-
数据结构与算法—双链表
前言
前面有很详细的讲过线性表(顺序表和链表),当时讲的链表以单链表为主,但在实际应用中双链表有很多应用场景,例如大家熟知的LinkedList。

双链表与单链表区别
单链表和双链表都是线性表的链式实现,它们的主要区别在于节点结构。单链表的节点包含数据字段
data和一个指向下一个节点的指针next,而双链表的节点除了data和next,还包含指向前一个节点的指针pre。这个区别会导致它们在操作上有些差异。单链表:
单链表的一个节点,有储存数据的
data,还有后驱节点next(指针)。单链表想要遍历的操作都得从前节点—>后节点。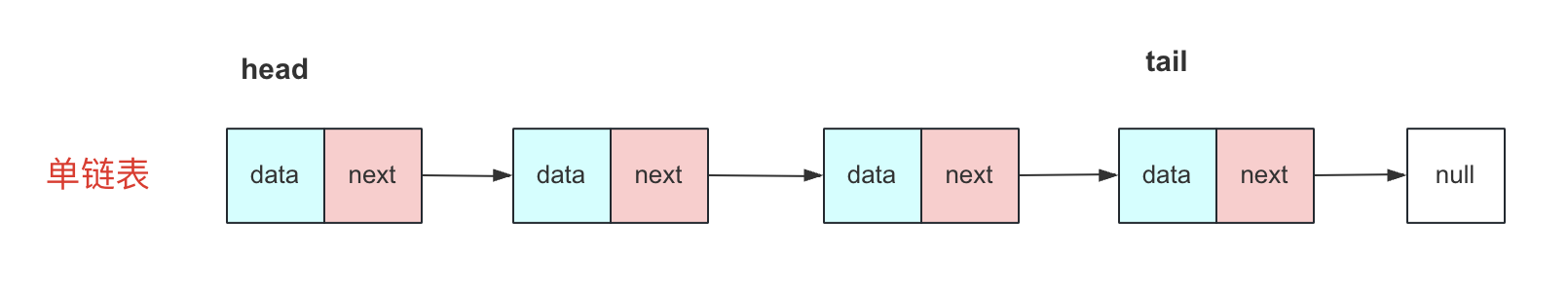
双链表:
双链表的一个节点,有存储数据的
data,也有后驱节点next(指针),这和单链表是一样的,但它还有一个前驱节点pre(指针)。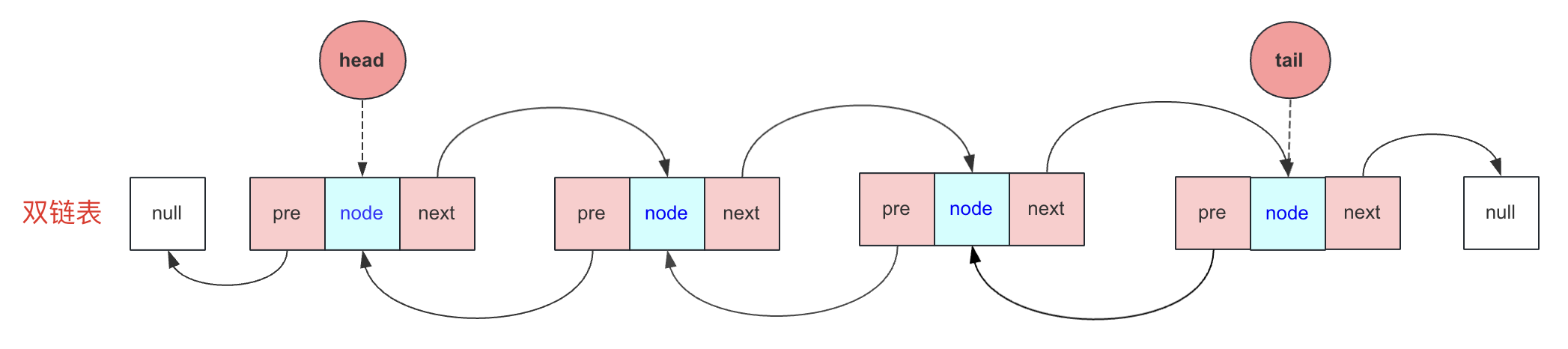
双链表结构的设计
上一篇讲单链表的时候,当时设计一个带头结点的链表就错过了不带头结点操作方式,这里双链表就不带头结点设计实现。所以本文构造的这个双链表是:不带头节点、带尾指针(tail)的双向链表。
对于链表主体:
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> { private Node<T> head; private Node<T> tail; private int size; public DoubleLinkedList(){ this.head = null; this.tail = null; size = 0; } public void addHead(T data){} public void add(T data, int index){} public void addTail(T data){} public void deleteHead(){} public void delete(int index){} public void deleteTail(int index){} public T get(int index){} public int getSize() { return size; } private static class Node<T> { T data; Node<T> pre; Node<T> next; public Node() { } public Node(T data) { this.data = data; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
具体操作分析
对于一个链表主要的操作还是增删,查询的话不做详细解释。
剖析增删其实可以发现大概有头插入、编号插入、末尾插入、头删除、编号删除、尾删除几种情况。然而这几种关于头尾操作的可能会遇到临界点比如链表为空时插入删除、或者删除节点链表为空。
这个操作是不带头结点的操作,所以复杂性会高一些!
头插入
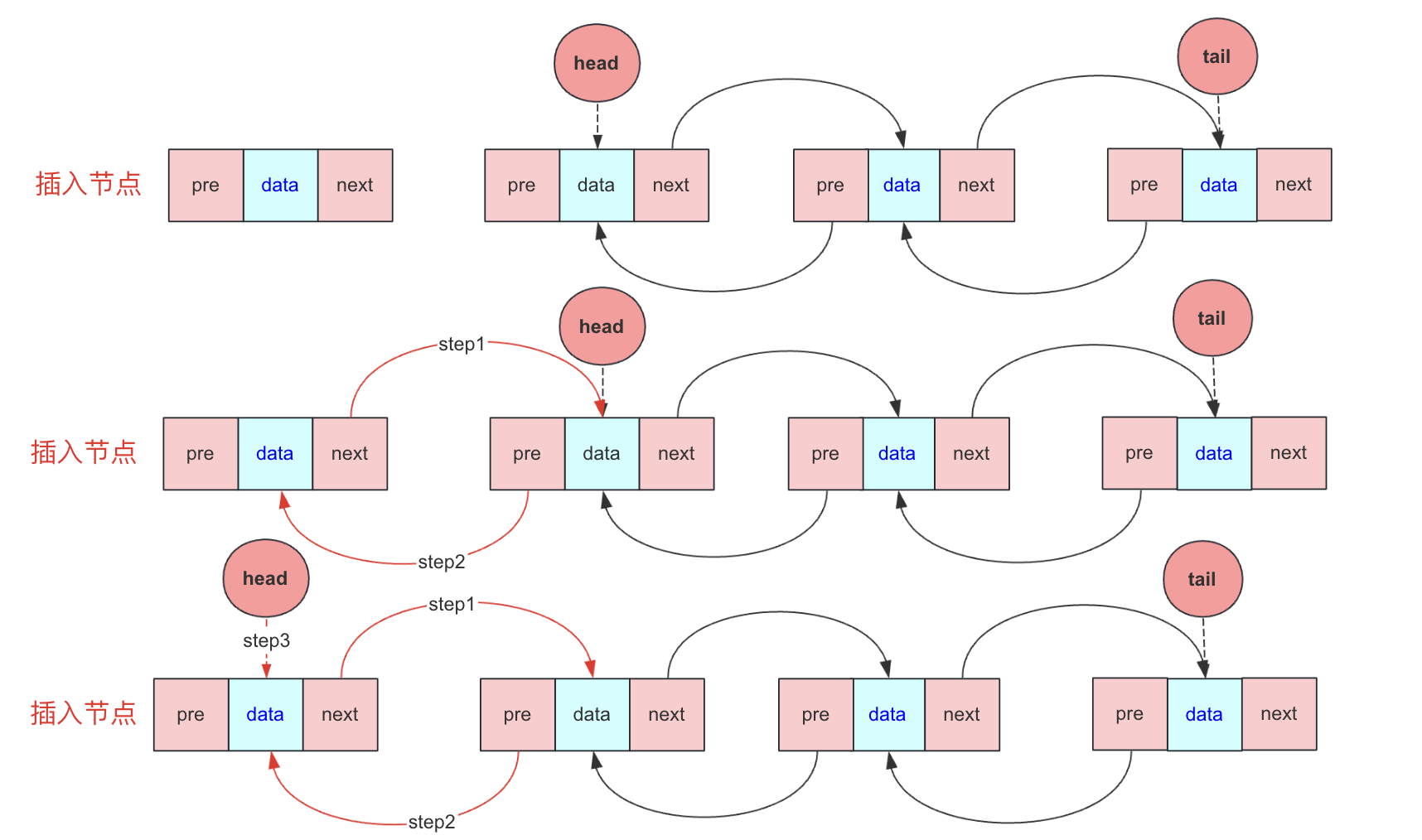
头插入区分头为空和头不为空两种情况
头为空:这种情况head和tail都指向新节点
头不为空:
- 新节点的next指向head
- head的pre指向新节点
- head指向新节点(认新节点为head)
尾插入
尾插需要考虑tail为null和不为null的情况。流程和头插类似,需要考虑tail指针最后的指向。
tail为null:此时head也为null,head和tail指向新节点。
tail不为null:
- 新节点的pre指向tail
- tail的next指向新节点
- tail指向新节点
编号插入
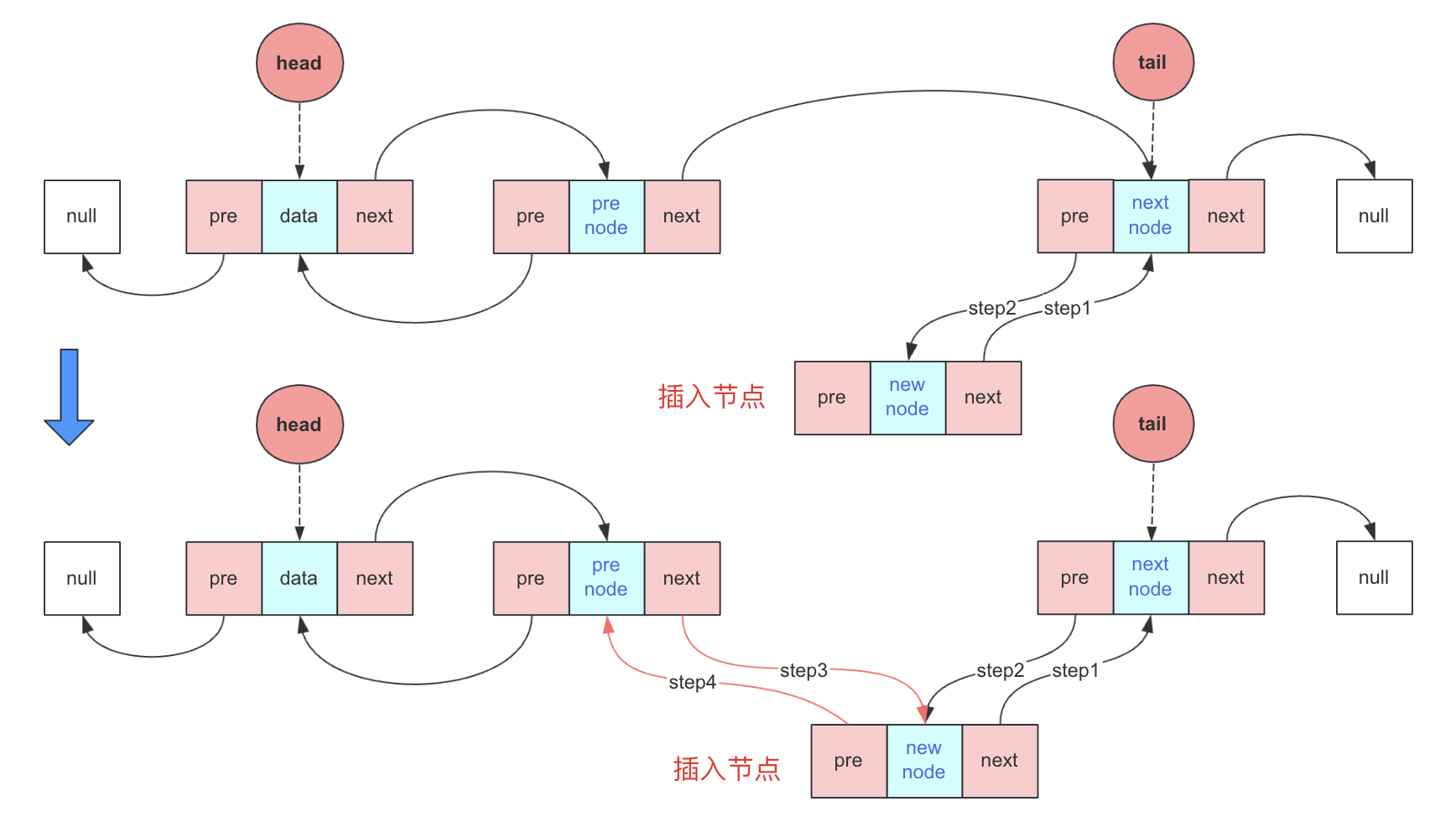
按编号插入分情况讨论,如果是头插或者尾插就直接调用对应的方法。普通方法的实现方式比较灵活,可以找到前驱节点和后驱节点,然后进行指针插入,但是往往很多时候只用一个节点完成表示和相关操作,就非常考验对表示的理解,这里假设只找到preNode节点。
index为0:调用头插index为size:调用尾插
index在(0,size):
- 找到前驱节点preNode
- 新节点next指向nextNode(此时用preNode.next表示)
- nextNode(此时新节点.next和preNode.next都可表示)的pre指向新节点
- preNode的next指向新节点
- 新节点的pre指向preNode
头删除
头删除需要注意的就是删除不为空时候头删除只和head节点有关
head不为null:
- head = head.next 表示头指针指向下一个节点
- head 如果不为null(有可能就一个节点),head.pre = null 断掉与前一个节点联系 ;head如果为null,说明之前就一个节点head和pre都指向第一个节点,此时需要设置tail为null。
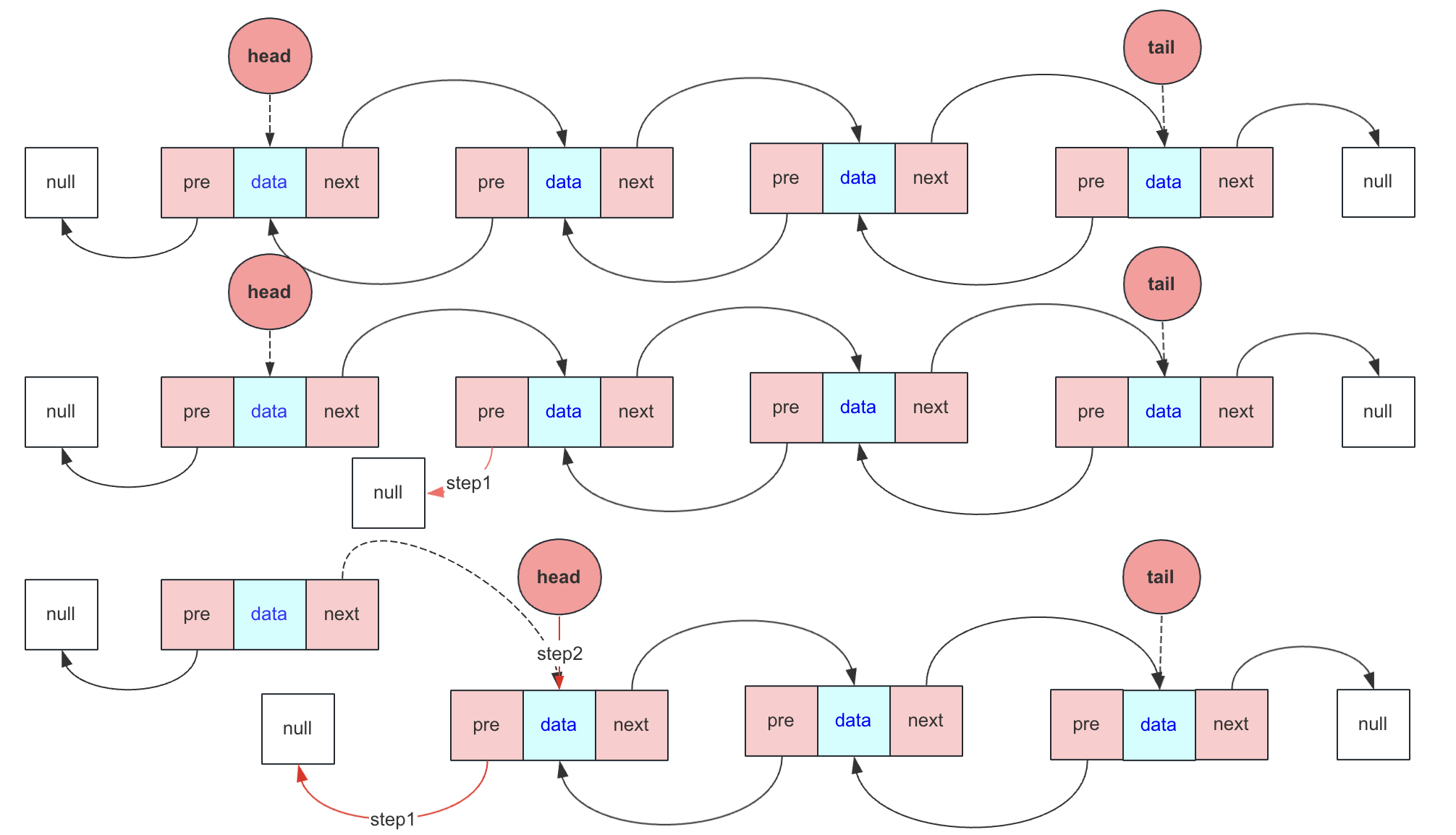
尾删除
尾删除和头删除类似,考虑好tail节点情况
如果tail不为null:
- tail = tail.pre
- 如果tail不为null,那么tail.next = null 表示删除最后一个,如果tail为null,说明之前head和tail都指向一个唯一节点,这时候需要head = null。
编号删除
编号删除和编号插入类似,先考虑是否为头尾操作,然后再进行正常操作。
index为0:调用头删
index为size:调用尾删
index在(0,size):
- 找到待删除节点current
- 前驱节点(current.pre)的next指向后驱节点(current.next)
- 后驱节点的pre指向前驱节点

完整代码
根据上面的流程,实现一个不带头结点的双链表,在查找方面,可以根据靠头近还是尾近,选择从头或者尾开始遍历。
代码:
/* * 不带头节点的 */ package code.linearStructure; /** * @date 2023.11.02 * @author bigsai * @param*/ public class DoubleLinkedList<T> { private Node<T> head; private Node<T> tail; private int size; public DoubleLinkedList() { this.head = null; this.tail = null; size = 0; } // 在链表头部添加元素 public void addHead(T data) { Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data); if (head == null) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; } else { newNode.next = head; head.pre = newNode; head = newNode; } size++; } // 在指定位置插入元素 public void add(T data, int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index is out of bounds"); } if (index == 0) { addHead(data); } else if (index == size) { addTail(data); } else { Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data); Node<T> preNode = getNode(index-1); //step 1 2 新节点与后驱节点建立联系 newNode.next = preNode; preNode.next.pre = newNode; //step 3 4 新节点与前驱节点建立联系 preNode.next = newNode; newNode.pre = preNode; size++; } } // 在链表尾部添加元素 public void addTail(T data) { Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data); if (tail == null) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; } else { newNode.pre = tail; tail.next = newNode; tail = newNode; } size++; } // 删除头部元素 public void deleteHead() { if (head != null) { head = head.next; if (head != null) { head.pre = null; } else { //此时说明之前head和tail都指向唯一节点,链表删除之后head和tail都应该指向null tail = null; } size--; } } // 删除指定位置的元素 public void delete(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index is out of bounds"); } if (index == 0) { deleteHead(); } else if (index == size - 1) { deleteTail(); } else { Node<T> current = getNode(index); current.pre.next = current.next; current.next.pre = current.pre; size--; } } // 删除尾部元素 public void deleteTail() { if (tail != null) { tail = tail.pre; if (tail != null) { tail.next = null; } else {//此时说明之前head和tail都指向唯一节点,链表删除之后head和tail都应该指向null head = null; } size--; } } // 获取指定位置的元素 public T get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index is out of bounds"); } Node<T> node = getNode(index); return node.data; } // 获取链表的大小 public int getSize() { return size; } private Node<T> getNode(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index is out of bounds"); } if (index < size / 2) { Node<T> current = head; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { current = current.next; } return current; } else { Node<T> current = tail; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) { current = current.pre; } return current; } } private static class Node<T> { T data; Node<T> pre; Node<T> next; public Node(T data) { this.data = data; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
结语
在插入删除的步骤,很多人可能因为繁琐的过程而弄不明白,这个操作的写法可能是多样的,但本质操作都是一致的,要保证能成功表示节点并操作,这个可以画个图一步一步捋一下,看到其他不同版本有差距也是正常的。
还有很多人可能对一堆next.next搞不清楚,那我教你一个技巧,如果在等号右侧,那么它表示一个节点,如果在等号左侧,那么除了最后一个.next其他的表示节点。例如node.next.next.next可以看成(node.next.next).next。
在做数据结构与算法链表相关题的时候,不同题可能给不同节点去完成插入、删除操作。这种情况操作时候要谨慎先后顺序防止破坏链表结构。
系列仓库地址:https://github.com/javasmall/bigsai-algorithm
csdn专栏:数据结构与算法原创不易,还请三连支持一下!
-
相关阅读:
Android 桌面小组件使用
hystrix
3DS Max中绘制圆锥箭头
nmap保存到扫描文件(局域网)
LeetCode --- 2068. Check Whether Two Strings are Almost Equivalent 解题报告
【Linux】标准输出和异常输出
LeetCode 69.x的平方
只能用于文本与图像数据?No!看TabTransformer对结构化业务数据精准建模
Android11 有线网和wifi优先级设置
【手写数字识别】GPU训练版本
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40693171/article/details/134277261
