-
2022年了,你还不会java多线程吗?
1.什么是多线程?
Java 给多线程编程提供了内置的支持。 一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
多线程是多任务的一种特别的形式,但多线程使用了更小的资源开销。
这里定义和线程相关的另一个术语 - 进程:一个进程包括由操作系统分配的内存空间,包含一个或多个线程。一个线程不能独立的存在,它必须是进程的一部分。一个进程一直运行,直到所有的非守护线程都结束运行后才能结束。
多线程能满足程序员编写高效率的程序来达到充分利用 CPU 的目的。
2.线程的基本使用
java中创建线程有两种方式:
- 通过继承
Thread类,重写run方法,创建线程 - 实现
Runnable接口,重写run方法,创建线程
通过继承
Thread类创建线程代码示例:(此程序的任务是开启一个猫猫线程,该线程循环8此打印输出我是修猫🐱,随后结束)/** * 多线程的基本使用 * 通过继承Thread类创建线程 */ public class ThreadUse { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat(); cat.start(); // 启动线程 } } /** * 继承Thread * 该类就可以当作线程使用 */ class Cat extends Thread { // 重写run方法,写自己的业务 // run方法实现了Runnable接口的run方法 @Override public void run() { int times = 0; while (true) { System.out.println("我是修猫🐱" + (++times)); // 让线程休眠1秒 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (times == 8) { break; } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
3.多线程控制机制
当我们开启一个线程类时,程序的调度机制时这样的:

此时如果CPU是多核就是并行执行,单核就是并发执行🎈
当程序启动一个子线程
Thread-0,主线程不会阻塞,会继续执行,主线程结束,Thread-0线程还未结束时,不会影响Thread-0执行,例如:/** * 多线程的基本使用 * 通过继承Thread类创建线程 */ public class ThreadUse { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Cat cat = new Cat(); cat.start(); // 启动线程 // 当程序自动一个子线程 Thread-0 ,主线程不会阻塞,会继续执行 System.out.println("我还可以被输出!"); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("我是修狗🐕"); } } /** * 继承Thread * 该类就可以当作线程使用 */ class Cat extends Thread { // 重写run方法,写自己的业务 // run方法实现了Runnable接口的run方法 @Override public void run() { int times = 0; while (true) { System.out.println("我是修猫🐱" + (++times)); if (times == 1){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } // 让线程休眠1秒 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (times == 8) { break; } } } } ---------------------------------- 输出: 我还可以被输出! 我是修猫🐱1 Thread-0 我是修猫🐱2 我是修狗🐕 我是修猫🐱3 我是修猫🐱4 我是修猫🐱5 我是修猫🐱6 我是修猫🐱7 我是修猫🐱8- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
4.start源码分析
当我们触发一个线程的时候,需要使用
start而非直接在主线程调用方法现在我们来看一下
start底层的真面目public synchronized void start() { if (this.threadStatus != 0) { throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); } else { this.group.add(this); boolean started = false; try { this.start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { this.group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable var8) { } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
在
start源码里面,真正触发多线程的是此句话:this.start0();- 1
它是一个本地方法,由JVM机进行调用,底层是C/C++实现
真正实现多线程的效果,其实是
strat0方法,而不是run方法😶🌫️
5.实现Runnable接口创建线程
java是单继承的,某些情况一个类可能已经继承了某一个父类,那么再通过继承
Thread类来实现多线程,显然是不可行的此时我们可以使用实现
Runnable接口来创建线程✨/** * 通过继承Runnable接口实现多线程 */ public class ThreadUseByRunnable { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Dog dog = new Dog(); // 通过创建Thread类传入dog从而执行线程 Thread thread = new Thread(dog); thread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println("主线程" + i); Thread.sleep(1000); } } } /** * 通过实现Runnable接口实现多线程 */ class Dog implements Runnable { int count = 0; @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println("小狗旺旺🐕" + (++count)); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (count == 8) { break; } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
6.多个子线程实例
/** * 多个子线程案例 */ public class ChildThreads { public static void main(String[] args) { T1 t1 = new T1(); T2 t2 = new T2(); Thread thread = new Thread(t1); Thread thread1 = new Thread(t2); thread.start(); thread1.start(); } } class T1 implements Runnable { int times = 0; @Override public void run() { // 每隔1秒输出一次hello world while (true) { System.out.println("hello world" + (++times)); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (times == 8) { break; } } } } class T2 implements Runnable { int times = 0; @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println("hi" + (++times)); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (times == 8) { break; } } } } ------------------------------- 两个线程交替输出: hello world1 hi1 hello world2 hi2 hello world3 hi3 hello world4 hi4 hello world5 hi5 hello world6 hi6 hello world7 hi7 hello world8 hi8- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
存在多个子线程时,系统的调度结构如下:
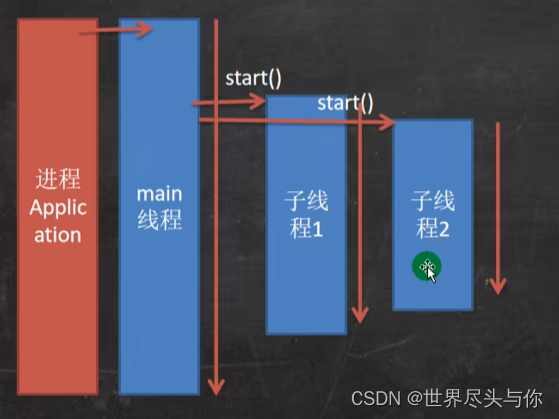
ThreadVSRunnable🐭(建议使用Runnable)- 创建线程本质上没有区别,都是通过
strat0方法 Runnable接口更加适合多个线程共享一个资源的情况,并且避免的单继承的限制
- 通过继承
-
相关阅读:
所有字母异位词
HTML的基础标签和HTML的Form表单
嵌入式Linux驱动开发(I2C专题)(三)
题目:2729.判断一个数是否迷人
深度学习跨平台环境问题
2-2Linux下文件操作常用命令
CMT2380F32模块开发19-LVD例程
Linux磁盘分区命令行工具大比拼,你该选哪个?
c#.NET技术做到ChatGPT流式响应并实现打字机效果 实现ChatGPT的Stream传输
深入理解计算机网络-10传输层2
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Gherbirthday0916/article/details/126078485