-
通过公式和源码解析 DETR 中的损失函数 & 匈牙利算法(二分图匹配)
上一篇文章:DETR 论文精读,并解析模型结构_Flying Bulldog的博客-CSDN博客
可以先了解概念,然后再分析源码。
匈牙利算法目的:完成最优分配,假设有六位老师和六种课程,通过匈牙利算法进行匹配后,每一位老师都会分到不同的一个课程。分享一个关于该算法的B站视频:二分图的匹配

图2:DETR使用传统的CNN主干来学习输入图像的2D表示。该模型将其扁平化,并在将其传递到转换器编码器之前用位置编码对其进行补充。然后,一个转换器解码器将固定数量的学习位置嵌入作为输入,我们称之为对象查询,并附加到编码器输出。
我们将解码器的每个输出嵌入传递给一个共享前馈网络( FFN ),该网络预测一个检测(class and bounding box)或一个"no object"类。
怎样判别预测框和真实框之间的差异呢?
答:直接进行集合预测损失,它迫使预测和真实值框之间的唯一匹配。匹配成功之后,对预测框的分数、类别、中心点坐标和宽高进行损失值的计算。所以,预测框和真实框大致有两方面差异:
- 一方面是进行二分图匹配时的差异,即没有匹配成功,类似于非极大值抑制的IoU过小,从而被筛选掉。
- 另一个方面是预测框和真实框之间的损失值很高,有极大的差异。
怎样通过目标检测集合预测损失?分为两步,具体解释如下:
********************************第一步:二分图匹配********************************
DETR在单次通过解码器时推断一个固定大小的有 N 个预测的集合,其中 N 被设置为显著大于图像中典型的物体数量。训练的主要困难之一是在 ground truth 方面对预测对象(类别、位置、大小)进行打分。我们的损失在预测对象和真实对象之间产生一个最佳的二分匹配,然后优化 object-specific ( bounding box ) 的损失。
用 y 表示对象的 ground truth 集合,
 表示有 N 个预测的集合。假设 N 远大于图像中物体的个数,我们考虑 y 也是一个大小为 N 的被
表示有 N 个预测的集合。假设 N 远大于图像中物体的个数,我们考虑 y 也是一个大小为 N 的被  ( no object ) 填充的集合。为了在这两个集合之间找到一个二分匹配,我们用最低的代价搜索 N 个元素
( no object ) 填充的集合。为了在这两个集合之间找到一个二分匹配,我们用最低的代价搜索 N 个元素  的一个置换:
的一个置换:
(1)
 是真值
是真值 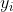 和具有索引
和具有索引  的一个预测之间的一个成对匹配代价( a pair-wise matching cost )。这个最优分配是通过匈牙利算法有效地计算的。匹配代价同时考虑了类预测以及预测框和真实框之间的相似性。
的一个预测之间的一个成对匹配代价( a pair-wise matching cost )。这个最优分配是通过匈牙利算法有效地计算的。匹配代价同时考虑了类预测以及预测框和真实框之间的相似性。(2)真实集合的每个元素 i 都可以看成一个
 ,其中
,其中 是目标类标签( 目标类标签也可能是
是目标类标签( 目标类标签也可能是  ),N/A即无类别。
),N/A即无类别。 是一个向量,它定义了真实框的中心坐标及其相对于图像大小的高度和宽度。
是一个向量,它定义了真实框的中心坐标及其相对于图像大小的高度和宽度。
- CLASSES = [
- 'N/A', 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus',
- 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light', 'fire hydrant', 'N/A',
- 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse',
- 'sheep', 'cow', 'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'N/A', 'backpack',
- 'umbrella', 'N/A', 'N/A', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee', 'skis',
- 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove',
- 'skateboard', 'surfboard', 'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'N/A', 'wine glass',
- 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple', 'sandwich',
- 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake',
- 'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed', 'N/A', 'dining table', 'N/A',
- 'N/A', 'toilet', 'N/A', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard',
- 'cell phone', 'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'N/A',
- 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier',
- 'toothbrush'
- ]
(3)对于索引 σ( i ) 的预测,我们定义类
 的概率为
的概率为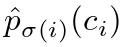 ,预测框为
,预测框为 。
。 利用以上这些符号,可以将
 定义为:
定义为:
对上述公式的解释:所有真实框中的每一个框和所有预测框进行匹配,损失值最小的预测框为该真实框的最佳匹配框,当所有真实框遍历完毕后,得到所有唯一匹配的框。
- # 计算分类成本。
- cost_class = -out_prob[:, tgt_ids]
- # Compute the L1 cost between boxes
- # 计算预测框和真实框之间的 L1 损失
- cost_bbox = torch.cdist(out_bbox, tgt_bbox, p=1)
- # Compute the giou cost betwen boxes
- # 计算预测框和真实框之间的 GIoU 损失
- cost_giou = -generalized_box_iou(box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(out_bbox),
- box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(tgt_bbox))
这种寻找匹配的过程与现代检测器中用于匹配提议或锚框到真实物体的启发式分配规则起到了相同的作用。主要的区别是,我们需要找到一对一的匹配,进行无重复的直接集合预测。
matcher = build_matcher(args) # HungarianMatcher 匈牙利匹配- class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, cost_class: float = 1, cost_bbox: float = 1, cost_giou: float = 1):
- super().__init__()
- self.cost_class = cost_class # 1
- self.cost_bbox = cost_bbox # 5
- self.cost_giou = cost_giou # 2
- assert cost_class != 0 or cost_bbox != 0 or cost_giou != 0, "all costs cant be 0"
- @torch.no_grad()
- def forward(self, outputs, targets):
- bs, num_queries = outputs["pred_logits"].shape[:2]
- # We flatten to compute the cost matrices in a batch
- # 我们展平以批量计算成本矩阵
- out_prob = outputs["pred_logits"].flatten(0, 1).softmax(-1) # [batch_size * num_queries, num_classes]
- out_bbox = outputs["pred_boxes"].flatten(0, 1) # [batch_size * num_queries, 4]
- # Also concat the target labels and boxes
- # 同时连接目标标签和框
- tgt_ids = torch.cat([v["labels"] for v in targets])
- tgt_bbox = torch.cat([v["boxes"] for v in targets])
- # Compute the classification cost. Contrary to the loss, we don't use the NLL,
- # but approximate it in 1 - proba[target class].
- # The 1 is a consatant that doesn't change the mtching, it can be ommitted.
- # 计算分类成本。
- cost_class = -out_prob[:, tgt_ids]
- # Compute the L1 cost between boxes
- # 计算预测框和真实框之间的 L1 损失
- cost_bbox = torch.cdist(out_bbox, tgt_bbox, p=1)
- # Compute the giou cost betwen boxes
- # 计算预测框和真实框之间的 GIoU 损失
- cost_giou = -generalized_box_iou(box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(out_bbox), box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(tgt_bbox))
- # Final cost matrix
- # 合并所有的损失
- C = self.cost_bbox * cost_bbox + self.cost_class * cost_class + self.cost_giou * cost_giou
- C = C.view(bs, num_queries, -1).cpu()
- sizes = [len(v["boxes"]) for v in targets]
- # linear_sum_assignment:解决线性和分配问题。
- indices = [linear_sum_assignment(c[i]) for i, c in enumerate(C.split(sizes, -1))]
- return [(torch.as_tensor(i, dtype=torch.int64), torch.as_tensor(j, dtype=torch.int64)) for i, j in indices]
- def build_matcher(args):
- # 1, 5, 2
- return HungarianMatcher(cost_class=args.set_cost_class, cost_bbox=args.set_cost_bbox, cost_giou=args.set_cost_giou)
********************************第二步:计算损失函数********************************
第二步是计算损失函数,即计算上一步中匹配的所有配对的匈牙利损失。我们定义的损失类似于常见目标检测器的损失,即类别预测的负对数和 box 损失的线性组合:

其中
 是第一步中计算的最优分配。
是第一步中计算的最优分配。在实际应用中,我们对对数概率项进行了降权处理,当
 时,通过因子 10 来解释类不平衡(源码如下)。这类似于Faster R-CNN训练过程如何通过子采样来平衡正/负建议。注意,一个对象和
时,通过因子 10 来解释类不平衡(源码如下)。这类似于Faster R-CNN训练过程如何通过子采样来平衡正/负建议。注意,一个对象和  之间的匹配成本并不依赖于预测,这意味着在这种情况下,成本是一个常数。
之间的匹配成本并不依赖于预测,这意味着在这种情况下,成本是一个常数。- # 无对象类的相对分类权重
- parser.add_argument('--eos_coef', default=0.1, type=float,
- help="Relative classification weight of the no-object class")
在匹配代价中,我们使用概率
 而不是对数概率。这使得类预测项对
而不是对数概率。这使得类预测项对 是可通约的(如下所述),并且我们观察到更好的性能表现。
是可通约的(如下所述),并且我们观察到更好的性能表现。Bounding box loss:匹配代价和匈牙利损失的第二部分是对边界框进行评分的
 。与许多将框预测作为
。与许多将框预测作为 一些初始猜测的检测器不同,我们直接进行框预测。虽然这种方法简化了实施,但它对损失的相对规模造成了问题。最常用的
一些初始猜测的检测器不同,我们直接进行框预测。虽然这种方法简化了实施,但它对损失的相对规模造成了问题。最常用的  loss 对于 small and large boxes 会有不同的尺度,即使它们的相对误差相似。为了缓解这一问题,我们使用
loss 对于 small and large boxes 会有不同的尺度,即使它们的相对误差相似。为了缓解这一问题,我们使用  损失和广义的 IoU 损失
损失和广义的 IoU 损失 的线性组合,
的线性组合, 是尺度不变的损失函数。
是尺度不变的损失函数。总的来说,我们的 box 损失是
 ,其被定义为:
,其被定义为:
其中,
 是超参数。这两个损失通过批内对象的数量进行归一化。
是超参数。这两个损失通过批内对象的数量进行归一化。广义的 IoU 损失
 定义如下:
定义如下:
补充:w.r.t.:with respect to,关于;谈及,谈到。
- # 计算所有损失函数
- # indices:匈牙利匹配的返回切片
- def get_loss(self, loss, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs):
- loss_map = {
- 'labels': self.loss_labels, # 分类损失
- 'cardinality': self.loss_cardinality, # 计数
- 'boxes': self.loss_boxes, # 预测框损失
- 'masks': self.loss_masks # 分割时用到的损失
- }
- assert loss in loss_map, f'do you really want to compute {loss} loss?'
- return loss_map[loss](outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs)
- # 分类损失
- def loss_labels(self, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, log=True):
- """Classification loss (NLL)
- targets dicts must contain the key "labels" containing a tensor of dim [nb_target_boxes]
- """
- assert 'pred_logits' in outputs
- src_logits = outputs['pred_logits']
- # 根据索引置换预测
- idx = self._get_src_permutation_idx(indices)
- # 利用交叉熵计算类别的损失
- target_classes_o = torch.cat([t["labels"][J] for t, (_, J) in zip(targets, indices)])
- target_classes = torch.full(src_logits.shape[:2], self.num_classes,
- dtype=torch.int64, device=src_logits.device)
- target_classes[idx] = target_classes_o
- # weight: 给每个类一个手动重新调整的权重。如果给定,则必须是大小为“C”的张量 [1, 1, 1 ... 1, 1, 0.1]
- loss_ce = F.cross_entropy(src_logits.transpose(1, 2), target_classes, self.empty_weight)
- losses = {'loss_ce': loss_ce}
- if log:
- # TODO this should probably be a separate loss, not hacked in this one here
- losses['class_error'] = 100 - accuracy(src_logits[idx], target_classes_o)[0]
- return losses
- @torch.no_grad()
- def loss_cardinality(self, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes):
- # 计算基数误差,即预测的非空框数量的绝对误差
- # 这并不是真正的损失,它仅用于记录。
- # 它不传播梯度
- """ Compute the cardinality error, ie the absolute error in the number of predicted non-empty boxes
- This is not really a loss, it is intended for logging purposes only. It doesn't propagate gradients
- """
- pred_logits = outputs['pred_logits']
- device = pred_logits.device
- tgt_lengths = torch.as_tensor([len(v["labels"]) for v in targets], device=device)
- # Count the number of predictions that are NOT "no-object" (which is the last class)
- # 计算不是“无对象”的预测数量(这是最后一类)
- card_pred = (pred_logits.argmax(-1) != pred_logits.shape[-1] - 1).sum(1)
- card_err = F.l1_loss(card_pred.float(), tgt_lengths.float())
- losses = {'cardinality_error': card_err}
- return losses
- # 预测框的损失
- def loss_boxes(self, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes):
- """Compute the losses related to the bounding boxes, the L1 regression loss and the GIoU loss
- targets dicts must contain the key "boxes" containing a tensor of dim [nb_target_boxes, 4]
- The target boxes are expected in format (center_x, center_y, w, h), normalized by the image size.
- """
- assert 'pred_boxes' in outputs
- # # 根据索引置换预测
- idx = self._get_src_permutation_idx(indices)
- # # 计算预测框的损失函数
- src_boxes = outputs['pred_boxes'][idx]
- target_boxes = torch.cat([t['boxes'][i] for t, (_, i) in zip(targets, indices)], dim=0)
- # L1 损失函数
- loss_bbox = F.l1_loss(src_boxes, target_boxes, reduction='none')
- # GIoU损失函数
- losses = {}
- losses['loss_bbox'] = loss_bbox.sum() / num_boxes
- loss_giou = 1 - torch.diag(box_ops.generalized_box_iou(
- box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(src_boxes),
- box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(target_boxes)))
- losses['loss_giou'] = loss_giou.sum() / num_boxes
- return losses
>>> 如有疑问,欢迎评论区一起探讨。
-
相关阅读:
MySQL——触发器(trigger)基本结构
40个高质量软件工程毕设项目分享【源码+论文】(四)
uView学习(持续更新中)
MySQL JDBC编程
国庆小练习
基于googlenet网络的动物种类识别算法matlab仿真
go-zero环境搭建
【问题思考总结】截得两部分质量相等的点是否就是质心?
【C语言刷题】指针入门三题|字符串长度、字符串复制、两数交换
STM32项目开发实战教程--CUME MX HAL库开发介绍
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54185421/article/details/125992305


