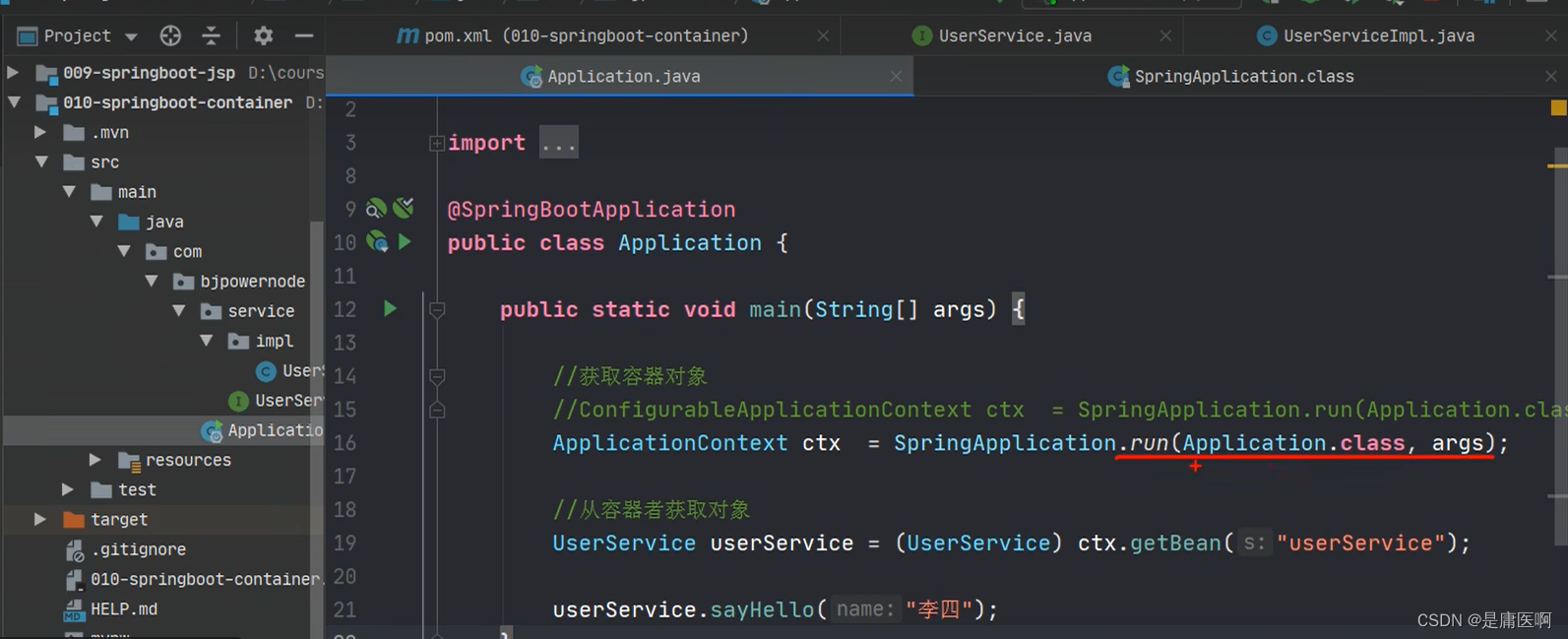
- public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class primarySource, String... args) {
- return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
- }
- ConfigurableApplicationContext : 接口,是ApplicationContext的子接口
- public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext
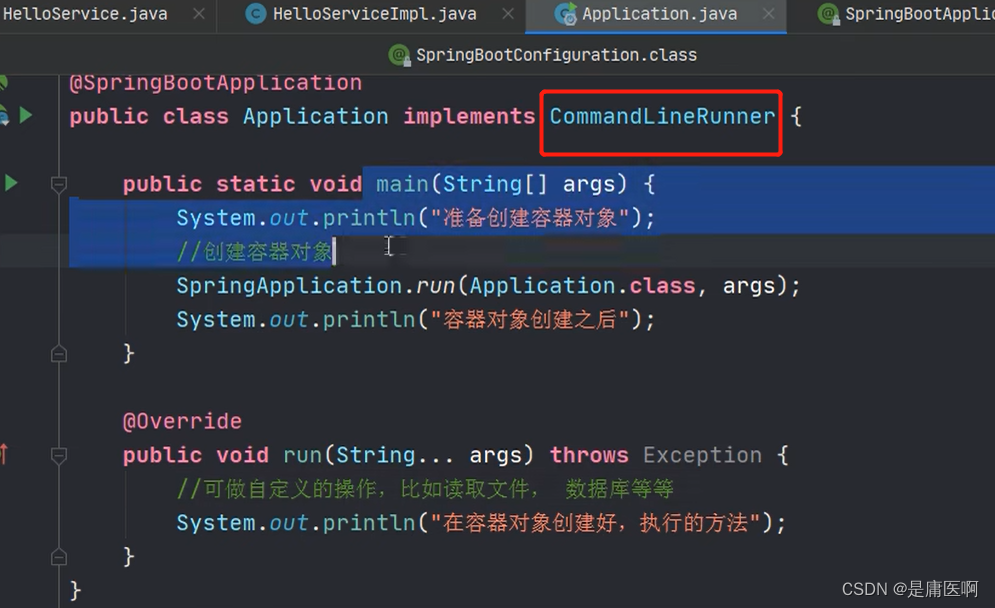
9 ComnandLineRunner 接口 , ApplcationRunner接口
这两个接口都 有一个run方法。 执行时间在容器对象创建好后, 自动执行run()方法。
可以完成自定义的在容器对象创建好的一些操作。
开发中可能会有这样的情景。需要在容器启动后执行一些内容。比如读取配置文件,数据库连接之类的。SpringBoot 给我们提供了两个接口来帮助我们实现这种需求。这两个接口分别为 CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner。他们的执行时机为容器启动完成的时候。这两个接口中有一个 run 方法,我们只需要实现这个方法即可。这两个接口的不同之处在于: ApplicationRunner 中 run 方 法 的 参 数 为 ApplicationArguments , 而CommandLineRunner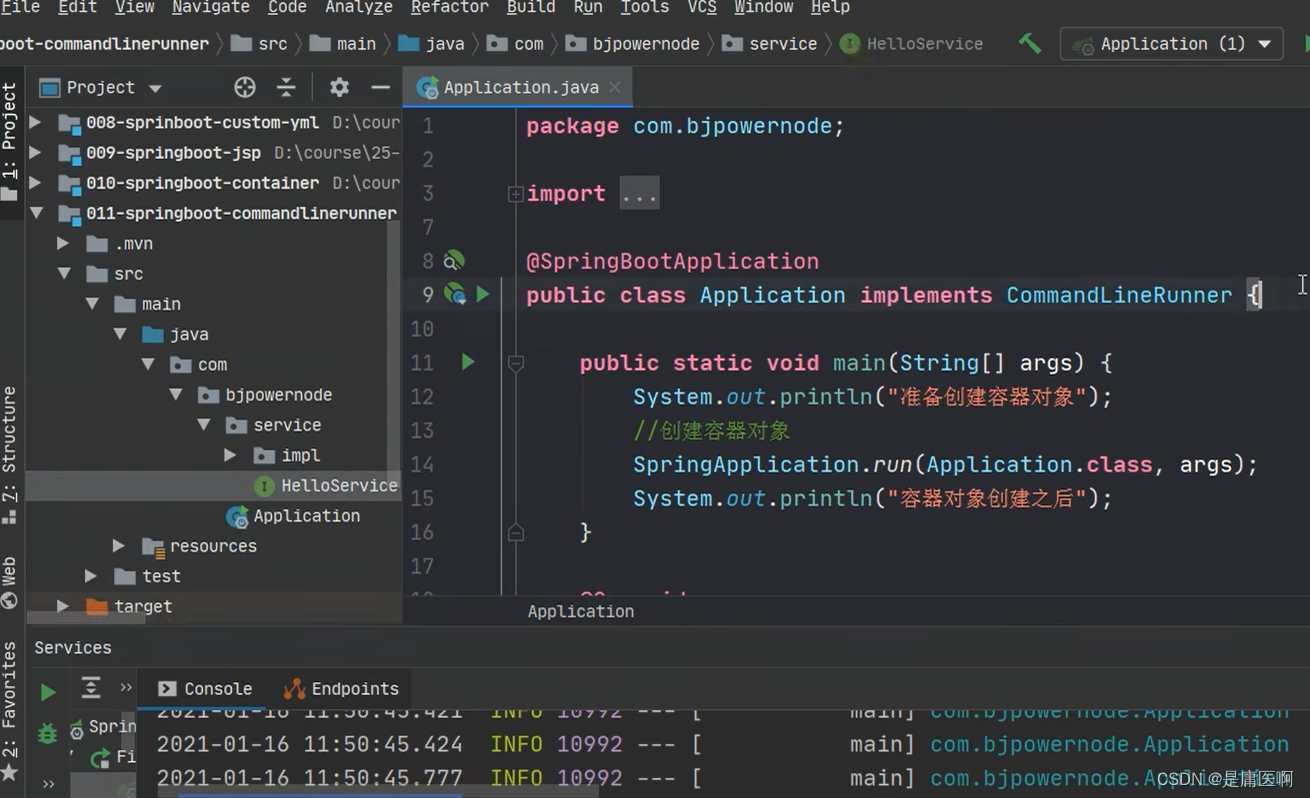
接口中 run 方法的参数为 String 数组
创建 Spring Boot 项目,不用选依赖,或者修改 010-springboot-container
创建 SomeService 接口和实现类,定义 sayHello()方法- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface CommandLineRunner {
- void run(String... args) throws Exception;
- }
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface ApplicationRunner {
- void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
- }

-
-
相关阅读:
OSI七层模型&TCP/IP四层&面试高频考点
.NET 扩展官方 Logger 实现将日志保存到本地文件
【计算机网络】网络编程 Socket
持续集成/持续部署:Git
数据挖掘note(赵老师语录)
Python中的设计模式 -- 单例
测试开发 | Java 接口自动化测试首选方案:REST Assured 实践
Postman 调用 Microsoft Graph API (InsCode AI 创作助手)
ansible command 模块
LeetCode每日一题(2017. Grid Game)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48826996/article/details/126252231
