-
线程中的join()、wait() 和 notify()详解及练习题
一、join()
Thread类提供了join()方法,用于等待当前线程所调用的其他线程执行完毕。1、当一个线程调用另一个线程的
join()方法时,它会被阻塞,直到被调用的线程执行完毕或达到指定的超时时间。比如:当主线程main中调用了另一个线程thread1,那么main线程会被阻塞,只有当thread1执行完毕,main线程才继续执行。
2、当然也可以调用
join()方法还有一个重载的形式,允许指定等待的最大时间:public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException在上述形式中,
millis参数表示等待的最大时间,以毫秒为单位。如果被调用的线程在指定的时间内没有执行完毕,当前线程将不再等待,继续执行后续的操作。join()方法通常用于实现线程之间的协作和同步。例如,可以创建多个线程,然后使用join()方法来确保这些线程按照特定的顺序执行。练习1:要求线程a执行完才开始线程b, 线程b执行完才开始线程c
- import org.junit.Test;
- /**
- * @Author xpf
- * @Date 2023/9/5 17:07
- * @Version 1.0
- * 要求线程a执行完才开始线程b, 线程b执行完才开始线程c
- */
- public class MyThreadJoin {
- public static class MyThread extends Thread{
- MyThread(String name){
- super(name);
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- for (int i= 1; i <= 10; i++){
- System.out.println(getName() + ":" + i);
- }
- }
- }
- //https://blog.csdn.net/shinecjj/article/details/103792151
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyThread t1 = new MyThread("a");
- MyThread t2 = new MyThread("b");
- MyThread t3 = new MyThread("c");
- try {
- t1.start();
- t1.join();
- t2.start();
- t2.join();
- t3.start();
- t3.join();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
结果:

二、wait() 和 notify()
1、wait() 和 notify() 是object对象的方法
2、wait():
可以使当前线程进入等待状态,直到其他线程调用 notify() 或者 notifyAll() 方法唤醒它。
在调用 wait() 方法时,当前线程会释放它所持有的锁,以便其他线程可以访问共享资源
3、notify():
用于唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程,如果有多个线程在等待,则只会唤醒其中一个线程。
notifyAll() 方法则会唤醒所有处于等待状态的线程。
wait和 notify 方法必须在同步块中使用,即在使用这两个方法的对象上获取锁。否则会抛出illegalMonitorStateException异常
练习1:两个线程轮流打印数字,一直到100
- /**
- * @Author xpf
- * @Date 2023/9/6 10:35
- * @Version 1.0
- * 2、两个线程轮流打印数字,一直到100
- * wait() 和 notify() 是object对象的方法
- * wait():可以使当前线程进入等待状态,直到其他线程调用 notify() 或者 notifyAll() 方法唤醒它。
- * 在调用 wait() 方法时,当前线程会释放它所持有的锁,以便其他线程可以访问共享资源
- * notify():用于唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程,如果有多个线程在等待,则只会唤醒其中一个线程。notifyAll方法则会唤醒所有处于等待状态的线程。
- * wait和 notify 方法必须在同步块中使用,即在使用这两个方法的对象上获取锁。否则会抛出illegalMonitorStateException异常
- */
- public class ThreadWaitNotify {
- static class TakeTurnsAdd{
- final Object lock = new Object();
- boolean getFlag = true;
- int sum = 1;
- public void add1(){
- synchronized (lock){
- String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
- for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
- if (getFlag){
- try {
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()前" );
- lock.wait();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()后" );
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- System.out.println(threadName + "a:" + sum++);
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()前" );
- getFlag = !getFlag;
- lock.notify();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()后" );
- }
- }
- }
- public void add2(){
- synchronized (lock){
- String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
- for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
- if (!getFlag){
- try {
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()前" );
- lock.wait();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()后" );
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- System.out.println(threadName + "b:" + sum++);
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()前" );
- getFlag = !getFlag;
- lock.notify();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()后" );
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TakeTurnsAdd takeTurnsAdd = new TakeTurnsAdd();
- new Thread(()->{takeTurnsAdd.add1();}).start();
- new Thread(()->{takeTurnsAdd.add2();}).start();
- }
- }
结果:

...

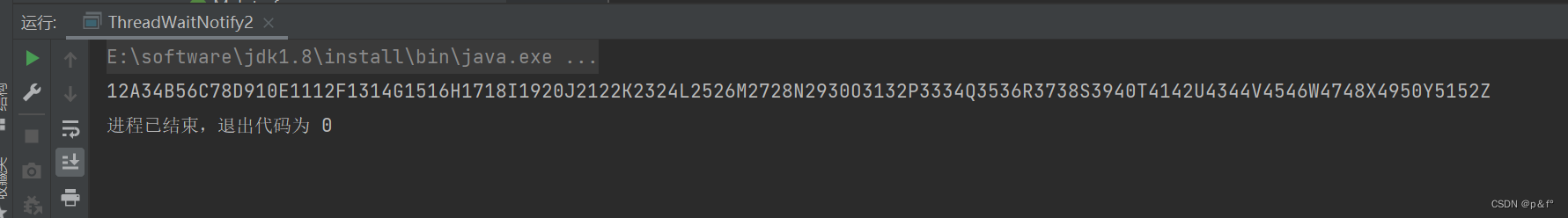
练习2:两线程,一个打印数字从1到52,另一个打印字母从A到Z,输出:12A34B56C...5152Z
- /**
- * @Author xpf
- * @Date 2023/9/6 10:35
- * @Version 1.0
- * 两线程,一个打印数字从1到52,另一个打印字母从A到Z,输出:12A34B56C...5152Z
- */
- public class ThreadWaitNotify2 {
- static class TakeTurnsAdd{
- final Object lock = new Object();
- boolean getFlag = false;
- int sum = 1;
- public void add1(){
- synchronized (lock){
- String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
- for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
- if (getFlag){
- try {
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()前" );
- lock.wait();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()后" );
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- System.out.print(sum++);
- System.out.print(sum++);
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()前" );
- getFlag = !getFlag;
- lock.notify();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()后" );
- }
- }
- }
- public void add2(){
- synchronized (lock){
- String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
- for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
- if (!getFlag){
- try {
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()前" );
- lock.wait();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "wait()后" );
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- System.out.print((char) (65+i));
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()前" );
- getFlag = !getFlag;
- lock.notify();
- // System.out.println(threadName + "notify()后" );
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TakeTurnsAdd takeTurnsAdd = new TakeTurnsAdd();
- new Thread(()->{takeTurnsAdd.add1();}).start();
- new Thread(()->{takeTurnsAdd.add2();}).start();
- }
- }
结果:
-
相关阅读:
通过API接口实现数据实时更新的方案(InsCode AI 创作助手)
Effective C++ 笔记
Automatic differentiation package - torch.autograd
hashmap的一些坑
hardhat 教程及 hardhat-deploy 插件使用
使用AWK进行文本处理
〔025〕Stable Diffusion 之 接口开发 篇
牛客网Verilog刷题 | 快速入门-基础语法
Android 应用启动过程优化
2022最新解析最清晰 Java 系列面试题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44299529/article/details/132719461
