-
数据结构之栈和队列
要努力,但不要急。繁花锦簇,硕果累累都需要过程!

1.栈
1.栈的概念:
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做压栈/进栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶
出栈:栈的删除操作叫出栈,出数据也在栈顶

2.栈的实现:
栈的实现一般使用数据或者是链表实现,但一般情况下使用顺序表,因为数据在尾插的时候代价比较小。

1.创建结构体:

缺点:指定内存大小,无法改变,因此一般使用动态增长的栈:

2.初始化栈:
void StackInit(ST* ps);

3.入栈:
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);

4.出栈:
void StackPop(ST* ps);

5.检查栈是否为空:
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);

6.获取栈中有效元素的个数:
int StackSize(ST* ps);

7.获取栈顶的元素:
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);

8.销毁栈:
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);

2.队列
1.概念:
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头

2.队列的实现:
队列的实现可以使用数组和链表,但是队列从头出数据,数组需要每次往前移动,时间复杂度为O(N),所以一般采用链表来实现队列
1.创建链式结构:表示队列

2.队列的结构:

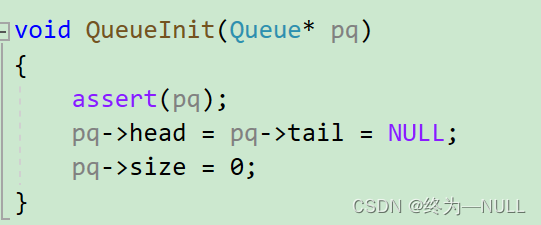
3.初始化队列:
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
4.队列插入数据:void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);

5.队列删除数据:
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);

6.判断队列是否为空:
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);

7.获取队列头部的元素:
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);

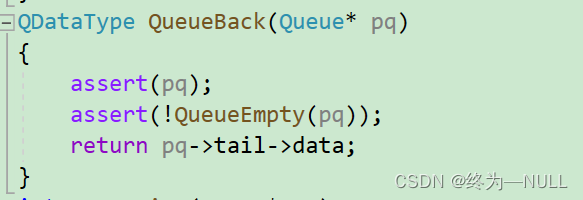
8.获取队列尾部的元素:
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
9.获取队列有效元素个数:
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);

10.销毁队列:
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);

3.栈和队列的面试题:
题目1:
括号匹配问题:
解法思路:将左括号放入栈中,然后取出来一一和外边的比较
不匹配的三种情况:
1.栈中的元素为空
2.栈中的元素不为空
3.类型不匹配
- typedef char STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* arr;
- int top;
- int capacity;//记录数组的容量
- }ST;
- //初始化栈:
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- //入栈:
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
- //出栈:
- void StackPop(ST* ps);
- //获取栈顶的元素:
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- //检查栈是否为空:
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
- //获取栈中有效元素的个数:
- int StackSize(ST* ps);
- //销毁栈:
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- //检查容量:
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- //增容:
- int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->arr = tmp;
- ps->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- void StackPop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
- }
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->arr);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
- }
- bool isValid(char * s){
- ST st;
- StackInit(&st);
- while(*s)
- {
- //将左括号放入栈中:
- if(*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '[')
- {
- StackPush(&st,*s);
- }
- else//取出栈中的括号和外边的比较:
- {
- //取到右括号,栈为空,说明左括号数量不匹配
- if(StackEmpty(&st))
- {
- StackDestroy(&st);
- return false;
- }
- char top = StackTop(&st);
- StackPop(&st);
- if((*s == '}' && top != '{')
- ||(*s == ']' && top != '[')
- ||(*s == ')' && top != '('))
- {
- StackDestroy(&st);
- return false;
- }
- }
- s++;
- }
- //栈不为空说明右括号数量不匹配:
- bool flag = StackEmpty(&st);
- StackDestroy(&st);
- return flag;
- }
题目二:
用两个队列实现一个栈:oj链接
解法思路:保持一个队列为空,然后进行转换

- typedef int QDataType;
- typedef struct QListNode
- {
- struct QListNode* next;
- QDataType data;
- }QNode;
- typedef struct Queue
- {
- QNode* head;//头指针
- QNode* tail;//尾指针
- int size;//记录队列元素个数
- }Queue;
- //初始化队列:
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
- //销毁队列:
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
- //队列插入数据:
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
- //队列删除数据:
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
- //判断队列是否为空:
- bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
- //获取队列头部的元素:
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
- //获取队列尾部的元素:
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
- //获取队列有效元素个数:
- int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- pq->size = 0;
- }
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- QNode* cur = pq->head;
- while (cur)
- {
- QNode* del = cur;
- cur = cur->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
- pq->head = NULL;
- pq->tail = NULL;
- }
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
- {
- assert(pq);
- QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail:");
- exit(-1);
- }
- else
- {
- newnode->next = NULL;
- newnode->data = x;
- }
- if (pq->tail == NULL)
- {
- pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
- }
- else
- {
- pq->tail->next = newnode;
- pq->tail = newnode;
- }
- pq->size++;
- }
- bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
- }
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- if (pq->head->next == NULL)
- {
- free(pq->head);
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- Queue* del = pq->head;
- pq->head = pq->head->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
- pq->size--;
- }
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- return pq->head->data;
- }
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- return pq->tail->data;
- }
- int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
- {
- return pq->size;
- }
- typedef struct {
- Queue q1;
- Queue q2;
- } MyStack;
- MyStack* myStackCreate() {
- MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
- QueueInit(&obj->q1);
- QueueInit(&obj->q2);
- return obj;
- }
- void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
- else
- QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
- }
- int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
- Queue* empty = &obj->q1;
- Queue* noEmpty = &obj->q2;
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- empty = &obj->q2;
- noEmpty = &obj->q1;
- }
- while(QueueSize(noEmpty) > 1)
- {
- QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noEmpty));
- QueuePop(noEmpty);
- }
- int top = QueueFront(noEmpty);
- QueuePop(noEmpty);
- return top;
- }
- int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
- else
- return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
- }
- bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
- return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
- }
- void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
- QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
- QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
- free(obj);
- }
题目三:
用栈实现队列:oj链接
解法思路:一个栈中专门用来存放数据,一个栈中专门用来删除数据

- typedef int STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* arr;
- int top;
- int capacity;//记录数组的容量
- }ST;
- //初始化栈:
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- //入栈:
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
- //出栈:
- void StackPop(ST* ps);
- //获取栈顶的元素:
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- //检查栈是否为空:
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
- //获取栈中有效元素的个数:
- int StackSize(ST* ps);
- //销毁栈:
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- //检查容量:
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- //增容:
- int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->arr = tmp;
- ps->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- void StackPop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
- }
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->arr);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
- }
- typedef struct {
- ST pushST;
- ST popST;
- } MyQueue;
- MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
- MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
- StackInit(&obj->pushST);
- StackInit(&obj->popST);
- return obj;
- }
- void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
- StackPush(&obj->pushST,x);
- }
- void pushSTTopopST(MyQueue* obj)
- {
- if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
- {
- while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
- {
- StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
- StackPop(&obj->pushST);
- }
- }
- }
- int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
- pushSTTopopST(obj);
- int front = StackTop(&obj->popST);
- StackPop(&obj->popST);
- return front;
- }
- int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
- pushSTTopopST(obj);
- return StackTop(&obj->popST);
- }
- bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
- return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) && StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
- }
- void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
- StackDestroy(&obj->pushST);
- StackDestroy(&obj->popST);
- free(obj);
- }
题目四:
设计循环队列:oj链接
解法思路:用数组实现
循环队列的逻辑结构:

定义两个下标依次插入数据,为了区分数据空和满的情况,需要多开辟一个空间,当back的下一个位置等于front的时候说明队列数据满了:
- typedef struct {
- int* a;
- int front;//标记头
- int back;//标记尾
- int N;//记录空间大小
- } MyCircularQueue;
- MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
- MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
- obj->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));//多开辟一个空间
- obj->front = 0;
- obj->back = 0;
- obj->N = k + 1;
- return obj;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- return obj->front == obj->back;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- //%obj->N 当back在最后的时候回到起始位置
- return (obj->back + 1) % obj->N == obj->front;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
- return false;
- obj->a[obj->back] = value;
- obj->back++;
- //当到队尾的时候,返回到起始位置
- obj->back %= obj->N;
- return true;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return false;
- obj->front++;
- // //当到队尾的时候,返回到起始位置
- obj->front %= obj->N;
- return true;
- }
- int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- return obj->a[obj->front];
- }
- int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- else if(obj->back == 0)
- return obj->a[obj->N-1];
- else
- return obj->a[obj->back-1];
- }
- void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- free(obj->a);
- obj->a = NULL;
- free(obj);
- obj = NULL;
- }
总结:
以上就是关于栈和队列的知识点和相关面试题,本质上栈和队列也是在内存中管理数据,是通过数组和链表的结构来实现的。
-
相关阅读:
利用PHP的特性做免杀Webshell
Linux内核驱动开发的需要掌握的知识点
〔003〕虚幻 UE5 基础教程和蓝图入门
java学习(常用类)
如何使用Docker安装最新版本的Redis并设置远程访问(含免费可视化工具)
Nginx下PHP连接到GBase 8s数据库 - PDO_GBASEDBT方式
【牛客刷题】每日一练—ArrayList的实例强化
进程调度算法详解
头哥实践平台之Linux 文件/目录管理
bind搭建内网DNS服务器架构(主从、子域授权、DNS转发器)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_65307907/article/details/126166669
