-
web 面试高频考点 —— HTML & CSS 篇
系列文章目录
HTML
理解 HTML 语义化
- 让人更容易读懂(增加代码可读性)
- 让搜索引擎更容易读懂(SEO)
示例:通过操作这两种方式能实现同样的效果,但我们更倾向于第一种写法
- 第一种:
<div> <ul> <li></li> </ul> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 第二种:
<div> <div> <div></div> </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
块状元素和内联元素
块状元素:div、h1-h5、table、ul、ol、p 等
diaplay: block/table- 1
内联元素:span、img、input、button 等
display: inline/inline-bolck- 1
block、inline、inline-block 的区别:

图示区别:
.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; display: block; } <div class="box">block</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; display: inline; } <div class="box">inline</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; display: inline-block; } <div class="box">inline</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

布局
盒模型宽度计算
offsetWidth:(内容宽度 + 内边距 + 边框),无外边距
示例:offsetWidth:100 + 10 + 10 + 1 + 1 = 122px
#div { width: 100px; padding: 10px; margin: 10px; border: 1px solid #ccc; } <div id="div"></div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
盒模型
示例:控制 offsetWidth 的值为 100px
#div { width: 100px; padding: 10px; margin: 10px; border: 1px solid #ccc; box-sizing: border-box; } <div id="div">this is div</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
盒模型2
margin 纵向重叠问题
相邻元素 的 margin-top 和 margin-bottom 会发生重叠
空白内容的
也会重叠示例:S 的 margin-bottom 为 15 px
p { font-size: 16px; line-height: 1; margin-top: 10px; margin-bottom: 15px; } <p>SSS</p> <p></p> <p></p> <p></p> <p>HHH</p>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

margin 负值问题
-
margin-top 和 margin-left 负值,元素向上、向左移动
-
margin-right 负值,右侧元素左移,自身不受影响
-
magin-bottom 负值,下方元素上移,自身不受影响
body { margin: 20px; } .float-left { float: left; } .clearfix:after { content: ''; display: block; clear: both; } .container { border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px; } .container .item { width: 100px; height: 100px; } .container .border-blue { border: 1px solid blue; } .container .border-red { border: 1px solid red; } <p>用于测试 margin top bottom 的负数情况</p> <div class="container"> <div class="item border-blue"> this is item 1 </div> <div class="item border-red"> this is item 2 </div> </div> <p>用于测试 margin left right 的负数情况</p> <div class="container clearfix"> <div class="item border-blue float-left"> this is item 1 </div> <div class="item border-red float-left"> this is item 2 </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 示例:top left
margin 负数情况
- 示例:right bottom
margin 负数情况2
BFC 理解与应用
Block format context,块级格式化上下文
一块独立渲染区域,内部元素的渲染不会影响边界以外的元素
形成 BFC 的常见条件
-
float 不是 none
-
position 是 absolute 或 fixed
-
overflow 不是 visible
-
display 是 flex item(直接子元素) 或 inline-block
示例:(不设置 bfc)
.container { background-color: #ccc; } .left { float: left; } <div class="container"> <img src="xxx.png" class="left"> <p>一段文字...</p> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

示例:(设置 bfc).container { background-color: #ccc; } .left { float: left; } .bfc { overflow: hidden; } <div class="container bfc"> <img src="xxx.png" class="left"> <p class="bfc">一段文字...</p> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

flex 布局
常用语法:flex 布局详解—参考链接
- flex-direction:设置主轴的方向
- justify-content:设置主轴上的子元素排列方式
- align-items:设置侧轴上的子元素排列方式(单行)
- flex-wrap:设置子元素是否换行
- align-self:控制子项自己在侧轴上的排列方式
示例:flex 布局画色子(三点)
.box { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 10px; padding: 20px; display: flex; /* flex 布局 */ justify-content: space-between; /* 两端对齐 */ } .item { display: block; width: 40px; height: 40px; border-radius: 50%; background-color: #666; } .item:nth-child(2) { align-self: center; /* 第二项居中对齐(垂直轴) */ } .item:nth-child(3) { align-self: flex-end; /* 第三项尾对齐 (垂直轴) */ } <div class="box"> <span class="item"></span> <span class="item"></span> <span class="item"></span> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29

示例:flex 布局画色子(五点)body>div { display: flex; width: 100px; height: 100px; border-radius: 4px; border: 2px solid red; box-sizing: border-box; } p { width: 15px; height: 15px; background-color: black; border-radius: 50%; margin: 2px; } .div5 { flex-direction: column; justify-content: space-around; } .div5 div { display: flex; justify-content: space-around; } <div class="div5"> <div> <p></p> <p></p> </div> <div> <p></p> </div> <div> <p></p> <p></p> </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38

CSS - 定位
absolute 和 relative 定位
- relative 依据 自身 定位
- absolute 依据 最近一层 的定位元素定位
定位元素:absolute relative fixed body
示例:测试 relative 和 absolute
body { margin: 20px; } .relative { position: relative; width: 400px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid #ccc; top: 20px; left: 50px; } .absolute { position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; top: 20px; left: 50px; } <p>absolute 和 relative 定位问题</p> <div class="relative"> <div class="absolute"> this is absolute </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
不加 top 和 left 时:

加上 top 和 left 后:
去除 position: relative 后,absolute 盒子相对于最近一层(body)定位:
水平居中和垂直居中
水平居中
- inline 元素:text-align: center
- block 元素:margin: auto
- absolute 元素:left: 50% + margin-left: 负值
示例:
.container { border: 1px solid #ccc; margin: 10px; padding: 10px; } .item { background-color: #ccc; } .container-1 { text-align: center; /* 居中 */ } .container-2 { width: 500px; margin: auto; /* 居中 */ } .container-3 { position: relative; height: 100px; } .container-3 .item { position: absolute; width: 300px; height: 100px; /* 居中 */ left: 50%; margin-left: -150px; } <div class="container container-1"> <span>一段文字</span> </div> <div class="container container-2"> <div class="item"> this is block item </div> </div> <div class="container container-3"> <div class="item"> this is absolute item </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
居中前:
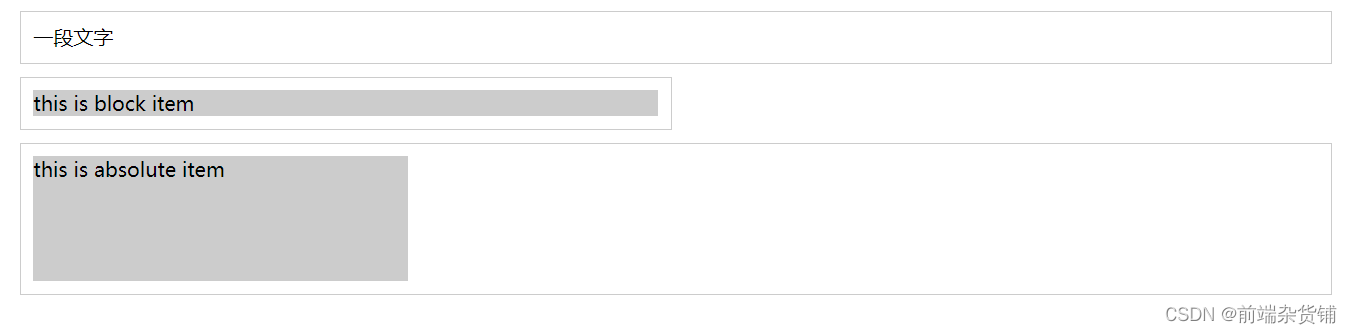
居中后:

垂直居中
- inline 元素:line-height 的值等于 height 值
- absolute 元素:top: 50% + margin-top 负值
- absolute 元素:transform(-50%, -50%)
- absolute 元素:top,left,bottom,right = 0 + margin: auto
示例:
.container { border: 1px solid #ccc; margin: 10px; padding: 10px; height: 130px; } .item { background-color: #ccc; } .container-1 { text-align: center; /* 垂直居中 */ line-height: 130px; height: 130px; } .container-2 { position: relative; } .container-2 .item { position: absolute; width: 300px; height: 100px; left: 50%; margin-left: -150px; /* 垂直居中 */ top: 50%; margin-top: -50px; } .container-3 { position: relative; } .container-3 .item { position: absolute; width: 300px; height: 100px; /* 垂直居中 */ left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translate(-50%, -50%); } .container-4 { position: relative } .container-4 .item { position: absolute; width: 100px; height: 50px; /* 垂直居中 */ top: 0; left: 0; bottom: 0; right: 0; margin: auto; } <div class="container container-1"> <span>一段文字</span> </div> <div class="container container-2"> <div class="item"> this is item </div> </div> <div class="container container-3"> <div class="item"> this is item </div> </div> <div class="container container-4"> <div class="item"> this is item </div> </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76

CSS - 图文样式
line-height(行高) 如何继承
- 写具体数值,如30px,则继承该值
- 写比例,如 2,则继承该比例
- 写百分比,如200%,则继承计算出来的值(重点注意)
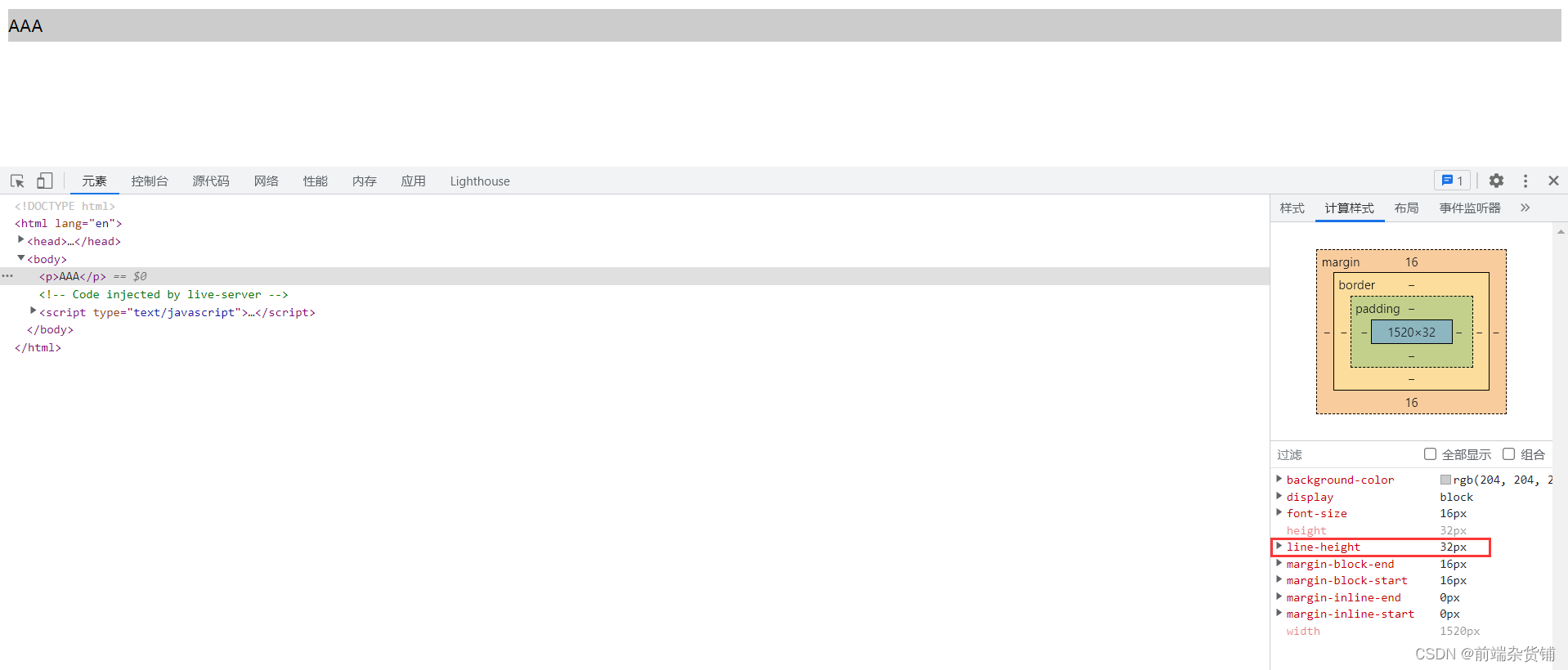
示例:p 标签的行高是多少?
示例 1:继承 body 的行高:30px
body { font-size: 20px; line-height: 30px; } p { background-color: #ccc; font-size: 16px; } <p>AAA</p>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

示例 2:自身的 font-size 乘以继承的 line-height => 16 * 2 = 32pxbody { font-size: 20px; line-height: 2; } p { background-color: #ccc; font-size: 16px; } <p>AAA</p>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
示例 3:继承的 font-size 乘以继承的 line-height => 20 * 2 = 40pxbody { font-size: 20px; line-height: 200%; } p { background-color: #ccc; font-size: 16px; } <p>AAA</p>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

CSS - 响应式
rem 是什么
- px,绝对长度单位,最常用
- em,相对长度单位,相对于父元素,不常用
- rem,相对长度单位,相对于根元素,常用于响应式布局
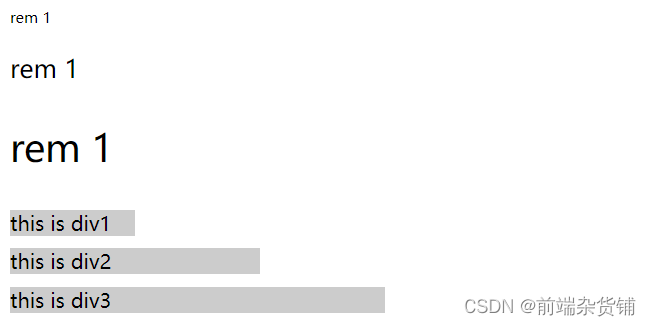
示例:设置一个 rem 为 100px,都会继承 html 里的 font-size。在这里,0.2 rem 就是 20px
html { font-size: 100px; } div { background-color: #ccc; margin-top: 10px; font-size: 0.16rem; } <p style="font-size: 0.1rem">rem 1</p> <p style="font-size: 0.2rem">rem 1</p> <p style="font-size: 0.3rem">rem 1</p> <div style="width: 1rem"> this is div1 </div> <div style="width: 2rem"> this is div2 </div> <div style="width: 3rem"> this is div3 </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
响应式布局的常用方案
- media-query,根据不同的屏幕宽度设置根元素 font-size
- rem,基于根元素的相对单位
示例:iPhone5、iPhone6/7/8、iPhone6/7/8Plus 机型
@media only screen and (max-width: 374px) { /* iphone5 的宽度(320px)比例设置 font-size */ html { font-size: 86px; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 375px) and (max-width: 413px) { /* iphone6/7/8 和 iphone x */ html { font-size: 100px; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 414px) { /* iphone6/7/8plus 的宽度(414px)比例设置 font-size */ html { font-size: 110px; } } body { font-size: 0.16rem; /* 根据机型响应式变化 */ } #div1 { width: 1rem; /* 根据机型响应式变化 */ background-color: #ccc; } <div id="div1"> this is div </div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29



网页视口尺寸
- window.screen.height => 屏幕高度(屏幕总高度)
- window.innerHeight => 网页视口高度(除去刘海和下巴的高度)
- document.body.clientHeight => body 高度(内容撑起来的高度)
vh 和 vw
- vh 网页视口高度的 1/100
- vw 网页视口宽度的 1/100
- vmax 取两者的最大值
- vmin 取两者的最小值
body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } #container { background-color: red; width: 10vw; height: 10vh; } <p>vm vh 测试</p> <div id="container"></div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

不积跬步无以至千里 不积小流无以成江海点个关注不迷路,持续更新中…
-
相关阅读:
Elasticsearch写入原理剖析
[BUG] runtime network not ready: NetworkReady=false reason:NetworkPluginNotRead
Redis教程(二十二):Redis的过期删除和缓存淘汰策略
Java:本地文件通过表单参数接口发送后大小变成0
【java学习—八】单例设计模式(5)
金融企业容器云建设中资源智能优化实践
关于Eslint语法检查
按图搜索义乌购商品(拍立淘) API
某男子因用本地虚拟机做压测,惨遭字节面试官当场嘲笑
代码随想录第四十三天|343. 整数拆分 ● 96.不同的二叉搜索树
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45902692/article/details/126056763
