-
Linux网络编程04
更高效的零拷贝

发送方过程零拷贝
sendfile
发送文件方的零拷贝,虽然之前我们就可以使用mmap来实现零拷贝但是存在一个方法sendfile也可以直接实现数据从内核区发送到网络发送区socket直接把内核里面你的文件数据不经过用户态,直接发送给另外一个文件对象
有一个限制,这里的in_fd是要可以mmap的,磁盘文件可以mmap,网络设备不能mmap,因此sendfile只能将磁盘文件取出来发送给网络,不能将网络的文件发送给磁盘(只能发送文件不能接受文件,因此可以改造服务端)
//将fd中的数据发送到netFd中偏移量为NULL空指针表示从0开始发送的大小为文件大小 send(netFd,fd,NULL,fileSize);- 1
- 2

接收文件的零拷贝(仅供了解)
之前我们讲述过使用
mmap方法让内核态和用户态映射同一块物理区域,可以实现零拷贝,但是我们还可以使用管道,来实现更快速的从socket发送数据到内核文件对象的零拷贝
flags的取值为SPLICE_F_MORE,表示其将数据进行移动,因为移动数据比拷贝数据简单
使用之前必须要先定义一个宏GNU_SOURCEint pipfds[2]; pipe(pipefds);//创建管道 int total = 0; while(1) {//读取网络数据 int ret = splice(sockFd,NULL,pipefds[1],NULL,4096,SPLICE_F_MORE); total += ret; splice(pipefd[0],NULL,fd,NULL,ret,SPLICE_F_MORE);//利用管道将网络数据传给内核文件对象 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

进程池的退出(重点)
给父进程发送10号信号(
SIGUSR1),kill 10 父进程,然后父进程先不要退出,父进程给子进程发送10号信号,退出子进程,此时父进程在退出在注册信号的时候,我们要先创建出子进程(
fork),在注册信号(signal),这样才能让每个子进程都可以收到10号信号(SIGUSR1)的执行。如果先signal后fork,子进程就和父进程拥有了相同的注册信号

执行命令kill -10 主进程pid就可以关闭进程池用异步拉起同步(重要)
先有一个全局管道,用主进程的epoll监听管道的读端,注册SIGUSR1,在其递送时,我们往管道中写入数据;当信号产生时,信号会递送,会开始写管道,然后读端就会就绪,epoll_wait就会就绪。可以减少全局变量的使用量,我们只需要佳能管道作为全局变量即可
0是管道的读端,1是管道的写端



上面那这个退出方式会导致加入子进程没有将任务做完就会被立刻退出;需求是如果子进程有任务就不要立刻退出,等待子进程将热任务做完再退出
方案1:用sigprocmask屏蔽信号,任务结束完再结束屏蔽
方案2:在父子进程间不使用信号,我们可以用文本信息代替信号,因为父子进程之间库存在管道,我们可以用主进程往管道里写入文本信息(close)告诉子进程退出,加入子进程在执行任务,是不会执行recv读取管道的,当子进程任务执行完毕之后就会调用recv读取信息,以此来实现子进程任务结束之后在关闭

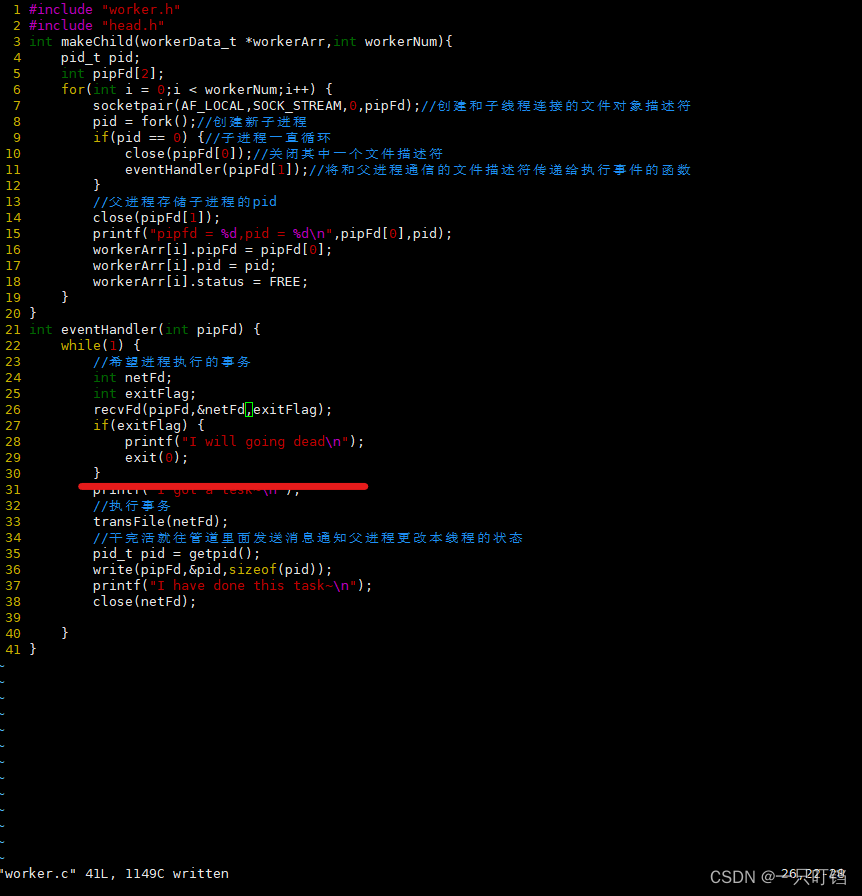
线程池
进程池(Nginx,chrome多进程)
优点:一个子进程崩溃,不影响其他子进程
缺点:一般子进程数量在一倍CPU到二倍CPU,进程间通信太困难,消耗资源比较多线程池架构
一个主线程建立客户端连接,主线程和子线程之间存在任务队列,主线程作为任务生产者,子线程作为任务消费者,因为任务队列是共享资源,因此需要用互斥锁保护,而且需要先是生产才能消费,所以是同步的,用条件变量来实现同步

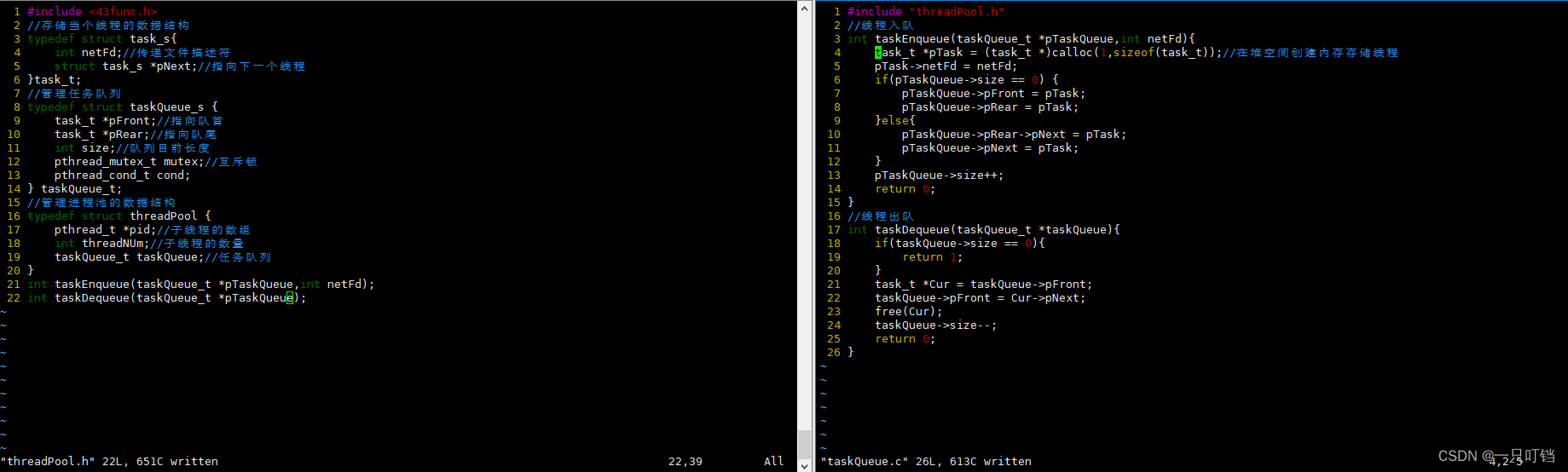
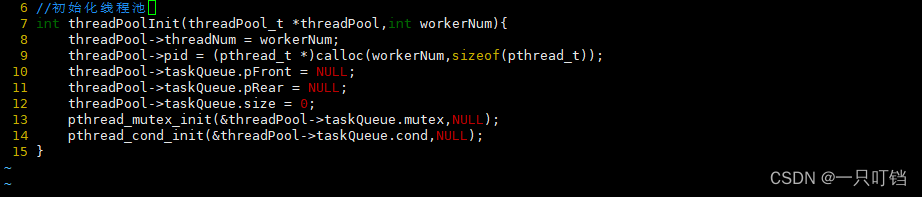
线程池的实现
//存储单个线程的数据结构 typedef struct task_s{ int netFd;//传递文件描述符 struct task_s *pNext;//指向链表中下一个线程 } task_t; //任务队列 typedef struct taskQueue_s { task_t *pFront;//队首指针 task_t *pRear;//队尾指针 int size;//队列现在的长度 pthread_mutex_t mutex;//互斥锁 pthread_cond_t connd;//条件变量 } taskQueue_t; //管理线程池的数据结构 typedef struct threadPool_s { pthread_t *tid;//子线程的数组 int threadNum;//子线程的数量 taskQueue_t taskQueue; } threadPool_t;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
初始化线程池
创建子线程
#include "threadPool.h" int makeWorker(threadPool_t *threadPoool){ for(int i = 0;i < threadPool->threadNum;i++) { //创建子线程并且让子线程执行事件handleEvent pthread_create(&threadPool->tid[i],NULL,handleEvent,(void *)threadPool); } } void *handleEvent(void *arg){ threadPool_t *threadPool = (threadPool_t *)arg; int netFd; while(1) { printf("I am free!\n"); pthread_mutex_lock(&threadPool->taskQueue.mutex);//给任务队列加锁 while(threadPool->taskQueue.size == 0) {//如果任务队列为空,那么线程处于等待,调用pthread_cond_wait会先把锁给解开,然后在使线程陷入等待 pthread_cond_wait(&threadPool->taskQueue.cond,&threadPool->taskQueue.mutex); } //子线程苏醒 netFd = threadPool->taskQueue.pFront->netFd;//拿到了对首收文件的文件描述符 taskDeQueue(&threadPool->taskQueue);//从任务队列中删除任务 pthread_mutex_unlock(&threadPool->taskQueue.mutex); printf("I am working! pid = %lu\n",pthread_self()); transFile(netFd);//下载文件 printf("done\n"); close(netFd);//关闭文件描述符 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
主进程
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { int workerNum = atoi(argv[3]); threadPool_t threadPool;//为线程池的任务队列,子线程的tid申请内存 threadPoolInit(&threadPool,workerNum);//初始化内存 makeWorker(&threadPool);//创建若干个子线程 int sockFd; tcpInit(&sockFd,argv[1],argv[2]);//主线程要初始化TCP连接 int epfd = epoll_create(1); epollAdd(sockFd,edfd);//用epoll把sockFd监听起来 struct epoll_event readyArr[2]; while(1) { int readyNum = epoll_wait(epfd,readyArr,2,-1); printf("epol_wait return \n"); for(int i = 0;i < readgNum;i++) { if(readyArr[i].data.fd == sockFd) {//说明客户端有新的连接到来 int netFd = accept(sockFd,NULL,NULL);//多个线程可以共享任务队列 //先加锁,为修改就绪线程队列长度 pthread_mutex_lock(&threadPool.taskQueue.mutex); taskEnqueue(&threadPool.taskQueue,netFd);//任务进队 printf("New task!\n"); pthread_cond_signal(&threadPool.taskQueue.cond);//通知处于就绪队列的线程 pthread_mutex_unlock(&threadPool.taskQueue.mutex);//主线程解锁 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26


多线程和信号不能直接混合使用,因为信号产生就会发送给目标进程,一个进程中可以存在多个线程,信号的递送不知道是由哪个线程来实现递送,因此不能直接混合使用
线程池的退出
我们创建两个进程,让子进程实现上面所说的线程池操作,而主进程执行连接,接收客户端信号的操作,然后再主进程与子进程之间创建一根管道,父进程注册
SIGUSR1信号,父进程递送信号决定写管道,子进程使用epoll监听子进程的读管道,子进程中主线程收到管道终止信号后,向子线程发送终止信号pthread_concal终止子进程,并且再终止自己//main.c int exitPipe[2];//创建管道用于父子进程通信 void sigFunc(int signum){//主进程发送终止管道消息的方法 printf("signum = %d\n",signum); write(exitPipe[1],"1",1); printf("Parent process is going to die!\n"); } int main() { //... pipe(exitPipe); if(fork() != 0) {//父进程执行的代码 close(exitPipe[0]); signal(SIGUSR1,sigFunc); wait(NULL); exit(0); } //子进程执行的代码 close(exitPipe[1]);//子进程关闭管道写端 //... epollAdd(exitPipe[0],epfd);//监听管道读端口 while(1) { for(int i = 0;i < readyNum;i++) { if(readyArr[i].data.fd == sockFd){} else if(readyArr[i].data.fd == exitPipe[0]) {//就绪的是管道 printf("child peocess,threadPool is going to die\n"); for(int j = 0;j < workerNum;j++) { pthread_cancel(threadPool.pid[i]);//给子线程发送终止信号 } for(int j = 0;j < workerNum;j++) { pthread_join(threadPool.pid[j],NULL);//等待回收子线程资源 } pthread_exit(NULL);//主线程退出 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
以上的退出方式存在问题,不能实现退出,因为我们再给主进程发送终止信号,主进程通过管道告诉子进程要终止,子进程的主线程收到终止信号,会执行终止,但是由于子线程都是处在睡眠状态,我们使用
pthread_cancle唤醒子线程,子线程首先执行pthread_mutex_lock,进行上锁,然后子线程就会终止,但是此时锁还没解开,因此会导致下一个线程被pthread_cancle唤醒之后无法上锁,导致无法正常关闭避免死锁
采用资源清理实现正常终止线程池
再lock之后pushpthread_cleanup_push
再原来unlock的地方poppthread_clean_pop//worker.c void cleanFunc(void *arg){//上锁 threadPool_t *pthreadPool = (threadPool_t *)arg; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pthreadPool->taskQueue.mutex); } //上锁位置 pthread_mutex_push(cleanFuunc,(void *)pthreadPool); //解锁位置 pthread_cleanup_pop(1);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
要实现优雅的退出,不能使用pthread_cancle
使用最简单的方式,设置一个flag,表示退出的标志位,主线程再管道exitPipe就绪时,将flag改为终止标志。子线程再接收任务前检查以下flag,如果为终止标志则终止
首先我们需要在结构体taskQueue_s中加入标志位exitflag,初始值位0(表示不退出)//main.c while(1) { for(int i = 0;i < workerNum;i++) { if(readyArr[i].data.fd == sockFd){} else if(readyArr[i].data.fd == exitPipe[0]) { threadPool.exitFlag = 1;//改标志位 pthread_cond_boradcast(&threadPool->taskQueue.cond);//将处于睡眠的进程唤醒 } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
//worker.c while(1) { //... while(pthreadPool->tyaskQueue.size == 0 && pthreadPool->exitFlag == 0) { pthread_cond_wait(...); } //子线程被唤醒 if(pthread->exitFlag != 0) { pthread_exit(NULL); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12


-
相关阅读:
Win10系统C++调用OpenCV实现网络摄像头录像和抓拍图片
面试问题梳理:项目中防止配置中的密码泄露-Jasypt
#边学边记 必修5 高项:对人管理 第2章 项目沟通管理和干系人管理 2-1 沟通的基本概念
本地运行feishu-chatgpt项目结合内网穿透实现无公网IP远程访问
Docker下部署安装Mysql
探索UWB模块的潜力:智能家居与物联网的连接者
IPSec NAT穿越原理
java基于SpringBoot+vue的社区报修维修平台 elementui
零基础可以学设计专业吗,怎么学?
聊聊编程是什么
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_48627750/article/details/134231999
