-
Spring Boot集成protobuf快速入门Demo
1.什么是protobuf?
Protobuf(Protocol Buffers)是由 Google 开发的一种轻量级、高效的数据交换格式,它被用于结构化数据的序列化、反序列化和传输。相比于 XML 和 JSON 等文本格式,Protobuf 具有更小的数据体积、更快的解析速度和更强的可扩展性。 Protobuf 的核心思想是使用协议(Protocol)来定义数据的结构和编码方式。使用 Protobuf,可以先定义数据的结构和各字段的类型、字段等信息,然后使用 Protobuf 提供的编译器生成对应的代码,用于序列化和反序列化数据。由于 Protobuf 是基于二进制编码的,因此可以在数据传输和存储中实现更高效的数据交换,同时也可以跨语言使用。
Protobuf 有以下几个优势:
- 更小的数据量:Protobuf 的二进制编码通常只有 XML 和 JSON 的 1/3 到 1/10 左右,因此在网络传输和存储数据时可以节省带宽和存储空间。
- 更快的序列化和反序列化速度:由于 Protobuf 使用二进制格式,所以序列化和反序列化速度比 XML 和 JSON 快得多。
- 跨语言:Protobuf 支持多种编程语言,可以使用不同的编程语言来编写客户端和服务端。这种跨语言的特性使得 Protobuf 受到很多开发者的欢迎(JSON 也是如此)。
- 易于维护可扩展:Protobuf 使用 .proto 文件定义数据模型和数据格式,这种文件比 XML 和 JSON 更容易阅读和维护,且可以在不破坏原有协议的基础上,轻松添加或删除字段,实现版本升级和兼容性。
2.代码工程
实验目标
rest api实现基于Protobuf 协议通信
pom.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <parent>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
- <version>3.2.1</version>
- </parent>
- <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
- <artifactId>protobuf</artifactId>
- <properties>
- <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
- <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
- <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
- <version>3.19.2</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- <build>
- <extensions>
- <extension>
- <groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
- <artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
- <version>1.6.1</version>
- </extension>
- </extensions>
- <plugins>
- <plugin>
- <groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
- <artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
- <version>0.6.1</version>
- <configuration>
- <protoSourceRoot>${basedir}/src/main/resources</protoSourceRoot>
- <protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.19.1:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
- <pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.43.1:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
- <outputDirectory>src/main/java</outputDirectory>
- <clearOutputDirectory>false</clearOutputDirectory>
- <pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
- </configuration>
- <executions>
- <execution>
- <goals>
- <goal>compile</goal>
- <goal>compile-custom</goal>
- </goals>
- </execution>
- </executions>
- </plugin>
- <plugin>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
- </plugin>
- </plugins>
- </build>
- </project>
controller
- package com.et.protobuf.controller;
- import com.et.protobuf.PhoneNumJson;
- import com.et.protobuf.ProtobufMessage;
- import com.et.protobuf.StudentJson;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- @RestController
- public class HelloWorldController {
- @RequestMapping("/json/{id}")
- public StudentJson showHelloWorld(@PathVariable Integer id){
- StudentJson studentJson = new StudentJson();
- studentJson.setId(id);
- studentJson.setFirstName("maxsm");
- studentJson.setLastName("sdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdf");
- studentJson.setEmail("1224sdfsfsdf344552@163.com");
- PhoneNumJson phoneNumJson = new PhoneNumJson();
- phoneNumJson.setNumber("12345sdfsdfsd6566666");
- phoneNumJson.setType(1);
- List
list = new ArrayList<>(); - list.add(phoneNumJson);
- studentJson.setPhoneNumList(list);
- return studentJson;
- }
- @RequestMapping("/protobuf/{id}")
- ProtobufMessage.Student protobuf(@PathVariable Integer id) {
- return ProtobufMessage.Student.newBuilder().setId(id).setFirstName("maxsm")
- .setLastName("sdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdf")
- .setEmail("1224sdfsfsdf344552@163.com")
- .addPhone(ProtobufMessage.Student.PhoneNumber.newBuilder().setNumber("12345sdfsdfsd6566666").setType(
- ProtobufMessage.Student.PhoneType.MOBILE).build()).build();
- }
- }
entity
- package com.et.protobuf;
- import java.util.List;
- /**
- * @author liuhaihua
- * @version 1.0
- * @ClassName StudentJson
- * @Description todo
- * @date 2024/08/05/ 16:32
- */
- public class StudentJson {
- private int id;
- private String firstName;
- private String lastName;
- private String email;
- private List<PhoneNumJson> phoneNumList;
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getFirstName() {
- return firstName;
- }
- public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
- this.firstName = firstName;
- }
- public String getLastName() {
- return lastName;
- }
- public void setLastName(String lastName) {
- this.lastName = lastName;
- }
- public String getEmail() {
- return email;
- }
- public void setEmail(String email) {
- this.email = email;
- }
- public List<PhoneNumJson> getPhoneNumList() {
- return phoneNumList;
- }
- public void setPhoneNumList(List
phoneNumList ) { - this.phoneNumList = phoneNumList;
- }
- }
- package com.et.protobuf;
- /**
- * @author liuhaihua
- * @version 1.0
- * @ClassName PhoneNum
- * @Description todo
- * @date 2024/08/05/ 16:35
- */
- public class PhoneNumJson {
- private int type;
- private String number;
- public int getType() {
- return type;
- }
- public void setType(int type) {
- this.type = type;
- }
- public String getNumber() {
- return number;
- }
- public void setNumber(String number) {
- this.number = number;
- }
- }
mxsm.proto
使用 Protobuf 的语言定义文件(.proto)可以定义要传输的信息的数据结构,可以包括各个字段的名称、类型等信息。同时也可以相互嵌套组合,构造出更加复杂的消息结构。
- syntax = "proto3";
- package mxsm;
- option java_package = "com.et.protobuf";
- option java_outer_classname = "ProtobufMessage";
- message Course {
- int32 id = 1;
- string course_name = 2;
- repeated Student student = 3;
- }
- message Student {
- int32 id = 1;
- string first_name = 2;
- string last_name = 3;
- string email = 4;
- repeated PhoneNumber phone = 5;
- message PhoneNumber {
- string number = 1;
- PhoneType type = 2;
- }
- enum PhoneType {
- MOBILE = 0;
- LANDLINE = 1;
- }
- }
头部全局定义
syntax = "proto3";指定 Protobuf 版本为版本 3(最新版本)package com.wdbyte.protobuf;指定 Protobuf 包名,防止有相同类名的message定义,这个包名是生成的类中所用到的一些信息的前缀,并非类所在包。option java_multiple_files = true;是否生成多个文件。若false,则只会生成一个类,其他类以内部类形式提供。option java_package =生成的类所在包。option java_outer_classname生成的类名,若无,自动使用文件名进行驼峰转换来为类命名。
消息结构具体定义
message Person定一个了一个 Person 类。 Person 类中的字段被optional修饰,被optional修饰说明字段可以不赋值。- 修饰符
optional表示可选字段,可以不赋值。 - 修饰符
repeated表示数据重复多个,如数组,如 List。 - 修饰符
required表示必要字段,必须给值,否则会报错RuntimeException,但是在 Protobuf 版本 3 中被移除。即使在版本 2 中也应该慎用,因为一旦定义,很难更改。
字段类型定义
修饰符后面紧跟的是字段类型,如
int32、string。常用的类型如下:int32、int64、uint32、uint64:整数类型,包括有符号和无符号类型。float、double:浮点数类型。bool:布尔类型,只有两个值,true 和 false。string:字符串类型。bytes:二进制数据类型。enum:枚举类型,枚举值可以是整数或字符串。message:消息类型,可以嵌套其他消息类型,类似于结构体。
字段后面的
=1,=2是作为序列化后的二进制编码中的字段的对应标签,因为 Protobuf 消息在序列化后是不包含字段信息的,只有对应的字段序号,所以节省了空间。也因此,1-15 比 16 会少一个字节,所以尽量使用 1-15 来指定常用字段。且一旦定义,不要随意更改,否则可能会对不上序列化信息。config
- package com.et.protobuf.config;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.http.converter.protobuf.ProtobufHttpMessageConverter;
- import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- @Configuration
- public class Config {
- @Bean
- RestTemplate restTemplate(ProtobufHttpMessageConverter hmc) {
- return new RestTemplate(Arrays.asList(hmc));
- }
- @Bean
- ProtobufHttpMessageConverter protobufHttpMessageConverter() {
- return new ProtobufHttpMessageConverter();
- }
- }
以上只是一些关键代码,所有代码请参见下面代码仓库
代码仓库
3.测试
启动Spring Boot应用
编写测试类
- package com.et.protobuf;
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
- import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
- import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
- import org.springframework.http.converter.protobuf.ProtobufHttpMessageConverter;
- import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- @SpringBootTest(classes = DemoApplication.class)
- public class ApplicationTest {
- // Other declarations
- private static final String COURSE1_URL = "http://localhost:8088/protobuf/1";
- @Autowired
- private RestTemplate restTemplate ;
- @Test
- public void whenUsingRestTemplate_thenSucceed() {
- ResponseEntity
student = restTemplate.getForEntity(COURSE1_URL, ProtobufMessage.Student.class); - System.out.println(student.toString());
- }
- }
结果如下
- <200 OK OK,id: 1
- first_name: "maxsm"
- last_name: "sdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdfsdf"
- email: "1224sdfsfsdf344552@163.com"
- phone {
- number: "12345sdfsdfsd6566666"
- }
- ,[X-Protobuf-Schema:"mxsm.proto", X-Protobuf-Message:"mxsm.Student", Content-Type:"application/x-protobuf;charset=UTF-8", Transfer-Encoding:"chunked", Date:"Mon, 05 Aug 2024 09:10:55 GMT", Keep-Alive:"timeout=60", Connection:"keep-alive"]>
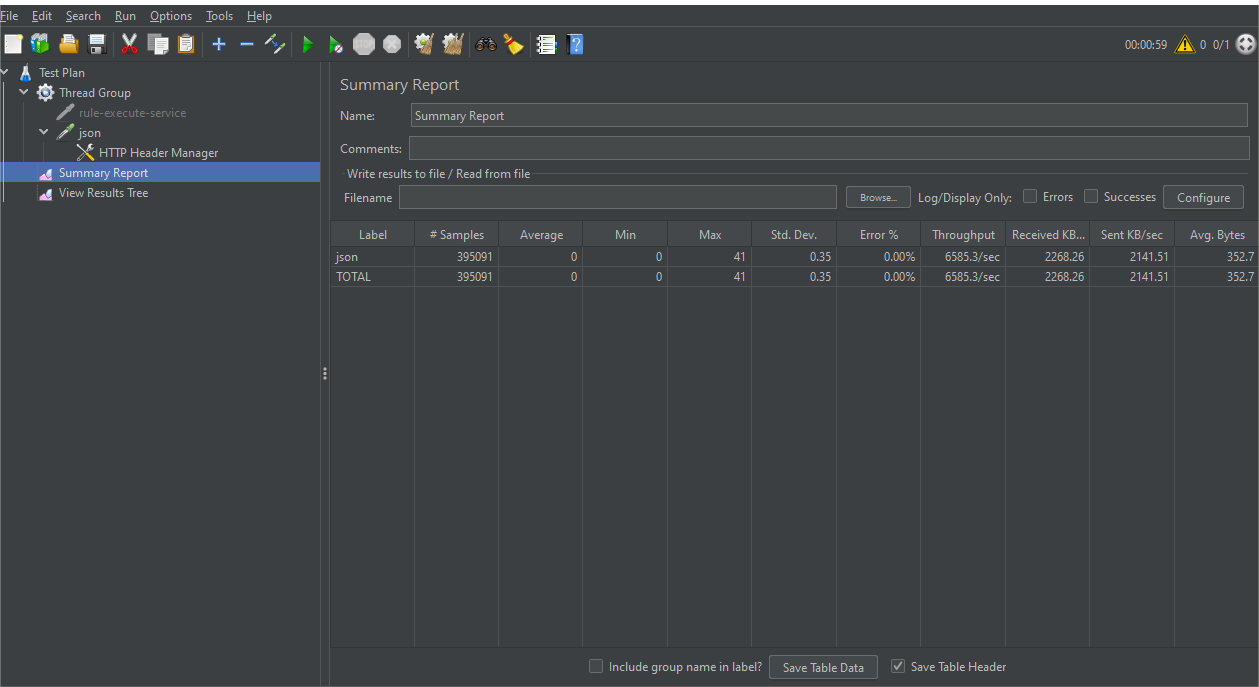
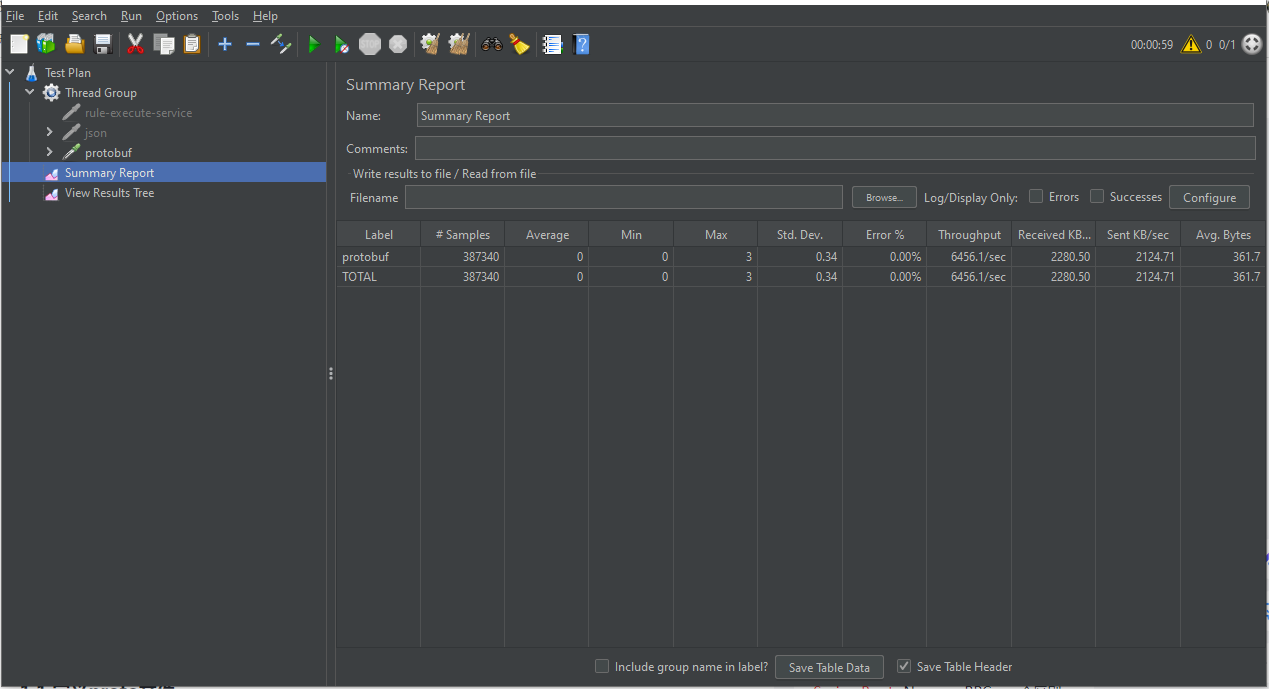
Json和protobuf性能比较
单个线程,循环1分钟
测试结果发现json性能甚至优于protobuf,并不符合预期结果!是我哪一步整错了吗?有大神知道怎么回事吗?
4.引用
-
相关阅读:
计算机毕业设计Java海康物流(源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档)
密码学与网络安全:量子计算的威胁与解决方案
扩散模型(Diffusion Model,DDPM,GLIDE,DALLE2,Stable Diffusion)
【前端】CSS-Grid网格布局
第一章 教育基础(07 心理学基础知识)
【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】2-1 Yarn 基础库概述
基于Java web的校园滴滴代驾管理系统 毕业设计-附源码260839
Python Pandas简介及基础教程+实战示例。
SpringCloud Gateway与Zuul的取舍选择及其工作流程
Laravel 6 - 第十七章 配置数据库
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dot_life/article/details/140965295