-
mysql高阶语句
(一)使用select语句,用order by来进行排序
1、select id,name from info order by 列名;
2、ASC:升序排序,默认就是升序,可以不加
(1)select id,name from info order by id;

3、desc:降序排序,需要添加
(1)select id,name from info order by id desc;

4、使用order by,结合where条件进行过滤
(1)select name,score from info where address='南京西路' ORDER BY score desc;
(2)select id,name,score from info where sex='女' ORDER BY id desc,score desc;
(只有第一个参数出现相同值时,也就是出现重复值时,第二个才会按照要求排序)
(二)区间判断查询和去重查询
1、and:且
select * from info where score > 80 and score <=90;

2、or:或
select * from info where score > 80 or score < 90;

3、嵌套条件:
(1)select * from info where score > 70 and ( score > 75 and score < 90 );

(2)select * from info where sex='男' and ( score > 80 and score < 90);

4、去重查询(重点)
(1)select distinct sex from info;

(2)select DISTINCT address from info where score = 90 and sex='男' ;
(三)分组查询:group by语句(一般结合聚合函数使用)
1、聚合函数(使用聚合函数,必须要加group by)
(1)count():统计有多少行
(2)sum():列的值相加,求和
(3)avg():列的值求平均数
(4)max():过滤出列的最大值
(5)min():过滤出列的最小值
2、分组
(1)分组的时候可以按照一个字段,也可以按照多个字段对结果进行分组
(2)分组的条件,要选用有多个重复值的列,过滤条件要用having语句过滤
3、格式:select count(name),sex from info GROUP BY sex;
4、统计行数count()
(1)select count(name),sex from info GROUP BY sex;

(2)根据where条件筛选,score>80
select count(name),sex,score from info where score >= 80 GROUP BY sex;

5、求和
(1)以地址为分组,对score求和
select sum(score),address from info group by address;

6、求平均值
(1)select avg(score),sex from info GROUP BY sex;

7、最小值
(1)select min(score),sex,name from info GROUP BY sex;

8、group by使用having语句实现条件过滤(having)
(1)select avg(score),address from info group by address having avg(score) > 60;
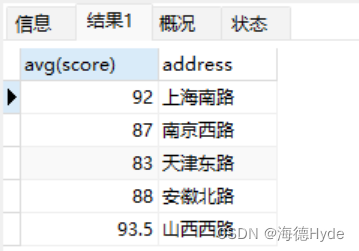
(2)按照地址分组,求成绩的平均值,然后>50,按照id的降序排序
select avg(score),address,id from info GROUP BY address having avg(score) > 50 order by id desc;

(3)统计name的行数,然后计算出学生的个数,然后把成绩也查出来,然后按照统计出来的学生个数,升序排列,按照地址分组,学生的成绩>=70
select count(name),score,address from info GROUP BY address having score >= 70 ORDER BY count(name);

(4)按照性别分组,求出男生和女生的最大成绩,最大成绩是否超过75分,满足条件的过滤出来
select max(score),sex from info GROUP BY sex having max(score) > 75;

(四)limit(限制输出的结果记录,查看表中的指定行)
1、格式:select * from info limit 3
2、select * from info limit 5,3;

3、快速查看后几行
(1)select * from info order by id desc limit 3;

(五)通配符
1、通配符
(1)通配符:主要用于替换字符串中的部分字符,通过部分字符的匹配将相关的结果查询出来
(2)通配符和like一起使用,使用where语句一起完成查询
(3)通配符可以结合在一起使用
2、通配符的种类
(1)%:表示0个、1个、或者多个
(2)_:表示单个字符
3、格式
(1)以什么为开头:select * from info where address like '南%';

(2)以什么为结尾:select * from info where address like '%西';

(3)表示内容当中包含:select * from info where address like '%西路%';
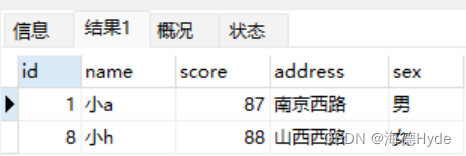
(4)表示单个字符:select * from info where name like '小_A';

(5)结合使用:select * from info where address like '山%__';

(六)别名
1、设置别名:alias (as)
(1)在mysql查询时,表的名字或者字段名太长,可以使用别名进行替代,方便书写
(2)可以给表起别名,但是要注意别名不能和数据库中其他的表名冲突
(3)列的别名在结果中可以显示,但是表的别名在结果中没有显示,只能用于查询
2、格式
(1)select name as 姓名,score as成绩 from info;

(2)select name 姓名,score 成绩 from info;

(3)给表设置别名:select name 姓名,score 成绩 from info a;
(4)select name 姓名,score 成绩 from info a where name ='小a' and id = a.id;
①id是info表的id
②a.id是info表(别名a)的id
(5)使用as复制表,约束不会被复制过来
①create table test1 as select * from info;
创建一个表test,test的数据结构从info复制过来,但是约束不会被复制


②create table test2 as select * from info where score >= 60;


(七)子查询(内查询、嵌套查询)
1、select.....(select)
(1)括号里面的查询语句会先于主查询语句执行,然后再把子查询的结果作为条件返回给主查询条件进行过滤
(2)子查询返回的结果只能是一列
(3)where条件in什么,子查询的列就是什么(一一对应)
(4)子查询语句还可以用在insert、update、delete
2、单表之间查询:
(1)select name,score from info where id in ( select id from info where score > 80);

3、多表联查(不能超过3张)
(1)select id,name,score from info where id in (select id from info1);


(2)select id,name,score from info where name in (select name from info1);



(3)select id,name,score from info where id not in (select id from info1 where score > 70);

3、子查询(insert、update、delete)
(1)insert into test1 select * from info where id in (select id from info where sex='女');

(2)insert into test1 select * from info where id in (select id from info where address like '%南京%');

(3)update info set score=50 where id in (select id from test1 where id=2);

(4)update info set score=100 where id not in (select id from test1 where id > 1);


(5)DELETE from info where id in (select id from test1 where score > 80);
4、exists语句
(1)exists:在子查询时,主要用于判断自查询的结构集是否为空。不为空返回true,为空返回false
(2)根据info表,查询出大于80分的同学,然后统计有多少个(限制内外id一致)
select count(*) from info a where EXISTS (select id from info where score > 80 and info.id=a.id);

(八)视图(view)
1、视图:在mysql当中是一个虚拟表,基于查询结果得出的一个虚拟表
(1)真表占了80%,视图适用于安全性要求比较高的场景,对外访问,一般都是视图
2、在工作中,查询的表未必是真表,有可能是基于真表查询结果的一个虚拟表
3、视图的作用:可以简化负载的查询语句,隐藏表的细节,提供安全的数据访问
4、创建视图表可以是一张表的结果集,也是多个表共同的查询的结果集
5、格式:create view v_score as select * from info where score >= 80;
6、视图表和真表之间的区别
(1)存储方式:真表存储实际数据,是真正写在磁盘当中;视图不存储任何数据,仅仅是一个查询结果集的虚拟表,不占任何存储空间
(2)数据更新:真表可以增删改查;视图表一般情况只能用于查、展示数据
(3)占用空间:真表真实占用空间;视图不占用空间
7、查看库中的视图表:show full tables in test where table_type like 'view';

8、删除:drop view v_score;
9、根据info的id,name,score,加上test3的age
(1)create view v_info(id,name,score,age) as select a.id 学号,a.name 姓名,a.score 分数,b.age 年龄 from info a,test3 b where a.name=b.name;


(2)原表和视图表数据同步
①原表数据发生变化时,视图表的数据会同步更新
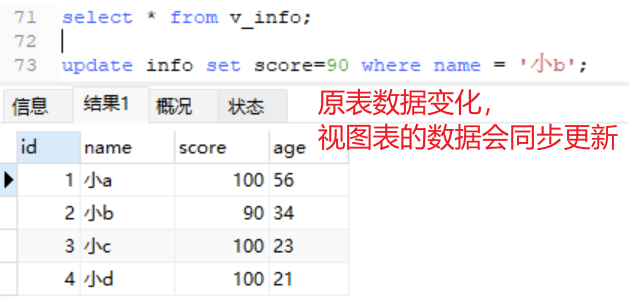
②视图表发生变化时,原表也会变化(一般不修改视图表)

(九)null值和空值
1、null:什么都没有,不被统计
2、空值:不代表什么都没有,会被统计
3、鉴别null和空值
(1)select * from info where score is null;

(2)select * from info where score is not null;


(3)统计空值:select count(address) from info;


(十)连接查询(重点)
1、种类
(1)内连接
(2)左连接
(3)右连接
2、内连接(inner join.....on)
(1)把两张表或者多张表(不超过3张),将同时符合特定条件的数据记录的组合
(2)一个或者多个列有相同值才会有查询的结果
(3)格式:select a.id,a.name from test3 a INNER JOIN info b on a.name=b.name;

3、左连接(左外连接——left join)
(1)在左连接当中,左侧表是基础表,它会接收左表的所有行,然后和右表(参考表)记录进行匹配(匹配左表当中的所有行,以及右表中符合条件的行)
(2)以左表为准,右表没有的以null值记录
(3)格式:select * from test3 a LEFT JOIN info b on a.name=b.name;


4、右连接(右外连接——right join)
(1)以右侧表为基础,接收右侧表的所有记录,匹配的记录,不匹配的记录null值
(2)格式:select a.name,b.name from test3 a RIGHT JOIN info b on a.name=b.name;

-
相关阅读:
Flinkcdcmysql实时同步pgsql报错,如何排查后面id
【论文阅读】(VAE-GAN)Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric
android——自定义控件(编辑框)、悬浮窗
unity unityWebRequest 通过http下载服务器资源
c语言(看一遍就会操作,小马教一步步教你如何文件操作)
基于SSH开发物流仓储调度系统 课程设计 大作业 毕业设计
K8s - Pod配置容器
android和java 线程Tread
华为机试 - 考古学家
机器学习的集成方法(bagging、boosting)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48145965/article/details/134265881