-
C++入门(3):引用,内联函数
一、引用
1.1 引用特性
- 引用必须初始化

-
一个变量可以有多个引用
-
引用一旦引用一个实体,就不能引用其他实体
int main() { int a = 10, C = 20; int& b = a; b = c; // 赋值?还是b变成c的别名? return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

1.2 常引用
引用权限可以平移或缩小,但是不能放大。
int main() { // 情形1 const int a = 10; // int& a1 = a; // error const int& a2 = a; // 情形2 // int& b = 10; // error const int& b1 = 10;// 10具有常属性,权限平移 // 情形3 int c = 10; // double& c1 = c;// error,类型不同 const double& c2 = c; // 隐式类型转换过程中,会创建一个具有常属性的临时变量 return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
1.3 使用场景
- 做参数
#includeusing namespace std; void Swap(int& x, int& y) { int tmp = x; x = y; y = x; } int main() { int a = 10; int b = 20; Swap(a, b); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 做返回值
观察以下几个场景。
(a).
#includeusing namespace std; int count1() { int n = 0; n++; return n; } int& count2()// 实际上是个错误程序 { int n = 0; n++; return n; } int& count3() { static int n = 0; n++; return n; } int main() { int ret1 = count1(); cout << ret1 << endl; int ret2 = count2(); cout << ret2 << endl; int& ret3 = count2(); // ret3是n的别名,count2函数栈帧销毁后,ret3/n 的值是不确定的 cout << ret3 << endl; cout << ret3 << endl; int& ret4 = count3(); cout << ret4 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
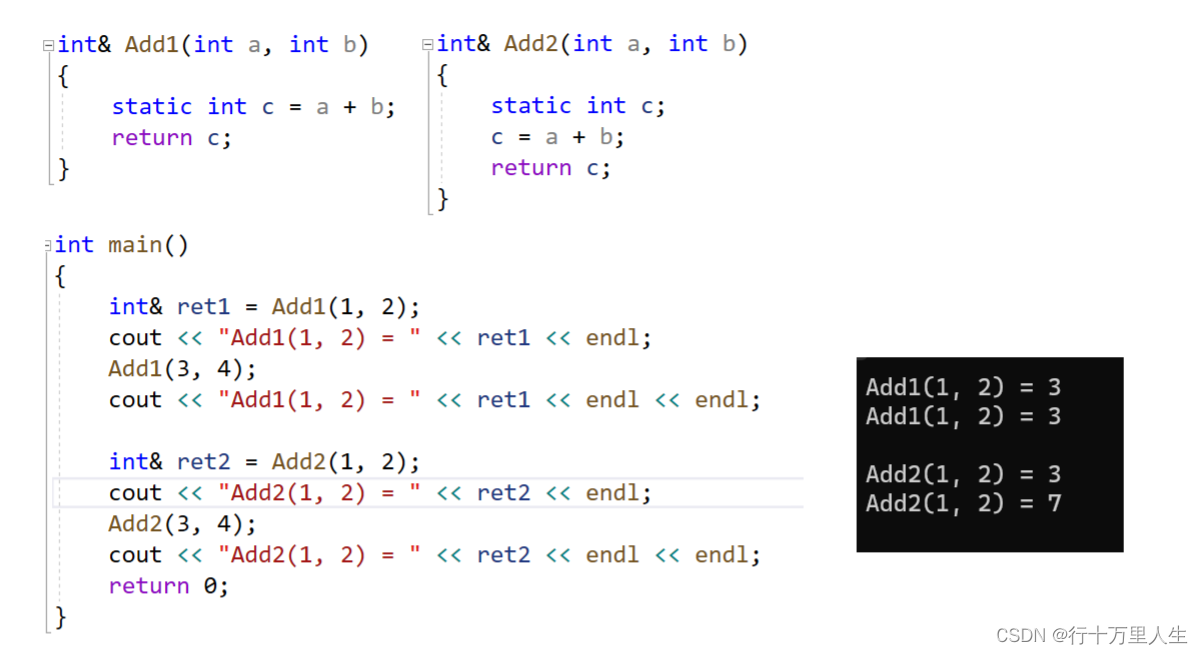
(b).
#includeusing namespace std; // static int& Add1(int a, int b) { static int c = a + b; return c; } int& Add2(int a, int b) { static int c; c = a + b; return c; } int main() { int& ret1 = Add1(1, 2); cout << "Add1(1, 2) = " << ret1 << endl; Add1(3, 4); cout << "Add1(1, 2) = " << ret1 << endl << endl; int& ret2 = Add2(1, 2); cout << "Add2(1, 2) = " << ret2 << endl; Add2(3, 4); cout << "Add2(1, 2) = " << ret2 << endl << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1.4 传值、传引用效率比较
以值作为参数或返回值类型,在传参和返回期间,函数不会传递实参或将变量本身直接返回,而是传递实参或返回变量的一份临时拷贝。因此用值作为参数或返回值类型,效率非常低下。
1.5 引用和指针的区别
在语法概念上,引用是被引用实体变量的别名,并没有开辟新的内存空间。

在底层实现上,实际开了空间。引用是按照指针的方式实现的。

二、内联函数
2.1 概念
内联函数是用关键词 inline 修饰的函数,可以代替宏函数(宏函数缺点:1. 语法细节多,易出错;2. 不可调试;3. 没有类型安全检查)。
编译时,C++编译器会在把内联函数在调用位置展开,没有建立函数栈帧的开销,在一定程度上提高程序运行效率。
(在debug模式下,编译器默认不会对代码进行优化,需要通过设置以观察到内联函数)
-
右击项目,进入 属性


2.2 特性
- inline 是一种以空间换时间的做法,在编译阶段,会用函数体替换函数调用。
- inline 对编译器来说只是一个“请求”,编译器可以选择忽略。一般建议:将函数规模较小、不是递归、频繁调用的函数用 inline 修饰,否则编译器会忽略 inline 特性。
- inline 不能声明和定义分离,分离会导致链接错误——inline 被展开就没有函数地址了。
// Func.h #includeusing namespace std; inline void f(int x); // Func.cpp #include "Func.h" void f(int x) { cout << "f(x)" << endl; } // test.cpp #include "Func.h" int main() { f(10); return 0; } // error: // 链接错误:Test.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 "void __cdecl f(int)" (?f@@YAXH@Z),函数 _main 中引用了该符号 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
正确做法:
// Func.h #includeusing namespace std; inline void f(int x) { cout << "f(x)" << endl; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
相关阅读:
Spring Cloud Gateway 服务网关的部署与使用详细介绍
[vmware to openstack] 安装virtio驱动
项目管理逻辑:老板为什么赔钱的项目也做?为什么害怕你闲着?
5.合宙Air32F103_LCD_key
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
Abaqus 2022x新功能介绍第二弹
2022年智慧城市与智能电网国际会议(CSCSG 2022)
UE4 C++设计模式:适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)
关于package-lock.json
龙蜥及其理事分获“2022 OSCAR 尖峰开源社区及项目、尖峰开源人物”奖项
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/taduanlangan/article/details/134009828
