-
java.lang.reflect.Field 解读
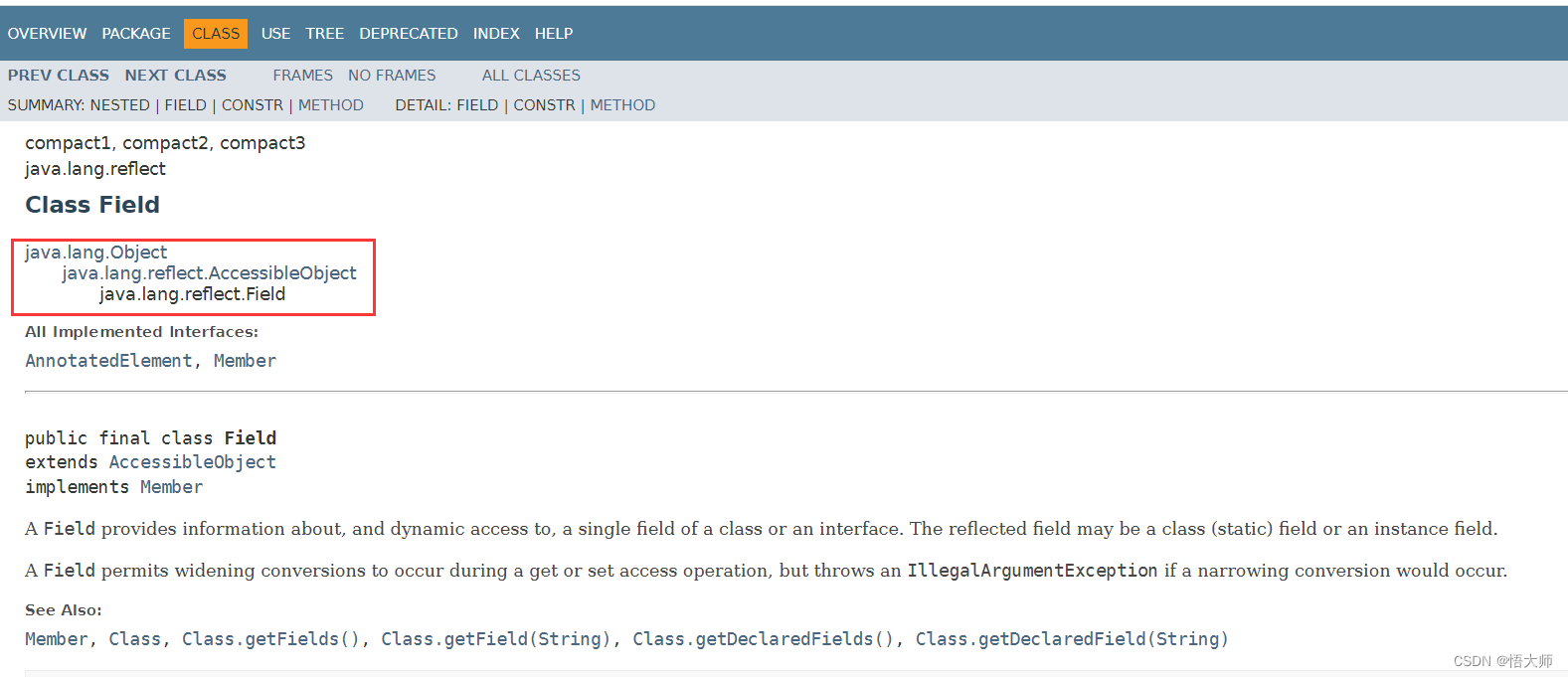
java.lang.reflect.Field
Java 中 Field 提供有关类或接口的单个字段的信息,以及对它的动态访问权限。反射的字段可能是一个类字段或实例字段。Field 是成员变量的意思。Field 也是一个类,该类位于
java.lang.reflect包下。https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/reflect/Field.html
-
获取变量的类型。
-
Field.getType():返回这个变量的类型。
-
Field.getGenericType():如果当前属性有签名属性类型就返回,否则就返回 Field.getType()。
-
isEnumConstant() : 判断这个属性是否是枚举类。
-
-
获取成员变量的修饰符。
- Field.getModifiers() : 以整数形式返回由此 Field 对象表示的字段的 Java 语言修饰符。
-
获取和修改成员变量的值。
-
getName() : 获取属性的名字。
-
get(Object obj) : 返回指定对象obj上此 Field 表示的字段的值。
-
set(Object obj, Object value) : 将指定对象变量上此 Field 对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值。
-
1. 获取field的类型
有两种方式可以获取到field的属性,
Field.getType()和Field.getGenericType(),其中getGenericType可以获取到泛型的标识符,如果这个field是泛型,则返回泛型的标识,如果不是泛型,这会转而调用getType获取到真正的类型,也就是Object。这里可以提一下,
Java里的泛型是假泛型,从字节码到可以执行文件的时候,已经把泛型擦除了,变成真正的类型,但是getType()调用时,并没有真正的类型代入,所以会返回所有的类的父类Object。我们举个例子:
public class FieldSpy<T> { public boolean[][] b = {{ false, false }, { true, true } }; public String name = "Alice"; public List<Integer> list; public T val; public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class<?> c = Class.forName(args[0]); Field f = c.getField(args[1]); System.out.format("Type: %s%n", f.getType()); System.out.format("GenericType: %s%n", f.getGenericType()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException x) { x.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchFieldException x) { x.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
执行命令以及执行结果:
$ java FieldSpy FieldSpy b Type: class [[Z GenericType: class [[Z $ java FieldSpy FieldSpy name Type: class java.lang.String GenericType: class java.lang.String $ java FieldSpy FieldSpy list Type: interface java.util.List GenericType: java.util.List<java.lang.Integer> $ java FieldSpy FieldSpy val Type: class java.lang.Object GenericType: T- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2. 检索和解析 Field 的修饰符
Field 的修饰符可以通过
public int getModifiers()方法获取,这个方法返回的是int型,代表意义可以参见修饰符,如果要判断一个 field 是否具有某个修饰符,可以通过位运算符&判断,比如判断一个 field 的修饰符是否有public属性:Field f = OneClass.getField("field"); int modify = f.getModifiers(); return modify&Modifier.PUBLIC == Modifier.PUBLIC- 1
- 2
- 3
可以看一个官方的例子:
enum Spy { BLACK , WHITE } public class FieldModifierSpy { volatile int share; int instance; class Inner {} public static void main(String... args) { try { Class<?> c = Class.forName(args[0]); int searchMods = 0x0; for (int i = 1; i < args.length; i++) { searchMods |= modifierFromString(args[i]); } Field[] flds = c.getDeclaredFields(); out.format("Fields in Class '%s' containing modifiers: %s%n", c.getName(), Modifier.toString(searchMods)); boolean found = false; for (Field f : flds) { int foundMods = f.getModifiers(); // Require all of the requested modifiers to be present if ((foundMods & searchMods) == searchMods) { out.format("%-8s [ synthetic=%-5b enum_constant=%-5b ]%n", f.getName(), f.isSynthetic(), f.isEnumConstant()); found = true; } } if (!found) { out.format("No matching fields%n"); } // production code should handle this exception more gracefully } catch (ClassNotFoundException x) { x.printStackTrace(); } } private static int modifierFromString(String s) { int m = 0x0; if ("public".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.PUBLIC; else if ("protected".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.PROTECTED; else if ("private".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.PRIVATE; else if ("static".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.STATIC; else if ("final".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.FINAL; else if ("transient".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.TRANSIENT; else if ("volatile".equals(s)) m |= Modifier.VOLATILE; return m; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
这个例子的大致意思是查找输入类名是否具有输入的修饰符的成员变量,并把成员变量名,并且输出其是否是编译器生成的和是否输入枚举变量。
输入输出:
$ java FieldModifierSpy FieldModifierSpy volatile Fields in Class 'FieldModifierSpy' containing modifiers: volatile share [ synthetic=false enum_constant=false ] $ java FieldModifierSpy Spy public Fields in Class 'Spy' containing modifiers: public BLACK [ synthetic=false enum_constant=true ] WHITE [ synthetic=false enum_constant=true ] $ java FieldModifierSpy FieldModifierSpy\$Inner final Fields in Class 'FieldModifierSpy$Inner' containing modifiers: final this$0 [ synthetic=true enum_constant=false ] $ java FieldModifierSpy Spy private static final Fields in Class 'Spy' containing modifiers: private static final $VALUES [ synthetic=true enum_constant=false ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 是否是编译器生成可以通过方法
field.isSynthetic()判断。 - 是否是枚举变量可以通过方法
field.isEnumConstant()判断。 - 是否是编译器我想很多人都明白,什么是编译器生成的成员变量呢?
- 比如枚举类型,每个枚举类型都有一个 VALUES 成员变量,这个变量我们并没有显式定义,但是可以通过它获取这个枚举类对应的所有没有常量,VALUES 就是编译器生成的。
2.1 Java 中冷门的 synthetic 关键字原理解读
看 JAVA 的反射时,看到有个
synthetic,还有一个方法isSynthetic()很好奇,就了解了一下:Any constructs introduced by a Java compiler that do not have a corresponding construct in the source code must be marked as synthetic, except for default constructors, the class initialization method, and the values and valueOf methods of the Enum class.- 1
大意为:由
java编译器生成的(除了像默认构造函数这一类的)方法,或者类2.1.1 例子
既然知道
synthetic 方法和synthetic类是由编译器生成的,那到底编译器会怎么生成这些东西,又在什么情况下会生成这些东西呢?先看一段代码:
import static java.lang.System.out; public final class DemonstrateSyntheticMethods { public static void main(final String[] arguments) { DemonstrateSyntheticMethods.NestedClass nested = new DemonstrateSyntheticMethods.NestedClass(); out.println("String: " + nested.highlyConfidential); } private static final class NestedClass { private String highlyConfidential = "Don't tell anyone about me"; private int highlyConfidentialInt = 42; private Calendar highlyConfidentialCalendar = Calendar.getInstance(); private boolean highlyConfidentialBoolean = true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
编译之后,可以看到三个文件:

其中,最下面的这个类文件很好解释,就是我们的主class,中间的文件,是我们的内部类,上面的文件,后面再讲,我们先看一下中间这个内部类
2.1.1.1 内部类的反编译结果
用
javap反编译DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$NestedClass.class,得到如下结果:javap DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$NestedClass.class Compiled from "DemonstrateSyntheticMethods.java" final class DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$NestedClass { DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$NestedClass(DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$1); static java.lang.String access$100(DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$NestedClass); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
先把构造函数放一边,我们来看这个标黑的方法
access$100这个是怎么回事呢?我们的源文件里找不到这个access方法啊?2.1.1.2 synthetic方法
这个方法就是编译器生成的
synthetic方法,读者不信的话,可以用method.isSynthetic()去验证一下。为何要生成这样一个方法呢?
可以看到,我们的
NestedClass类中,highConfidential是一个私有属性,而我们在外部类DemonstrateSyntheticMethods中,直接引用了这个属性。作为一个内部类,NestedClass的属性被外部类引用,在语义上毫无问题,但是这却苦了编译器。为了能让一个
private的变量被引用到,编译器生成了一个package scope的access方法,这个方法就是一个get方法,在外部类使用highConfidential这个属性时,实际是使用了这个access方法。在
javap中可以看到直接的证据: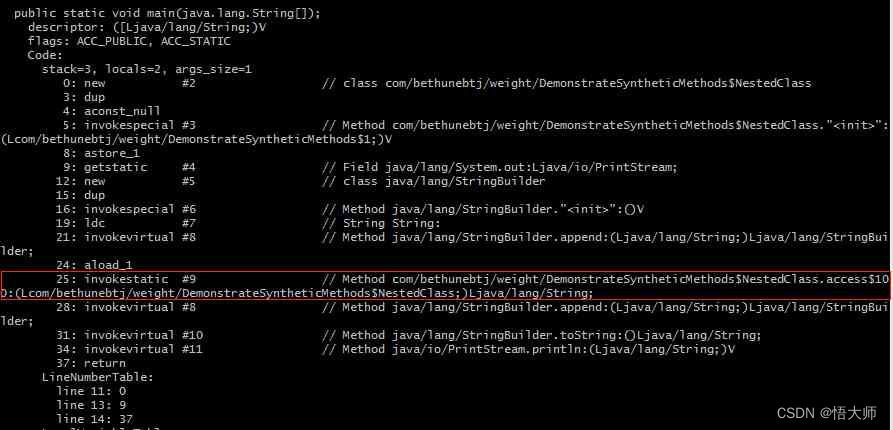
图中红框的位置,可以很清楚的看到
main方法实际上调用了access$100这个方法。所以,结论很清楚了,编译器为了方便内部类的私有成员被外部类引用,生成了一个
get方法,这可以被理解为一个trick,绕开了private成员变量的限制。2.1.1.3 synthetic类
定义已经提到,编译器不仅仅会生成方法,也会生成
synthetic类。我们回过头来看
2.1提到的最后一个类DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$1.class这个类是一个完全的空类,反编译后是这个样子:
// $FF: synthetic class class DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$1 { }- 1
- 2
- 3
这个类只出场了一次,作为内部类
NestedClass的package scope的构造函数,如图所示:
那么,这个类的作用呢?笔者查了很多资料,都没有明确的说明这个类的用途,只能根据代码做推测如下:
NestedClass作为一个private类,其默认构造函数也是private的。那么,事实上,作为外部类的DemonstrateSyntheticMethods类,没有办法new这个内部类的对象,而这和我们需要的语义相违背。那么,为了实现语义,编译器又用了一个
trick,悄悄的生成了一个构造函数NestedClass(DemonstrateSyntheticMethods$1 obj),这个构造函数是包可见的。3. 检索Field的注解
获取所有的注解可以用
field.getDeclaredAnnotations()方式。获取单个的可以用:
- getAnnotatedType()
- getAnnotation(Class annotationClass)
- getAnnotationsByType(Class annotationClass)
实际上这几个方法都是从
class java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject继承而来的,这里就不做详细介绍了。4. 设置和获取Field的值
set(Object obj, Object value)来设置Field,除了这个方式还有多种确定Field类型的方式,比如void setDouble(Object obj, double d)Object get(Object obj)来获取Field的值,和set方法一直,get方法也有多种确定Field类型的方式,比如double getDouble(Object obj)。以上方法都可能抛出
NoSuchFieldException和IllegalAccessException异常。官方文档上有一句话是这样说的:因为这种访问通常违反了该类的设计意图,因此应尽可能谨慎的使用它。前面就讲过,反射是破坏封装性的,违反的类的设计原则,所以能少用就少用。这里要提一下
setXXXX()内部如果是基础类型时要小心,这个方法不会进行装箱和拆箱操作,因为装箱和拆箱操作是编译器做的,运行时,JVM并不能做这个事情。比如下面的例子就会抛出异常。public class FieldTrouble { public Integer val; public static void main(String... args) { FieldTrouble ft = new FieldTrouble(); try { Class<?> c = ft.getClass(); Field f = c.getDeclaredField("val"); f.setInt(ft, 42); // IllegalArgumentException } catch (NoSuchFieldException x) { x.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException x) { x.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Can not set java.lang.Integer field reflect.FieldTrouble.val to (int)42 at sun.reflect.UnsafeFieldAccessorImpl.throwSetIllegalArgumentException(UnsafeFieldAccessorImpl.java:167) at sun.reflect.UnsafeFieldAccessorImpl.throwSetIllegalArgumentException(UnsafeFieldAccessorImpl.java:191) at sun.reflect.UnsafeObjectFieldAccessorImpl.setInt(UnsafeObjectFieldAccessorImpl.java:114) at java.lang.reflect.Field.setInt(Field.java:949) at reflect.FieldTrouble.main(FieldTrouble.java:14)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
做set方式之前可以通过
isAssignableFrom方法来进行检测,检测之后再进行处理:Integer.class.isAssignableFrom(int.class) == false; int.class.isAssignableFrom(Integer.class) == false- 1
- 2
另外,final 标识的成员变量是不能用set方法重新设置其值的,会抛出
IllegalAccessException异常。 -
-
相关阅读:
python-矩阵加法(赛氪OJ)
嵌入式Linux C进程间通信——IPC概述和信号
基于Springboot+Vue的社区医院管理系统
分闸合闸电源监视继电器JZZS-1120/DC220V
linux0.11-文件系统
基于Siamese网络的zero-shot意图分类
路由的hash模式和history模式(适用于3.x版本的vue-router)
go 语言 负载均衡 为反向代理添加负载均衡 拓展ReverseProxy
2023考研常识之学硕和专硕哪个更好,有哪些不同?
渗透实战靶机2wp
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46371399/article/details/128060600