insert into 表 values(值,值....);
insert into product values(null,'小米电脑',5888,10);
insert into product values(null,'华硕电脑',5888,null);
insert into product values(null,'苹果电
insert into product values(null,'华为5G手 机',30000,20);
insert into product values(null,'小米手机',1800,30);
insert into product values(null,'iPhonex',8000,10);
insert into product values(null,'苹果电脑',8000,100);
insert into product values(null,'iPhone7',6000,200);
values(null,'iPhone6s',4000,1000);
insert into product values(null,'iPhone6',3500,100);
values(null,'iPhone5s',3000,100);
insert into product values(null,'方便面',4.5,1000);
除了整数
\
小数类型外
,
其他字段类型的值必须使用引号引起来
(
建议单引号
)
如果要插入空值
,
可以不写字段
,
或者插入
null
4.2 更新记录
语法
update 表名 set 列 =值, 列 =值 [where 条件]
-- 语法: update 表名 set 列 =值, 列 =值 [where 条件]
update product set price = 5000;
update product set price = 8000,num = 20 where id = 2;
update product set price = 18000 where pname = 'Mac'
-- 将商品名是Mac的价格修改为17000,数量修改为5
update product set price = 17000,num = 5 where pname
-- 将商品名是方便面的商品的价格在原有基础上增加2元
update product set price = price + 2 where pname = '方便面'
4.3 删除记录
delete
语法:
delete from 表 [where 条件]
truncate
语法:
truncate table 表;
delete from product where pname = 'Mac'
delete from product where price < 5001
delete
和
truncate
区别【面试题】
DELETE
删除表中的数据,表结构还在
;
删除后的数据可以找
回
,
一条一条的删除
.
TRUNCATE
删除是把表直接
DROP
掉,然后再创建一个同样
的新表。删除的数据不能找回。执行速度比
DELETE
快。
工作里面的删除
物理删除
:
真正的删除了
,
数据不在
,
使用
delete
就属于物理删
除
逻辑删除
:
没有真正的删除
,
数据还在
.
搞一个标记
,
其实逻辑
删除是更新
例如
: state 1
启用
0
禁用
五,基本查询语法
select [*] [列名 ,列名] [列名 as 别名 ...] [distinct 字段] from 表名 [where 条件]
六.简单查询
查询所有的列的记录
查询某张表特定列的记录
去重查询 :去重针对某列
, distinct
前面不能先出现列
名
别名查询
运算查询
(+,-,*,/
等
)
:运算查询 列名与列名之间是可以 运算的
-- 查询所有的列语法:select * from 表名
-- 查询某张表特定列:select 列名,列名,... from 表 名
-- 需求:查询product表中的pname,price字段的值
select pname,price from product;
-- 去重查询:select distinct 列名 from 表名
-- 需求:查询price字段,[去重]单个字段去重
select distinct price from product;
-- 需求:查询pname,price字段,[同时去重]多个字段去重
select distinct pname,price from product;
select id,distinct price from product;-- 报 错
-- 对字段取别名:select 字段 as 别名,字段 as 别 名,... from 表名。注意: as可以省略,一般都会省略
select pname as 商品名称,num as 商品数量 from product;
select pname 商品名称,num 商品数量 from product;
-- 对表取别名:select 表1别名.字段名,... from 表1 as 表1别名。注意: as可以省略 一般都会省略
select p.pname,p.price from product as p;
select p.pname,p.price from product p;
-- 运算查询(+,-,*,/等),null和其他数据进行运算得到 是null
select price,num from product;
select price*num from product;
select price * num 总价 from product;
select price * ifnull(num,0) 总价 from product;
七.条件查询
语法:
select ... from 表 where 条件;
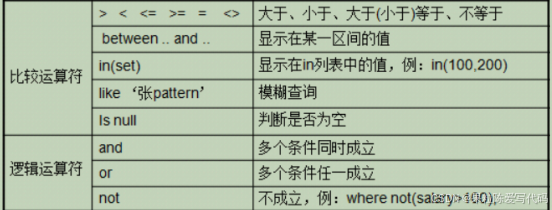
between...and...
区间查询
where price between 1000 and 3000 相当于 1000<=price<=3000
in(
值,值
..)
select * from t_product where id = 1
select * from t_product where id = 3
select * from t_product where id = 5
select * from t_product where id = 7
select * from t_product where id in(1,3,5,7)
like
模糊查询 。一般和
_
或者
%
一起使用
_
占一位
%
占
0
或者
n
位
name like '张%' --查询姓张的用户, 名字的字数没有 限制name like '张_' --查询姓张的用户 并且名字是两个 字的
and
多条件同时满足
where 条件1 and 条件2 and 条件3
or
任意条件满足
where 条件1 or 条件2 or 条件3
需求:
查询商品价格
>3000
的商品
查询
id=1
的商品
查询
id<>1
的商品
查询价格在
3000
到
6000
之间的商品
查询
id
在
1
,
5
,
7
,
15
范围内的商品
查询商品名以
iPho
开头的商品
(iPhone
系列
)
查询商品价格大于
3000
并且数量大于
20
的商品
(
条件
and
条件
and...)
查询
id=1
或者价格小于
3000
的商品
select * from product where price > 3000;
select * from product where pid = 1;
select * from product where pid <> 1;
select * from product where pid != 1;
select * from product where price between 3000 and 6000;
select * from product where price >= 3000 and price <= 6000;
select * from product where pid in(1,5,7,15);
-- 查询商品名以iPho开头的商品(iPhone系列)
select * from product where pname like 'iPho%';
-- 查询商品价格大于3000并且数量大于20的商品 (条 件 and 条件 and...)
select * from product where price > 3000 and num > 20;
select * from product where pid = 1 or price < 3000;
八.排序查询
有时候我们需要对查询出来的结果排序显示,那么就可
以通过
ORDER BY
子句将查询出的结果进行排序。排序可
以根据一个字段排,也可以根据多个字段排序,排序只
是对查询的结果集排序,并不会影响表中数据的顺序。
环境的准备
sid INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
sname VARCHAR(40), sex VARCHAR(10),
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'zs','男',18,98.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'ls','女',18,96.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'ww','男',15,50.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'zl','女',20,98.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'tq','男',18,60.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'wb','男',38,98.5);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'小 丽','男',18,100);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'小 红','女',28,28);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'小 强','男',21,95);
单列排序:
只按某一个字段进行排序,单列排序
SELECT 字段名 FROM 表名 [WHERE 条件] ORDER BY 字段名 [ASC|DESC]; //ASC: 升序,默认值; DESC: 降序
需求
:
以分数降序查询所有的学生
select * from student order by score desc;
组合排序:
同时对多个字段进行排序,如果第
1
个字段
相等,则按第
2
个字段排序,依次类推
SELECT 字段名 FROM 表名 WHERE 字段=值 ORDER BY 字段名1 [ASC|DESC], 字段名2 [ASC|DESC];
需求:以分数降序查询所有的学生
,
如果分数一致
,
再
以
age
降序
select * from student order by score desc ,age desc;
九,聚合函数
之前我们做的查询都是横向查询,它们都是根据条件一
行一行的进行判断,而使用聚合函数查询是
纵向查询
,
它是对一列的值进行计算,然后返回
一个结果值
。聚合
函数会忽略空值
NULL
需求:
求出学生表里面的最高分数
求出学生表里面的最低分数
求出学生表里面的分数的总和
(
忽略
null
值
)
求出学生表里面的平均分
统计学生的总人数
(
忽略
null)
SELECT MAX(score) FROM student;
SELECT MIN(score) FROM student;
SELECT SUM(score) FROM student;
SELECT AVG(score) FROM student;
SELECT COUNT(sid) FROM student;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student;
我们发现对于
NULL
的记录不会统计,建议如果统计个数
则不要使用有可能为
null
的列,但如果需要把
NULL
也统
计进呢?我们可以通过
IFNULL(
列名,默认值
)
函数来解
决这个问题
.
如果列不为空,返回这列的值。如果为
NULL
,则返回默认值。
-- 注意: 聚合函数会忽略null -- 准备添加2条数据
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'小 明','男',21,null);
INSERT INTO student VALUES(null,'小 黑','男',22,98);
select sum(score) from student; -- 结果: 824 忽略null
select count(score) from student; -- 结果: 10个 忽略null
select avg(score) from student; -- 结果: 82.4
select avg(ifnull(score,0)) from student; - - 结果: 74.9090909090909
select sum(age+score) from student; - - 结果:
1040 select sum(age) + sum(score) from student; - - 结果: 1061
十.分组查询
分组查询是指使用
GROUP BY
语句对查询信息进行分
组。
GROUP BY
怎么分组的? 将分组字段结果中相同内容作
为一组,如按性别将学生分成两组。
GROUP BY
将分组字段结果中相同内容作为一组,并且
返回每组的第一条数据,所以单独分组没什么用处。分
组的目的就是为了统计,一般分组会跟聚合函数一起使
用。
分组:语法
SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名 [where 条件] GROUP BY 列 [HAVING 条件];
需求:根据性别分组
,
统计每一组学生的总人数
SELECT sex, count(*) FROM student GROUP BY sex;
分组后筛选
having
-- 练习根据性别分组, 统计每一组学生的总人数> 5的(分 组后筛选)
SELECT sex, count(*) FROM student GROUP BY sex HAVING count(*) > 5
-- 练习复杂: 统计sid为8之前的的, 根据性别分组, 每 一组学生的总人数 > 2的(分组后筛选)
select sex,count(*) from student where sid < 8 group by sex having count(*) > 2
注意事项
根据某一列进行分组
,
将分组字段结果中相同内容
作为一组
;
有几组 返回的记录就有几条
单独分组 没有意义
,
返回每一组的第一条记录
分组的目的一般为了做统计使用
,
所以经常和聚合
函数一起使用
在分组里面
,
如果
select
后面的列没有出现在
group
by
后面 展示这个组的这个列的第一个数据
where
和
having
的区别【面试】
十一.分页查询
LIMIT
是限制的意思,所以
LIMIT
的作用就是限制查询记
录的条数
.
经常用来做分页查询
语法
select * from 表名 limit m,n;
m是指从哪开始查;记录开始的index,从0开始,表示第一 条记录 n是指查多少条。
需求:分页查询学生
,
每一页查询
4
条
select * from student limit 0,4; -- 第1页
select * from student limit 4,4; -- 第2页
select * from student limit 8,4; -- 第3页
 between...and... 区间查询
between...and... 区间查询

