-
JUC系列(六) 线程池
📣 📣 📣 📢📢📢
☀️☀️你好啊!小伙伴,我是小冷。是一个兴趣驱动自学练习两年半的的Java工程师。
📒 一位十分喜欢将知识分享出来的Java博主⭐️⭐️⭐️,擅长使用Java技术开发web项目和工具
📒 文章内容丰富:覆盖大部分java必学技术栈,前端,计算机基础,容器等方面的文章
📒 如果你也对Java感兴趣,关注小冷吧,一起探索Java技术的生态与进步,一起讨论Java技术的使用与学习
✏️高质量技术专栏专栏链接: 微服务,数据结构,netty,单点登录,SSM ,SpringCloudAlibaba等
😝公众号😝 : 想全栈的小冷,分享一些技术上的文章,以及解决问题的经验
⏩当前专栏:JUC系列线程池
池化技术、
程序的运行 本质: 占用系统的资源 ! 优化资源的使用 =>池化技术
线程池,连接池,内存吃,对象池, 频繁的创建销毁 十分的浪费资源
线程池的好处:
- 降低资源的消耗
- 提高响应的速度
- 方面管理
线程的复用 可以控制最大并发数量,管理线程
三大方法
下图来自 阿里巴巴开发规约手册

代码实例
public class poolDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //单个线程 ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); // 创建一个固定的线程池大小 //ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //可以伸缩的 遇强则强 // ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); try { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Threadpool.execute(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=> ok"); }); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //线程池使用完毕 一定要关闭 Threadpool.shutdown(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
三大方法的创建代码
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); } public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); } public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
七大参数
七大参数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, //核心线程池大小 int maximumPoolSize,// 最大核心线程数大小 long keepAliveTime,// 超时了没有人调用就会释放 TimeUnit unit,// 超时单位 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,// 阻塞队列 ThreadFactory threadFactory, // 线程工厂,创建线程的 RejectedExecutionHandler handler// 拒绝策略 )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这七个参数分别有什么作用呢,思路图

手动创建线程池,不用封装好的方法,使用原生的线程池方法
ThreadPoolExecutor threadpool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), // 这个时候 举例子,银行的人满了 这种方式就是 不处理 抛出异常 new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
线程池四种拒绝策略
-
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() 银行的人满了 这种方式就是 不处理 抛出异常
执行效果

-
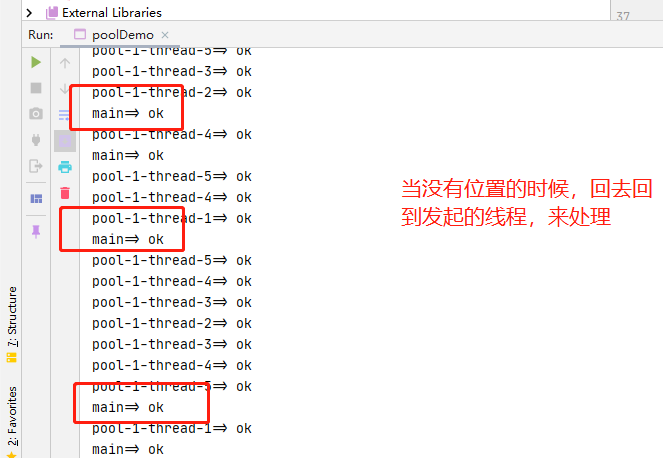
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() 银行人满了,哪里来的去哪里,回到调用线程输出,不会异常
执行结果
-
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() 队列满了 就抛出全部任务,
执行结果

-
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() 尝试和最早的线程竞争 查看是否有位置,没有就抛出任务
执行结果

代码实例
public class poolDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor threadpool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() ); //单个线程 //ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); // 创建一个固定的线程池大小 //ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //可以伸缩的 遇强则强 // ExecutorService Threadpool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); try { //最大承载如何计算 : 阻塞队列+max数量 //超过的话就会 爆出异常 :RejectedExecutionException for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) { threadpool.execute(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=> ok"); }); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //线程池使用完毕 一定要关闭 threadpool.shutdown(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
最大负载
-
CPU密集型 有几个核心就定义几个,可以保证效率最高
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() //获取cpu 核心数- 1
-
IO 密集型 判断程序中 十分消耗IO资源的线程,如: 程序 有 15个大型任务,io 十分占中资源,那么设定的比任务数量大 就可以保证一定性能、
-
相关阅读:
学习Opencv(蝴蝶书/C++)相关——1. 前言 和 第1章.概述
ASEMI整流桥26MT160参数,26MT160三相,26MT160插件
技术学习:Python(21)|爬虫篇|selenium自动化操作浏览器
java基础---static,多态,抽象类,接口,匿名内部类
前端面试系列之工程化篇
MATLAB算法实战应用案例精讲-【图像处理】机器视觉(补充篇)
Vue的mixins(混入)机制使用
2023下半年信息系统集成设计师案例
LeetCode 2407. 最长递增子序列 II
FPGA SERDESE2 (SDR收发仿真)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/doomwatcher/article/details/128153089
