-
JDBC学习笔记(三)高级篇
一、JDBC 优化及工具类封装
1.1 现有问题

1.2 JDBC 工具类封装 V1.0
resources/db.properties配置文件:
- driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- url=jdbc:mysql:///atguigu
- username=root
- password=123456
- initialSize=10
- maxActive=20
工具类代码:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util;
- import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
- import javax.sql.DataSource;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.SQLException;
- import java.util.Properties;
- /**
- * JDBC工具类(V1.0)
- * 1.维护一个连接池对象
- * 2.对外提供在连接池中获取连接的方法
- * 3.对外提供回收连接的方法
- * 【注意】:工具类仅对外提供共性的功能代码,所以方法均为静态方法!
- */
- public class JDBCUtil {
- //创建连接池引用,因为要提供给当前项目的全局使用,所以创建为静态的
- private static DataSource dataSource;
- //在项目启动时,即创建连接池对象,赋值给 dataSource
- static {
- try {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
- properties.load(inputStream);
- dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- //对外提供在连接池中获取连接的方法
- public static Connection getConnection(){
- try {
- return dataSource.getConnection();
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- //对外提供回收连接的方法
- public static void release(Connection connection){
- try {
- connection.close();
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }
测试代码:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtil;
- import org.junit.Test;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- public class JDBCUtilTest {
- @Test
- public void testGetConnection() {
- Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connection);
- //CRUD
- JDBCUtil.release(connection);
- }
- }
1.3 ThreadLocal (本地线程)
问题:
同一用户线程多次操作获取了多个连接,造成连接资源的浪费
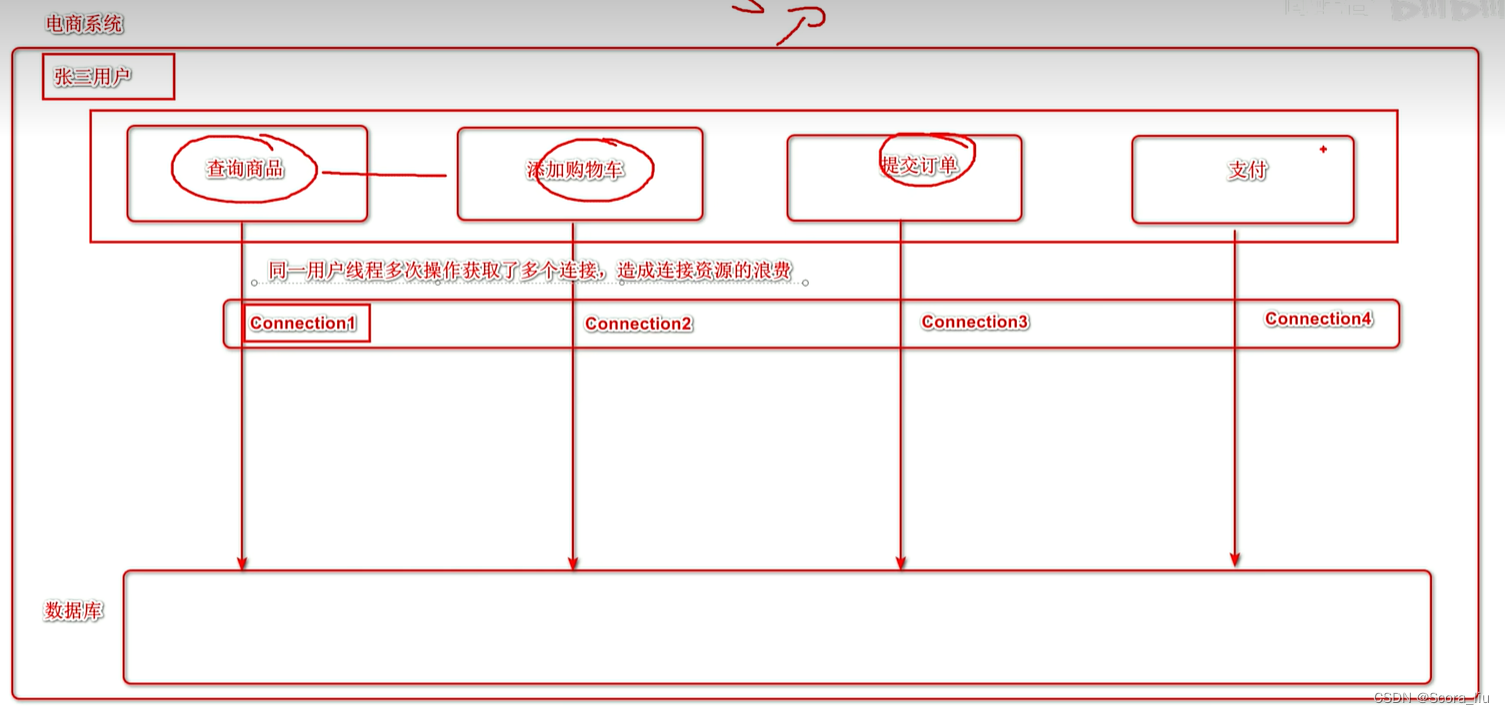

怎么取?
怎么存?
怎么移除?
- 在进行对象跨层传递的时候,使用ThreadLocal可以避免多次传递,打破层次间的约束
- 线程间数据隔离
- 进行事务操作,用于存储线程事务信息
- 数据库连接, Session 会话管理
- ThreadLocal对象.get:获取ThreadLocal中当前线程共享变量的值
- ThreadLocal对象.set:设置ThreadLocal中当前线程共享变量的值
- ThreadLocal对象.remove:移除ThreadLocal中当前线程共享变量的值。
1.4 JDBC 工具类封装 V2.0
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util;
- import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
- import javax.sql.DataSource;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.SQLException;
- import java.util.Properties;
- /**
- * JDBC工具类(V2.0)
- * 1.维护一个连接池对象,维护了一个线程绑定变量的ThreadLocal对象
- * 2.对外提供在ThreadLocal中获取连接的方法
- * 3.对外提供回收连接的方法,回收过程中,将要回收的连接从ThreadLocal中移除!
- * 【注意】:工具类仅对外提供共性的功能代码,所以方法均为静态方法!
- * 【注意】:使用ThreadLocal就是为了一个线程在多次数据库操作过程中,使用的是同一个连接!
- */
- public class JDBCUtilV2 {
- //创建连接池引用,因为要提供给当前项目的全局使用,所以创建为静态的
- private static DataSource dataSource;
- private static ThreadLocal
threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); - //在项目启动时,即创建连接池对象,赋值给 dataSource
- static {
- try {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
- properties.load(inputStream);
- dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- //对外提供在连接池中获取连接的方法
- public static Connection getConnection(){
- try {
- //在ThreadLocal中获取Connection
- Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
- //threadLoacl里没有存储Connection,也就是第一次获取
- if(connection == null){
- connection = dataSource.getConnection();
- threadLocal.set(connection);
- }
- return connection;
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- //对外提供回收连接的方法
- public static void release(){
- try {
- Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
- if (connection != null){
- //从threadLocal中移除当前已经存储的Connection对象
- threadLocal.remove();
- //将Connection对象归还给连接池
- connection.close();
- }
- connection.close();
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }
测试代码
- @Test
- public void testJDBCV2(){
- /*
- JDBCUtil 获取连接
- */
- Connection connection1 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- Connection connection2 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- Connection connection3 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println("================================");
- /*
- JDBCUtilV2 获取连接
- */
- Connection connectionA = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- Connection connectionB = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- Connection connectionC = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connectionA);
- System.out.println(connectionB);
- System.out.println(connectionC);
- }
二、DAO封装及BaseDAO 工具类
2.1 DAO 概念
1、DAO:Data Access Object,数据访问对象。
2、Java 是面向对象语言,数据在 Java 中通常以对象的形式存在。一张表对应一个实体类,一张表的操作对应一个 DAO 对象。
3、在 Java 操作数据库时,我们会将对同一张表的增删改查操作统一维护起来,维护的这个类就是 DAO 层。
4、DAO 层只关注对数据库的操作,供业务层 Service 调用,将职责划分清楚!

EmployeeDao.java
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.pojo.Employee;
- import java.util.List;
- /**
- * EmployeeDao 这个类对应的是 t_emp 这张表的增删改查的操作
- */
- public interface EmployeeDao {
- /**
- * 数据库对应的查询所有的操作
- * @return 表中所有的数据
- */
- List
selectAll(); - /**
- * 数据库对应的根据empId查询单个员工数据操作
- * @param empId
- * @return 一个员工对象(一行数据)
- */
- Employee selectByEmpId(Integer empId);
- /**
- * 数据库对应的新增一条员工数据
- * @param employee ORM思想中的一个员工对象
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- int insert(Employee employee);
- /**
- * 数据库对应的修改一条员工数据
- * @param employee ORM思想中的一个员工对象
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- int update(Employee employee);
- /**
- * 数据库对应的根据empId删除一条员工数据
- * @param empId 主键列
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- int delete(Integer empId);
- }
EmployeeDaoImpl.java
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.impl;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.EmployeeDao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.pojo.Employee;
- import java.util.List;
- public class EmployeeDaoImpl implements EmployeeDao {
- @Override
- public List
selectAll() { - //1.注册驱动
- //2.获取连接
- //3.预编译SQL语句
- //4.为占位符赋值,执行SQL,接受返回结果
- //5.处理结果
- //6.释放资源
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public Employee selectByEmpId(Integer empId) {
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public int insert(Employee employee) {
- return 0;
- }
- @Override
- public int update(Employee employee) {
- return 0;
- }
- @Override
- public int delete(Integer empId) {
- return 0;
- }
- }
2.2 BaseDAO 概念
基本上每一个数据表都应该有一个对应的 DAO 接口及其实现类,发现对所有表的操作(增、删、改、查)代码重复度很高,所以可以抽取公共代码,给这些 DAO 的实现类可以抽取一个公共的父类,复用增删改查的基本操作,我们称为 BaseDAO。
2.3 BaseDAO 搭建
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtilV2;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
- /**
- * 将共性的数据库的操作代码封装在BaseDAO里
- */
- public class BaseDAO {
- /**
- * 通用的增删改的方法
- * @param sql 调用者要执行的SQL语句
- * @param params SQL语句中的占位符要赋值的参数
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- public int executeUpdate(String sql,Object... params) throws Exception {
- //1.通过JDBCUtilV2获取数据库连接
- Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- //3.预编译SQL语句
- PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- //4.为占位符赋值,执行SQL,接受返回结果
- if (params != null && params.length > 0){
- for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++){
- //占位符是从1开始的,参数的数组是从0开始的
- preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
- }
- }
- int row = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
- //5.释放资源
- preparedStatement.close();
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- //6.返回结果
- return row;
- }
- }
2.4 BaseDAO 的应用
1、BaseDAO 搭建通用查询方法思路


- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtilV2;
- import java.lang.reflect.Field;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
- import java.sql.ResultSet;
- import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- /**
- * 将共性的数据库的操作代码封装在BaseDAO里
- */
- public class BaseDAO {
- /**
- * 通用的增删改的方法
- * @param sql 调用者要执行的SQL语句
- * @param params SQL语句中的占位符要赋值的参数
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- public int executeUpdate(String sql,Object... params) throws Exception {
- //1.通过JDBCUtilV2获取数据库连接
- Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- //3.预编译SQL语句
- PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- //4.为占位符赋值,执行SQL,接受返回结果
- if (params != null && params.length > 0){
- for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++){
- //占位符是从1开始的,参数的数组是从0开始的
- preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
- }
- }
- int row = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
- //5.释放资源
- preparedStatement.close();
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- //6.返回结果
- return row;
- }
- /**
- * 通用的查询:多行多列、单行多列、单行单列
- * 多行多列:List
- * 单行多列:Employee
- * 单行单列:封装的是一个结果。Double、Integer......
- *
- * 封装的过程:
- * 1.返回的类型:泛型:类型不确定,调用者知道,调用时,将此次查询的结果类型告知BaseDAO就可以了
- * 2.返回的结果:通用,List 可以存储多个结果,也可也存储一个结果 get(0)
- * 3.结果的封装:反射,要求调用者告知BaseDAO要封装对象的类对象。Class
- */
- public
List executeQuery(Class clazz, String sql,Object... params) throws Exception { - //获取连接
- Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- //预编译SQL语句
- PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- //设置占位符的值
- if(params != null && params.length > 0){
- for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++){
- preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
- }
- }
- //执行SQL,并接受返回的结果集
- ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
- //获取结果集中的元数据对象
- //包含了:列的数量、每个列的名称
- ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
- //获取列的数量
- int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
- List
list = new ArrayList (); - //处理结果
- while (resultSet.next()){
- //循环一次,代表有一行数据,通过反射创建一个对象
- T t = clazz.newInstance();
- //循环遍历当前行的列,循环几次,看有多少列
- for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount ; i++) {
- //通过下标获取列的值
- Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
- //获取到的列的value值,这个值就是 t这个对象中的某一个属性
- //获取当前拿到的列的名字 = 对象的属性名
- String fieldName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
- //通过类对象和fieldName(字段名)获取要封装的对象的属性
- Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
- //突破封装的private
- field.setAccessible(true);
- field.set(t, value);
- }
- list.add(t);
- }
- //资源的关闭
- resultSet.close();
- preparedStatement.close();
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- return list;
- }
- }
2、BaseDAO 搭建查询单个结果方法
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtilV2;
- import java.lang.reflect.Field;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
- import java.sql.ResultSet;
- import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- /**
- * 将共性的数据库的操作代码封装在BaseDAO里
- */
- public class BaseDAO {
- /**
- * 通用的增删改的方法
- * @param sql 调用者要执行的SQL语句
- * @param params SQL语句中的占位符要赋值的参数
- * @return 受影响的行数
- */
- public int executeUpdate(String sql,Object... params) throws Exception {
- //1.通过JDBCUtilV2获取数据库连接
- Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- //3.预编译SQL语句
- PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- //4.为占位符赋值,执行SQL,接受返回结果
- if (params != null && params.length > 0){
- for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++){
- //占位符是从1开始的,参数的数组是从0开始的
- preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
- }
- }
- int row = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
- //5.释放资源
- preparedStatement.close();
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- //6.返回结果
- return row;
- }
- /**
- * 通用的查询:多行多列、单行多列、单行单列
- * 多行多列:List
- * 单行多列:Employee
- * 单行单列:封装的是一个结果。Double、Integer......
- *
- * 封装的过程:
- * 1.返回的类型:泛型:类型不确定,调用者知道,调用时,将此次查询的结果类型告知BaseDAO就可以了
- * 2.返回的结果:通用,List 可以存储多个结果,也可也存储一个结果 get(0)
- * 3.结果的封装:反射,要求调用者告知BaseDAO要封装对象的类对象。Class
- */
- public
List executeQuery(Class clazz, String sql,Object... params) throws Exception { - //获取连接
- Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- //预编译SQL语句
- PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- //设置占位符的值
- if(params != null && params.length > 0){
- for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++){
- preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
- }
- }
- //执行SQL,并接受返回的结果集
- ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
- //获取结果集中的元数据对象
- //包含了:列的数量、每个列的名称
- ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
- //获取列的数量
- int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
- List
list = new ArrayList (); - //处理结果
- while (resultSet.next()){
- //循环一次,代表有一行数据,通过反射创建一个对象
- T t = clazz.newInstance();
- //循环遍历当前行的列,循环几次,看有多少列
- for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount ; i++) {
- //通过下标获取列的值
- Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
- //获取到的列的value值,这个值就是 t这个对象中的某一个属性
- //获取当前拿到的列的名字 = 对象的属性名
- String fieldName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
- //通过类对象和fieldName(字段名)获取要封装的对象的属性
- Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
- //突破封装的private
- field.setAccessible(true);
- field.set(t, value);
- }
- list.add(t);
- }
- //资源的关闭
- resultSet.close();
- preparedStatement.close();
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- return list;
- }
- /**
- * 通用查询:在上面查询的集合结果中获取第一个结果,简化了获取单行单列的获取、单行多列的获取
- */
- public
T executeQueryBean(Class clazz, String sql, Object... params) throws Exception{ - List
list = this.executeQuery(clazz, sql, params); - if (list == null || list.size() == 0){
- return null;
- }
- return list.get(0);
- }
- }
3、DAO 结合 BaseDAO 完成 CRUD
工具类:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.impl;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.BaseDAO;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.EmployeeDao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.pojo.Employee;
- import java.util.List;
- public class EmployeeDaoImpl extends BaseDAO implements EmployeeDao {
- @Override
- public List
selectAll() { - //1.注册驱动
- //2.获取连接
- //3.预编译SQL语句
- //4.为占位符赋值,执行SQL,接受返回结果
- //5.处理结果
- //6.释放资源
- try {
- String sql = "select emp_id empId, emp_name empName, emp_salary empSalary, emp_age empAge from t_emp";
- return executeQuery(Employee.class,sql,null);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public Employee selectByEmpId(Integer empId) {
- try {
- String sql = "select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,emp_salary empSalary,emp_age empAge from t_emp where emp_id = ?";
- return executeQueryBean(Employee.class,sql,empId);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public int insert(Employee employee) {
- try {
- String sql = "insert into t_emp(emp_name,emp_salary,emp_age) values(?,?,?)";
- return executeUpdate(sql,employee.getEmpName(),employee.getEmpSalary(),employee.getEmpAge());
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public int update(Employee employee) {
- try {
- String sql = "update t_emp set emp_salary = ? where emp_id = ?";
- return executeUpdate(sql,employee.getEmpSalary(),employee.getEmpId());
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public int delete(Integer empId) {
- try {
- String sql = "delete from t_emp where emp_id = ?";
- return executeUpdate(sql,empId);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }
测试代码:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.impl.EmployeeDaoImpl;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.pojo.Employee;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtil;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.util.JDBCUtilV2;
- import org.junit.Test;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.util.List;
- public class JDBCUtilTest {
- @Test
- public void testGetConnection() {
- Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connection);
- //CRUD
- JDBCUtil.release(connection);
- }
- @Test
- public void testJDBCV2(){
- /*
- JDBCUtil 获取连接
- */
- Connection connection1 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- Connection connection2 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- Connection connection3 = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println(connection1);
- System.out.println("================================");
- /*
- JDBCUtilV2 获取连接
- */
- Connection connectionA = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- Connection connectionB = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- Connection connectionC = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- System.out.println(connectionA);
- System.out.println(connectionB);
- System.out.println(connectionC);
- }
- @Test
- public void testEmployeeDao() {
- //1.创建DAO实现类
- EmployeeDaoImpl employeeDao = new EmployeeDaoImpl();
- /*
- //2.调用查询所有方法
- List
employeeList = employeeDao.selectAll(); - //3.处理结果
- for (Employee employee : employeeList) {
- System.out.println("employee = " + employee);
- }
- */
- /*
- //调用根据id查询单个员工方法
- Employee employee = employeeDao.selectByEmpId(1);
- System.out.println("employee = " + employee);
- */
- /*
- //调用添加员工的方法
- Employee employee = new Employee(null,"tom",300.65,38);
- int insert = employeeDao.insert(employee);
- System.out.println("insert = " + insert);
- */
- /*
- //调用更新员工信息的方法
- Employee employee = new Employee(20009,"tom",656.65,38);
- int update = employeeDao.update(employee);
- System.out.println("update = " + update);
- */
- //调用删除的方法
- int delete = employeeDao.delete(20009);
- System.out.println("delete = " + delete);
- }
- }
三、事务
3.1 事务回顾

- 数据库事务就是一种SQL语句执行的缓存机制,不会单条执行完毕就更新数据库数据,最终根据缓存内的多条语句执行结果统一判定!一个事务内所有语句都成功及事务成功,我们可以触发 commit 提交事务来结束事务,更新数据!一个事务内任意一条语句失败,即为事务失败,我们可以触发 rollback 回滚结束事务,数据回到事务之前状态!
- 一个业务涉及多条修改数据库语句!例如:
- 经典的转账案例,转账业务(A账户减钱和B账户加钱,要一起成功)
- 批量删除(涉及多个删除)
- 批量添加(涉及多个插入)
- 事务的特性:
- 原子性(Atomicity)原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生
- 一致性(Consistency)事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态。
- 隔离性(Isolation)事务的隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
- 持久性(Durability)持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来的其他操作和数据库故障不应该对其有任何影响
- 事务的提交方式:
- 自动提交:每条语句自动存储一个事务中,执行成功自动提交,执行失败自动回滚!
- 手动提交:手动开启事务,添加语句,手动提交或者手动回滚即可!

3.2 JDBC 中事务实现
关键代码:
- @Test
- public void testTransaction(){
- BankDaoImpl bankDao = new BankDaoImpl();
- Connection connection = null;
- //1.获取连接,将连接的事务提交改为手动提交
- try {
- connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
- connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务,将当前连接的自动提交关闭,改为手动提交!
- //2.操作减钱
- bankDao.subMoney(1,100);
- int i = 10 / 0;
- //3.操作加钱
- bankDao.addMoney(2,100);
- //4.前置的多次dao操作,没有异常,提交事务
- connection.commit();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- try {
- connection.rollback();
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- throw new RuntimeException(ex);
- }
- } finally {
- JDBCUtilV2.release();
- }
- }
3.3 JDBC 事务代码实现
- 准备数据库表
-
- -- 继续在atguigu 的库中创建银行表
- CREATE TABLE t_bank(
- id int primary key auto_increment comment '账号主键',
- account varchar(20) not null unique comment '账号',
- money int unsigned comment '金额,不能为负值'
- );
- insert into t_bank(account, money) VALUES ('zhangsan',1000),('lisi',1000);
-
- DAO 接口代码:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao;
- public interface BankDao {
- public int addMoney(Integer id, Integer money);
- public int subMoney(Integer id, Integer money);
- }
接口实现代码:
- package com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.impl;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.BankDao;
- import com.atguigu.advanced.senior.dao.BaseDAO;
- public class BankDaoImpl extends BaseDAO implements BankDao {
- @Override
- public int addMoney(Integer id, Integer money) {
- try {
- String sql = "update t_bank set money = money + ? where id = ?";
- return executeUpdate(sql,money,id);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public int subMoney(Integer id, Integer money) {
- try {
- String sql = "update t_bank set money = money - ? where id = ?";
- return executeUpdate(sql,money,id);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }
【注意】当开启事务后,切记一定要根据代码执行结果来决定是否提交或回滚!否则数据库看不到数据的操作结果!
-
相关阅读:
Leetcode.714 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
字节二面,差点没答好
7. 吴恩达机器学习-PCA
Pandas进阶修炼120题-第五期(一些补充,101-120题)
【SA8295P 源码分析 (一)】02 - SA8295P 的 LUN 及 分区表 配置详解
解决Oracle死锁问题
JavaSE运算符
MySQL中索引的基本知识
1. 获取数据-requests.get()
redis中怎么用分布式token
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43470538/article/details/139426545