-
WeetCode2滑动窗口系列
一丶[无重复字符的最长子串](3. 无重复字符的最长子串 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
维护一个窗口,窗口中不存在重复的字符,窗口右边界从第一个字符移动到最后,使用一个变量记录窗口大小的最大值
那么问题就变成了:怎么确保窗口中不存在重复的字符,我们可以使用一个set,每次发现right位置的字符A重复后,就一直移动到之前A字符位置的下一个。比如 BACDHA,此时right位于第二个A,set中包含字符BACDH,为了维持不重复,我们要将左边界移动到第一个C的位置,while循环让left右移,并删除left位置的字符,直到第一个A被删除
继续思考下,其实没必要使用一个set,直接使用一个map即可,map需要记录字符和这个字符
最近出现的位置,当前字符重复A的时候,就让left移动到A最近出现位置的前一个。比如BACDHA,此时right为A,map中记录了B->0,A->1等信息,我们只需要让left移动到1+1(A最近出现于下标1,left需要移动到2位置)然后再map中重新记录A->5即可代码:#
- public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
- //空字符串
- if(s==null||s.length()==0){
- return 0 ;
- }
- //窗口大小 最大值
- int res = 0;
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- int len = s.length();
- //key字符,value 这个字符最近在什么位置出现
- HashMap<Character,Integer> recentLocation = new HashMap<>();
- while(right<len){
- //当前子u发
- char curChar = s.charAt(right);
- //获取这个字符出现的位置
- Integer index = recentLocation.get(curChar);
- //如果不为null 说明这个字符曾经出现过 那么这时候需要 让left 移动
- if(index!=null){
- left = Math.max(index+1,left);
- }
- //记录下最近的位置
- recentLocation.put(curChar,right);
- right++;
- //窗口最大长度更新
- res = Math.max(res,right-left);
- }
- return res;
- }
二丶[最小覆盖子串](76. 最小覆盖子串 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
使用一个Map表示当前滑动串口亏欠t中字符的数量,
key 字符 value 当前窗口中亏欠的数目,亏欠的意思是当前窗口至少还需要多少个key的字符才满足t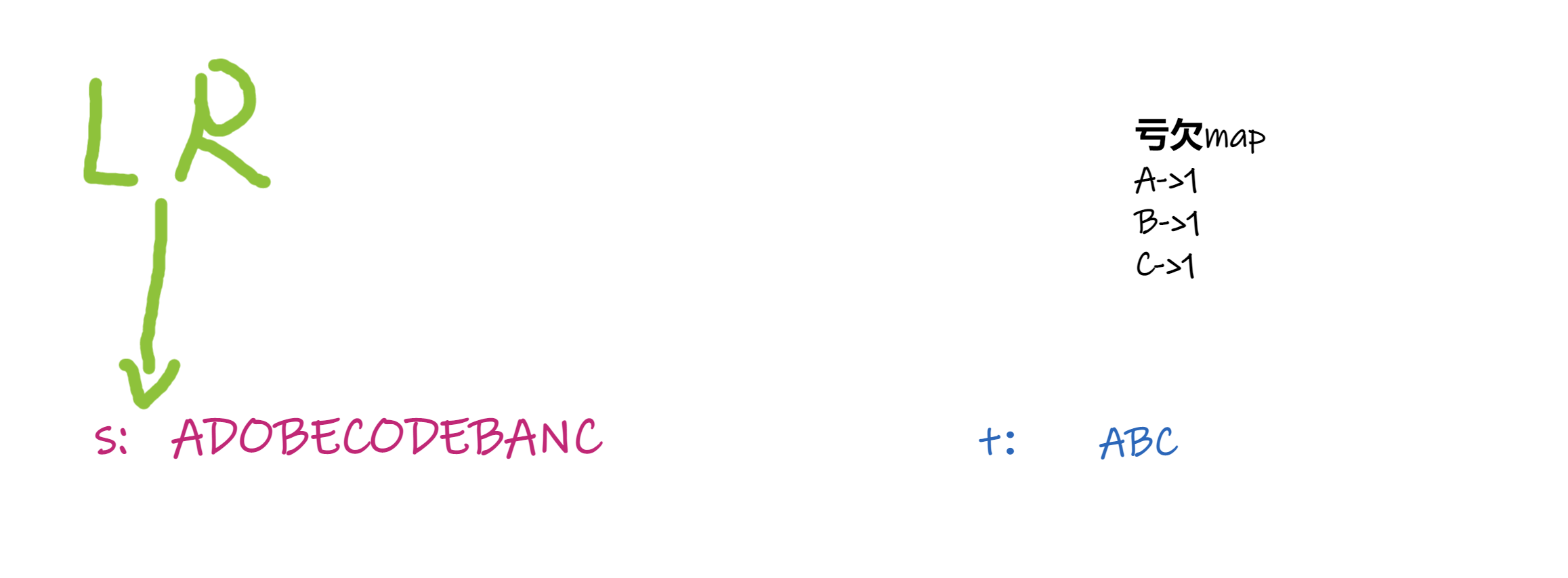
当left小于right的时候,我们尽可能让left向右滑动,那么什么时候left可以向右滑昵?——当前left是一个t中根本不存在的字符,或者窗口中left位置的字符数量大于t中的数量(对应下面两图)(这其实是有贪心的思想在其中的,题目是找最短的,那么left越接近right 那么越短)并且亏欠map需要同时维护


然后我们需要移动right指针,同时维护亏欠map
那么什么时候窗口中满足要求包含了t中所有字符昵——亏欠map中不存在value大于0的entry,这时候我们需要更新最佳结果
并且找到一个答案之后,我们需要left向右移动一个位置,并维护亏欠map,比如
s=ADOBECODEBANC,t=ABC我们第一次找到符合的结果是ADOBEC,这时候需要left向右,因为后面存在更优秀的答案。代码:#
- class Solution {
- public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
- //逆天用例
- if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
- return null;
- }
- if(s.length() < t.length()){
- return "";
- }
- char[] tCharArray = t.toCharArray();
- // key 字符 value 当前窗口中亏欠的数目,亏欠的意思是当前窗口至少还需要多少个key的字符才满足t
- // value 为正数 表示窗口欠 t,0表示互不亏欠,负数表示窗口中此字符数目多于t
- Map<Character, Integer> owesCharCountMap = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
- //初始化亏欠的数目
- for (char loop : tCharArray) {
- owesCharCountMap.put(loop, owesCharCountMap.getOrDefault(loop, 0) + 1);
- }
- String res = null;
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- while (right < s.length()) {
- //如果left对应字符是无关紧要的字符(t中不包含的字符)
- //或者left对应的字符那怕删掉 窗口中的字符也不会亏钱t中的字符
- //满足上面任意一点 那么 left++
- while (left < right && !isNecessary(left, s, owesCharCountMap)) {
- //当前left的字符
- char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
- left++;
- //当前窗口亏欠窗口中多少个
- Integer count = owesCharCountMap.get(leftChar);
- //如果不为null 说明leftChar 是t中的字符
- if (count != null) {
- //亏欠数++
- owesCharCountMap.put(leftChar, count + 1);
- }
- }
- //right位置的字符
- char rightChar = s.charAt(right);
- //right位置字符 窗口亏欠的数目
- Integer count = owesCharCountMap.get(rightChar);
- //right处字符是一个t中的字符 那么亏欠数-1
- if (count != null) {
- owesCharCountMap.put(rightChar, count - 1);
- }
- //如果窗口满足要求——指最起码不欠t中字符,及包含了所有t中的字符,那怕存在富足
- if (meetRequirementsOrNot(owesCharCountMap)) {
- //sub以下
- String tempRes = s.substring(left, right + 1);
- //记录
- if (res == null || tempRes.length() < res.length()) {
- res = tempRes;
- }
- //从窗口中 强制删除left位置处的字符
- //比如s=ADOBECODEBANC t = ABC 此时窗口中字符为ADOBEC 我们找到了一种结果,但是后续可能存在更好的答案
- //删除left位置的A 我们继续找更好的结果
- char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
- Integer leftCount = owesCharCountMap.get(leftChar);
- if (leftCount!=null){
- owesCharCountMap.put(leftChar,leftCount+1);
- }
- left++;
- }
- right++;
- }
- return res == null ? "" : res;
- }
- private boolean meetRequirementsOrNot(Map<Character, Integer> owesCharCountMap) {
- for (Integer v : owesCharCountMap.values()) {
- if (v == null) {
- continue;
- }
- if (v > 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- private boolean isNecessary(int left, String s, Map<Character, Integer> owesCharCountMap) {
- //left 位置的字符
- char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
- //当前亏欠map中的对应的亏欠数目
- Integer count = owesCharCountMap.get(leftChar);
- //为null 说明这个字符都不是t字符串中的字符 那么说明left位置的字符没必要存在于窗口中
- if (count == null) {
- return false;
- }
- //如果大于等于0 说明当前亏欠这个字符, 或者刚刚好,
- //如果移动那么窗口中的字符数将不够覆盖t中所有字符
- if (count >= 0) {
- return true;
- }
- //说明left处的字符不是必要的
- //说明 当前窗口中这个字符的数量已经大于t中这个字符的数量
- return false;
- }
- }
三丶[串联所有单词的子串](30. 串联所有单词的子串 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
我的思路其实和第二题一样,也是恢复一个亏欠map 然后进行滑动窗口,只是这个开始滑动的位置应该是1~单个单词长度这个范围都进行滑动窗口,这一点很关键。
然后我们需要处理两种情况
- 滑动窗口中包含了 words中不存在的单词 ,那么前功尽弃,我们需要从这个不存在单词的结尾继续滑动
- 滑动窗口中包含单词1的数量大于了words数组中单词1的数量,那么其实我们应该从第一个出现单词1位置的下一个位置开始滑动
这个题推荐看题解30. 串联所有单词的子串 - 力扣(Leetcode)我的解法并不是很优秀
代码:#
- class Solution {
- public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
- List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
- int singleWordLen = words[0].length();
- if (singleWordLen * words.length > s.length()) {
- return res;
- }
- //亏欠map
- Map<String, Integer> owensMap = new HashMap<>();
- for (String loop : words) {
- owensMap.put(loop, owensMap.getOrDefault(loop, 0) + 1);
- }
- int roundStartPos = 0;
- //从第一个位置开始 ,第二个位置开始 。。到单个单词长度个位置
- while (roundStartPos < singleWordLen) {
- Map<String, Integer> owensMapTemp = new HashMap<>(owensMap);
- int left = roundStartPos;
- int right = roundStartPos;
- //滑动窗口
- while (right <= s.length() - singleWordLen) {
- //left 位置的单词 不是必要的
- while (left < right && !isNecessary(left, singleWordLen, s, owensMapTemp)) {
- String temp = s.substring(left, left + singleWordLen);
- Integer count = owensMapTemp.get(temp);
- if (count != null) {
- owensMapTemp.put(temp, count + 1);
- }
- left += singleWordLen;
- }
- //right位置的单词
- String rightString = s.substring(right, right + singleWordLen);
- Integer count = owensMapTemp.get(rightString);
- //right位置的单词 是我们需要的 那么维护亏欠map
- if (count != null && count >= 1) {
- owensMapTemp.put(rightString, count - 1);
- right += singleWordLen;
- } else {
- //right 位置的单词 不是words数组中的单词 那么直接然后right 跨过这个单词,直接从下一个单词开始
- if (count == null) {
- right = right + singleWordLen;
- left = right;
- owensMapTemp = new HashMap<>(owensMap);
- } else {
- //right位置的单词是words数组中的单词 但是当前窗口中这个单词数量 已经 大于words数组中这个单词数量的单词
- //那么删除头部的第一个单词 然后继续,
- String temp = s.substring(left, left + singleWordLen);
- Integer tempCount = owensMapTemp.get(temp);
- if (tempCount != null) {
- owensMapTemp.put(temp, tempCount + 1);
- }
- left += singleWordLen;
- }
- }
- //符合要求 那么left 移动到下一个单词 并继续 找出所有答案
- if (meetRequire(owensMapTemp)) {
- res.add(left);
- String temp = s.substring(left, left + singleWordLen);
- Integer tempCount = owensMapTemp.get(temp);
- if (tempCount != null) {
- owensMapTemp.put(temp, tempCount + 1);
- }
- left += singleWordLen;
- }
- }
- roundStartPos++;
- }
- return res;
- }
- private boolean isNecessary(int left, int singleWordLen, String s, Map<String, Integer> owensMapTemp) {
- String temp = s.substring(left, left + singleWordLen);
- Integer count = owensMapTemp.get(temp);
- if (count == null) {
- return false;
- }
- if (count < 0) {
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
- private boolean meetRequire(Map<String, Integer> owensMapTemp) {
- for (Integer c : owensMapTemp.values()) {
- if (c == null) {
- continue;
- }
- if (c > 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
四丶[重复的DNA序列](187. 重复的DNA序列 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
这个题挺逆天的,很难想到怎么用滑动窗口做,使用2进制表示字母A,C,G,T,分别使用00,01,02,03,这样窗口滑动的时候就是第一个字母出去,意味着二进制表示左移位2,右边字符进来,使用位操作
代码:#
- class Solution {
- public List<String> findRepeatedDnaSequences(String s) {
- if(s == null || s.length()<=10){
- return new ArrayList<>();
- }
- List<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
- Map<Integer,Integer> memory = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
- int right = 0;
- int firstBi = 0;
- while(right<10){
- firstBi = (firstBi<<2)| binaryOf(s.charAt(right));
- right++;
- }
- memory.put(firstBi,1);
- while(right < s.length()){
- int bi = binaryOf(s.charAt(right));
- //左边字符出去 右边字符进来
- firstBi = ((firstBi<<2) |bi)&((1<<20)-1);;
- int count =memory.getOrDefault(firstBi,0)+1;
- memory.put(firstBi,count);
- if(count == 2){
- res.add(s.substring(right+1-10,right+1));
- }
- right++;
- }
- return res;
- }
- private int binaryOf(char a){
- if(a == 'A'){
- return 0;
- }
- if(a == 'C'){
- return 1;
- }
- if(a == 'G'){
- return 2;
- }
- if(a == 'T'){
- return 3;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- }
五丶[长度最小的子数组](209. 长度最小的子数组 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:太简单了,窗口描述当前子数据,使用sum记录当前和,如果大于target那么更新长度,如果减去左边界的值还能大于,那么left++。直到right到 数组边界
- class Solution {
- public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
- if(nums == null||nums.length == 0){
- return 0;
- }
- int left = 0;
- int right = 1;
- int sum =nums[0];
- int minLen = sum>target?1:0;;
- while(right<nums.length){
- sum +=nums[right];
- while(left<right && sum - nums[left]>=target){
- sum -= nums[left];
- left++;
- }
- if(sum>=target){
- if(minLen == 0||minLen>right-left+1){
- minLen = right - left+1;
- }
- }
- right++;
- }
- return minLen;
- }
- }
六丶[存在重复元素 II](219. 存在重复元素 II - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
维护一个长度为k的滑动窗口,使用set记录窗口中的数字,每次left位置的数据从窗口中出去,right位置的数进来,首先删除set中left代表的数字,然后如果right位置的数字存在于set中那么说明重复
代码:#
- public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
- if(nums == null || nums.length<=1){
- return false;
- }
- if(k == 0){
- return false;
- }
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- Set<Integer>memory = new HashSet<Integer>();
- while(right<k+1 && right<nums.length){
- if(!memory.add(nums[right])){
- return true;
- }
- right++;
- }
- while(right <nums.length){
- int newNum = nums[right];
- memory.remove(nums[left++]);
- right++;
- if(!memory.add(newNum)){
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
七丶[存在重复元素 III](220. 存在重复元素 III - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
思路和六类似,但是问题在于,我们如何快速的判断是否存在一个数,它和窗口中的数满足
abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= t,这时候我们应该想到TreeSet,基于红黑树进行如此的判断的速度是logN代码:#
- class Solution {
- public boolean containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(int[] nums, int indexDiff, int valueDiff) {
- if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- if (indexDiff == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>();
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- while (right < indexDiff + 1 && right < nums.length) {
- if (exist(ts,nums[right],valueDiff)){
- return true;
- }
- ts.add(nums[right]);
- right++;
- }
- while (right < nums.length) {
- ts.remove(nums[left++]);
- if (exist(ts,nums[right],valueDiff)){
- return true;
- }
- ts.add(nums[right++]);
- }
- return false;
- }
- private boolean exist(TreeSet<Integer> ts, int value, int diff) {
- //Set中是否 存在一个数A 满足 abs(A-value)<=diff
- //A>=value 最小的数 min 是否满足 min - value <= diff
- //A<=value 最大的数max 是否满足 value - max<= diff
- Integer min = ts.ceiling(value);
- if (min != null && min - value <= diff) {
- return true;
- }
- Integer max = ts.floor(value);
- if(max!=null&&value - max<=diff){
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
八丶[滑动窗口最大值](239. 滑动窗口最大值 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
窗口大小恒定为k大小,从头移动到尾巴,我们需要一种数据结构记录窗口此时的最大值,第一反应使用优先队列,入队时right位置的值,出队是left位置的值,但是这存在一个问题,如1,3,-1,3,2,2,k=3.当前窗口运动到1,【3,-1,3】,2,2 优先队列记录了3,-1紧接着left位置元素删除的时候会导致队列中只有一个1,随后right位置入队,队列维护了-1,2导致结构少了一个3。我们需要转变思想,队列每一个元素记录两个内容——值和对应的下标,当我们发生堆顶元素下标不在窗口中的时候进行删除。
上面优先队列的使用是整个复杂度来到NLogN,其实还有另外一个数据结构可以实现这个功能,单调栈——我们维护一个单调递减的栈,当j
代码:#
1.优先队列#
- public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
- //优先队列 维护滑动窗口中的最大值
- if(nums == null || nums.length < k ){
- return nums;
- }
- int[]res = new int[nums.length - k +1];
- //优先使用值进行比较,值越大越在堆顶
- //其次使用下标进行比较,下表越大越在堆顶,下标越大 活得越久
- PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((i,j)->i[0]!=j[0]?j[0]-i[0]:j[1]-i[1]);
- int right = 0;
- while(right<k){
- q.add(new int[]{nums[right],right});
- right++;
- }
- res[0] = q.peek()[0];
- int count = 1;
- while(right<nums.length){
- q.offer(new int[]{nums[right],right});
- while(q.peek()[1] <= right - k){
- q.poll();
- }
- right++;
- res[count++]=q.peek()[0];
- }
- return res;
- }
2.单调栈#
- public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
- if(nums == null ){
- return nums;
- }
- int[]res = new int[nums.length - k +1];
- //队列中的值是下标 但是必须保证这些下标值是单调递减的
- //当前 i<j nums[j]>=nums[i] 这时候num[i]对应下标 不需要维护了
- //说是单调栈其实是双向队列,因为我们需要看栈底元素
- LinkedList<Integer> ll = new LinkedList<Integer>();
- int right = 0;
- //初始化双端队列
- while(right < k){
- //nums[ll.getLast()] <= nums[right]
- //对应 1,2,3,4 k =3 初始化的时候 【1,2,3】4 这时候我们只需要维护3即可
- while(!ll.isEmpty() && nums[ll.getLast()] <= nums[right]){
- ll.removeLast();
- }
- ll.addLast(right);
- right++;
- }
- res[0] = nums[ll.getFirst()];
- int count = 1;
- while(right < nums.length){
- //同上
- while(!ll.isEmpty() && nums[ll.getLast()] <= nums[right]){
- ll.removeLast();
- }
- ll.addLast(right);
- //如果队列头 也就是最大的值 将不处于窗口外
- while(ll.getFirst() <= right-k){
- ll.removeFirst();
- }
- res[count++] = nums[ll.getFirst()];
- right++;
- }
- return res;
- }
九丶[找到字符串中所有字母异位词](438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
滑动窗口大小为p长度,使用一个map记录窗口中字符和对应的数量,当每种字符数量和p相同是,记录下left的位置,left++的时候更新map,right++的时候更新map
代码:#
- class Solution {
- public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
- if(s == null || s.length()<p.length()){
- return new ArrayList<>();
- }
- List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
- if(s.equals(p)){
- res.add(0);
- return res;
- }
- //记录p中的字符和对应的数量,因为都是小写字母,26长度的数组足以
- int[] pCharCount = new int[26];
- for(int i= 0; i<p.length();i++){
- char c = p.charAt(i);
- pCharCount[c-'a']++;
- }
- //记录窗口中字符和队友的数量
- int[] windowCharCount = new int[26];
- int left = 0 ;
- int right = 0;
- while(right<s.length()){
- //左边界++
- while(right - left + 1 > p.length()){
- windowCharCount[s.charAt(left)-'a']--;
- left++;
- }
- //右边界++
- windowCharCount[s.charAt(right)-'a']++;
- //字符和数目 和p一样
- if(meetRequire(pCharCount,windowCharCount)){
- res.add(left);
- }
- right++;
- }
- return res;
- }
- private boolean meetRequire(int[] pCharCount,int[] windowCharCount ){
- for(int i =0;i<26;i++){
- if(pCharCount[i]!=windowCharCount[i]){
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
十丶[替换后的最长重复字符](424. 替换后的最长重复字符 - 力扣(Leetcode))#

思路:#
维护一个窗口,我们需要保证窗口中的字符替换k次之后,都是相同的字符——字符总数-最大字符出现次数<=k
如果不满足这个条件 那么左边界++,直到满足
代码:#
- class Solution {
- public int characterReplacement(String s, int k) {
- if(s == null ){
- return 0;
- }
- if(s.length() <=k){
- return s.length();
- }
- int res = 0;
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- int[]charCount = new int[26];
- while(right<s.length()){
- charCount[s.charAt(right)-'A']++;
- while(!meetRequire(charCount,k)){
- charCount[s.charAt(left)-'A']--;
- left++;
- }
- res = Math.max(res,right - left+1);
- right++;
- }
- return res;
- }
- private boolean meetRequire(int[]charCount,int k){
- int max = -1;
- int sum = 0;
- for(int c : charCount){
- sum+=c;
- max = Math.max(max,c);
- }
- return sum-max<=k;
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
redisson常用api
项目经理如何做好跨部门沟通?
如何使用JMeter操作Elasticsearch
【MYSQL】表的增删改查
Word2Vec
2022-08-30 第五组 张明敏 学习笔记
【MicroPython ESP32】通过sdcard模块读取SD卡实例
交叉编译器arm-linux-gcc,aarch64-himix200-linux-gcc命令找不到 not found ,所有原因全方位解析
FOC程序cubemx配置-ADC配置
33岁程序员的年中总结
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jh035512/article/details/128109865
