-
MyBatis操作数据库实现
说明:MyBatis是作用于三层架构开发,数据访问层(Data Access Object)的框架,用于访问数据库,对数据进行操作。
一、环境搭建
首先,创建一个SpringBoot模块,然后把MyBatis的环境搭建起来。因为MyBatis是作用于Dao层的,故先省去Service层,重点关注Dao层中与数据库的交流。
(1)创建Springboot模块
我这里是手动创建SpringBoot模块方式,在idea中创建一个SpringBoot模块,参考(http://t.csdn.cn/RJ2gu)
pom.xml文件中添加的继承和依赖

(2)添加MyBatis依赖
在SpringBoot模块基础上,添加MyBatis依赖和数据库的配置文件
添加MyBatis依赖

添加数据库的配置文件(application.properties)
放在 src/main/resources 目录下,注意 数据库链接(数据库端口号、数据库名)、用户名和密码

(3)添加其他依赖
启动项目,我们还需要一些额外的依赖(lombok、druid、test),方便开发和测试,另外数据库的配置文件也添加一些额外配置
pom.xml文件
lomhok:可以帮助我们一键生成javaBean的set()、get()、toString()方法;
druid:使用阿里巴巴提供的连接池;
test:方便测试功能;

数据库的配置文件(application.properties)
开启驼峰支持:Java和MySQL的命名规范不同,如createTime对应的是MySQL中的create_time,开启此设置,可以自动匹配;
SQL日志:可以将执行的SQL语句打印在控制台中,方便我们排查SQL语句是否执行错误;

(4)准备数据库
创建数据库,注意数据库名和上面application.properties中配置的数据库名要一致
创建表,添加一些数据
create database mybatis; use mybatis; create table tb_stu( id int auto_increment primary key comment '序列号', name varchar(10) comment '姓名', gender varchar(2) comment '性别', age tinyint comment '年龄', create_time date comment '创建日期' ) comment '学生表'; insert into tb_stu values (null, '加缪', '男', 20, null), (null, '萨特', '男', 25, null), (null, '陀思妥耶夫斯基', '男', 30, '2023-06-08'), (null, '阿加莎克里斯蒂','女','27', null);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
(5)创建类
创建学生类(Student)
@Data、@NoArgsConstructor、@AllArgsConstructor,相当于自动为类添加了set()、get()、toString()、无参和全参构造方法
package com.essay.domain; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.time.LocalDate; /** * 学生类 */ @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private String gender; private Integer age; private LocalDate createTime; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
创建Mapper类
Mapper,是Dao层中,MyBatis的取名方式,也是Dao层的具体表现之一。
package com.essay.mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; @Mapper public interface StuMapper { /** * 访问数据库,处理数据 */ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
创建启动类(Start)
package com.essay; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Start { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Start.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
创建测试类(MyTest),模拟Controller层。本来应该注入Service层依赖,因为是介绍MyBatis,我这里直接注入Mapper(Dao层)依赖
package com.essay; import com.essay.mapper.StuMapper; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest public class MyTest { // 注入Mapper依赖 @Autowired private StuMapper stuMapper; // 接收前端请求,响应数据 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
另外,还需要注意两点:
a. 测试类的目录要与main中的启动类平行

b. 测试类的类名,不要取名为Test,因为测试的注解也是Test(@Test)
至此,环境搭建完成,可以开始紧张又刺激的开发了。
二、注解方式
注解方式,是将对数据库进行操作的SQL语句,写在Dao层的各个方法上。
(1)查找所有:
在MyTest(Controller层)中接收请求
@SpringBootTest public class MyTest { // 注入Mapper依赖 @Autowired private StuMapper stuMapper; /** * 查找所有 */ @Test public void findAll(){ List<Student> list = stuMapper.findAll(); System.out.println(list); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
在StuMapper(Dao层)中访问数据库,返回数据
@Mapper public interface StuMapper { /** * 查找所有 */ @Select("select * from tb_stu") List<Student> findAll(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

(2)添加数据:
在MyTest(Controller层)中接收请求
这里是我手动创建的对象,在正式业务中,数据会由前端传过来,封装成一个对象(需要使用@RequestParam注解),另外对象的创建时间会在Service层中设置,之后再传至Dao层写入数据库。
/** * 添加记录 */ @Test public void insertStu(){ Student s = new Student(); s.setName("伏尔泰"); s.setGender("男"); s.setAge(40); s.setCreateTime(LocalDate.now()); stuMapper.insertStu(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
在StuMapper(Dao层)中访问数据库,添加数据
#{},表示对象s中的对应的属性值,所以一定要注意,#{}里面的名称是对象里面的属性名,而不是数据库里面的字段名
/** * 添加记录 */ @Insert("insert into tb_stu(name,gender,age,create_time) value(#{name},#{gender},#{age},#{createTime})") void insertStu(Student s);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

(3)修改数据:
在MyTest(Controller层)中接收请求,同样,具体业务中,被修改的对象会被前端传过来,我这里是手动创建模拟修改
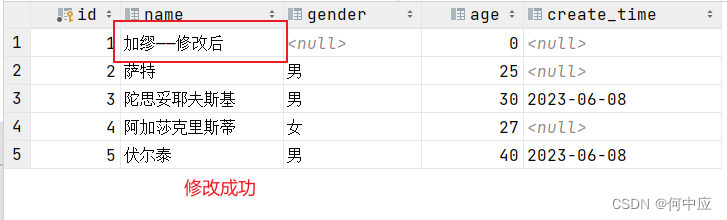
/** * 根据ID修改记录 */ @Test public void updateStu(){ Student s = new Student(); s.setId(1); s.setName("加缪——修改后"); stuMapper.updateStu(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
在StuMapper(Dao层)中访问数据库,修改数据
/** * 修改记录 */ @Update("update tb_stu set name=#{name},gender=#{gender},age=#{age} where id=#{id}") void updateStu(Student s);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这里,问题出现了,除了name,其他字段也被修改成了。这是因为传进来的对象,仅设置了name,其他属性未设置默认是null。那有没有一种方案,修改时判断对象的属性值是否为空,不为空说明需要修改此字段,则修改数据库中的数据;为空说明不需要修改此字段,那么数据库中就不修改,在xml方式中可以解决此问题(在修改之前,根据ID把数据库中的对象值先找出来,然后在Service层做逻辑判断,是否也可以解决?)。
(4)删除数据:
在MyTest(Controller层)中接收请求,我这里模拟删除ID是为1的记录
/** * 根据ID删除记录 */ @Test public void deleteStu(){ Integer id = 1; stuMapper.delete(id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
在StuMapper(Dao层)中访问数据库,删除数据
/** * 根据ID删除记录 */ @Delete("delete from tb_stu where id=#{id}") void delete(Integer id);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5


小结
以上展现了使用注解方式,对数据库进行查找所有、添加数据、根据ID修改和删除操作,如果还需要做条件查找、删除所有记录等功能,可以先写好SQL语句,根据SQL语句所需要的参数,再设计好Controller层的代码。
三、xml方式
除了注解方式,MyBatis还提供了xml的方式,将方法对应的SQL语句配置到xml文件中,通过方法调用,实现对数据操作。首先,创建好Mapper类对应的xml文件。
创建xml文件
创建xml文件,需要注意以下两点:
a. xml文件需要和Mapper类平行同包同名

b. 在Resource文件夹中创建多级目录,不能使用点(.),要用斜杠(/)


以上两点至关重要,这是xml文件与Mapper类建立联系的过程,联系建立不起来,程序跑不起来。
文件创建好之后,首先在xml文件开头添加约束,不要手敲,建议从官网复制过来(https://mybatis.net.cn/getting-started.html)

约束添加后,敲一个mapper标签,属性namaspace为Mapper类的全类名。同样,也不要手敲,点击类文件,快捷键ctrl+alt+shift+c,复制粘贴过来。

(1)查找所有:
在xml文件中配置查找所有方法
StuMapper.xml文件
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.essay.mapper.StuMapper"> <select id="findAll" resultType="com.essay.domain.Student"> select * from tb_stu; select> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
StuMapper类(前面写的注解删掉)
/** * 查找所有 */ List<Student> findAll();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
需要注意以下两点:
a. xml文件中标签id要与StuMapper类中的对应的方法名一致;
b. resultType为返回类型,即返回的数据,需要封装为对象的对象的类全名。

(2)添加数据:
在xml文件中配置添加数据方法
<insert id="insertStu"> insert into tb_stu(name,gender,age,create_time) value(#{name},#{gender},#{age},#{createTime}) insert>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
StuMapper类(前面写的注解删掉)
/** * 添加记录 */ void insertStu(Student s);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
MyTest(测试类)
/** * 添加记录 */ @Test public void insertStu(){ Student s = new Student(); s.setName("卢梭"); s.setGender("男"); s.setAge(20); s.setCreateTime(LocalDate.now()); stuMapper.insertStu(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

(3)修改数据:
前文说过使用注解方式修改数据的问题,修改指定字段的数据,因为传入Dao层的是一个新建的javaBean对象,未设置的属性,是null,修改数据库时会覆盖原数据。导致欲修改的字段,修改成功;未设置的字段,因为修改被置空。
使用xml方式,可以解决这个问题。使用if标签,判断传入的属性值是否为空,不为空说明是前端请求需要修改的字段,就修改;为空,说明是前端不需要修改的字段,就不修改。
StuMapper.xml文件(注意不要漏掉最后的where语句)
<update id="updateStu"> update tb_stu <set> <if test="name!=null and name!='' "> name=#{name}, if> <if test="gender!=null and gender!='' "> gender=#{gender}, if> /*因为age是Integer类型,仅判断不为null就行,下面的时间格式也是*/ <if test="age!=null" > age=#{age}, if> <if test="createTime!=null "> create_Time=#{createTime}, if> set> where id=#{id} update>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
StuMapper类(前面写的注解删掉)
/** * 修改记录 */ void updateStu(Student s);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
MyTest(测试类),测试只修改ID为1的姓名字段
/** * 根据ID修改记录 */ @Test public void updateStu(){ Student s = new Student(); s.setId(1); s.setName("加缪——修改后"); stuMapper.updateStu(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行程序,达到了预期结果。

需要注意以下两点
a. 不要在set标签里面写注释,程序执行时会把注释也当做SQL语句的内容的,所以程序会报错;

b. set标签里面的每一个修改语句,末尾都要加一个英文逗号(,)
(4)删除数据:
StuMapper.xml文件
<delete id="deleteStu"> delete from tb_stu where id=#{id} delete>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
StuMapper类(前面写的注解删掉)
/** * 根据ID删除记录 */ void deleteStu(Integer id);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
MyTest(测试类),测试删除ID为1的记录
/** * 根据ID删除记录 */ @Test public void deleteStu(){ Integer id = 1; stuMapper.deleteStu(id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8


小结
使用xml方式的where(条件查找)、set、if标签,可以完成一些复杂的SQL语句,另外,使用include标签,可以将重复的SQL语句抽取出来,给其他的语句复用。
如我们查询所有语句,使用全字段id,name,gender,age,create_time比使用*效率高,我们就可以把这部分抽出来。
<sql id="selectAll"> select id,name,gender,age,create_time sql> <select id="findAll" resultType="com.essay.domain.Student"> <include refid="selectAll">include> from tb_stu select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
需要注意,写在sql片段内的SQL语句末尾不要加分号(建议xml内的所有语句末尾都不要加分号)。因为分号表示语句结束,加了分号被其他操作引用时,其他语句操作都会失效。

总结
(1)如果执行过程中出现以下异常,排查方向如下:
空指针异常:(1)检查数据库配置文件;(2)检查依赖注入和控制反转相关的注解
SQL异常:检查注解和xml文件中的SQL语句是否有错误
(2)关于注解方式和xml方式的选择,在MyBatis中文官网(https://mybatis.net.cn/getting-started.html)中有段话,值得参考。

-
相关阅读:
网易易盾某 拼图验证码
Android NDK篇-C++之 线程、锁、条件变量与生产消费模型
复制CSDN代码的方式
conda
有2023最新的批量混剪软件的排名榜单吗?
leetcode刷题(122)——62. 不同路径
Linux操作系统网络模块
从零开始实现lmax-Disruptor队列(三)多线程消费者WorkerPool原理解析
财务数字化转型是什么?_光点科技
面试突击37:线程安全问题的解决方案有哪些?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42108331/article/details/131098492
