-
Pytorch 中Label Smoothing CrossEntropyLoss实现
一. 前言
一般情况下我们都是直接调用Pytorch自带的交叉熵损失函数计算loss,但涉及到魔改以及优化时,我们需要自己动手实现loss function,在这个过程中如果能对交叉熵损失的代码实现有一定的了解会帮助我们写出更优美的代码。
其次是标签平滑这个trick通常简单有效,只需要改改损失函数既可带来性能上的提升,通常与交叉熵配合食用。
因此,本文基于这两个出发点,介绍基于Pytorch框架下的交叉熵损失实现以及标签平滑的实现。
二. CrossEntropyLoss
相信大家对于如何计算交叉熵已经非常熟悉,常规步骤是①计算softmax得到各类别置信度;②计算交叉熵损失。但其实从Pytorch的官方文档可以看出,还有更一步到位的方法,如下:
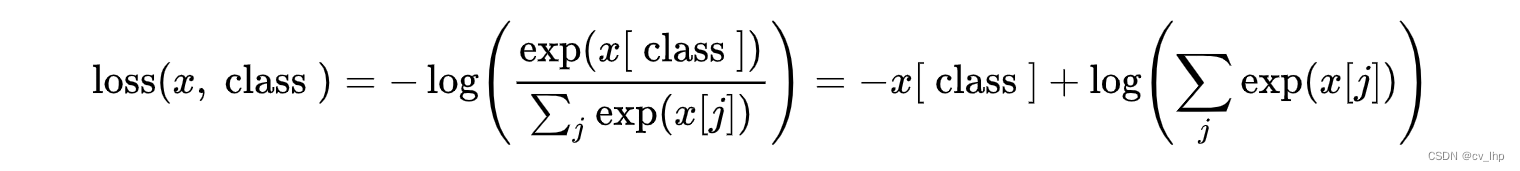
这避免了softmax的计算。三. 代码实现
class CELoss(nn.Module): ''' Cross Entropy Loss''' def __init__(self): super().__init__() def forward(self, pred, target): ''' Args: pred: prediction of model output [N, M] target: ground truth of sampler [N] ''' eps = 1e-12 # standard cross entropy loss loss = -1.*pred.gather(1, target.unsqueeze(-1)).reshape(-1,1) + torch.log(torch.exp(pred+eps).sum(dim=1)).reshape(-1,1) return loss.mean()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
具体细节参考我前面的文章 Pytorch中CrossEntropyLoss()详解。
四. Label Smoothing
Label Smoothing也称之为标签平滑,其实是一种防止过拟合的正则化方法。传统的分类loss采用softmax loss,先对全连接层的输出计算softmax,视为各类别的置信度概率,再利用交叉熵计算损失。


在这个过程中尽可能使得各样本在正确类别上的输出概率为1,这要使得对应的z值为+∞,这拉大了其与其他类别间的距离。
现在假设一个多分类任务标签是[1,0,0],如果它本身的label的出现了问题,这对模型的伤害是非常大的,因为在训练的过程中强行学习一个非本类的样本,并且让其概率非常高,这会影响对后验概率的估计。并且有时候类与类之间的并不是毫无关联,如果鼓励输出的概率间相差过大,这会导致一定程度上的过拟合。
因此Label Smoothing的想法是让目标不再是one-hot标签,而是变为如下形式:

其中ε为一个较小的常数,这使得softmax损失中的概率优目标不再为1和0,同时z值的最优解也不再是正无穷大,而是一个具体的数值。这在一定程度上避免了过拟合,也缓解了错误标签带来的影响。五. Label Smoothing CrossEntropyLoss实现
基于上一节的交叉熵实现增加标签平滑功能,代码如下:
class CELoss(nn.Module): ''' Cross Entropy Loss with label smoothing ''' def __init__(self, label_smooth=None, class_num=137): super().__init__() self.label_smooth = label_smooth self.class_num = class_num def forward(self, pred, target): ''' Args: pred: prediction of model output [N, M] target: ground truth of sampler [N] ''' eps = 1e-12 if self.label_smooth is not None: # cross entropy loss with label smoothing logprobs = F.log_softmax(pred, dim=1) # softmax + log target = F.one_hot(target, self.class_num) # 转换成one-hot # label smoothing # 实现 1 # target = (1.0-self.label_smooth)*target + self.label_smooth/self.class_num # 实现 2 # implement 2 target = torch.clamp(target.float(), min=self.label_smooth/(self.class_num-1), max=1.0-self.label_smooth) loss = -1*torch.sum(target*logprobs, 1) else: # standard cross entropy loss loss = -1.*pred.gather(1, target.unsqueeze(-1)).reshape(-1,1) + torch.log(torch.exp(pred+eps).sum(dim=1)).reshape(-1,1) return loss.mean()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
实现1采用了 (1.0-self.label_smooth)*target +self.label_smooth/self.class_num 实现,与原始公式不太一样。
后续在了解到pytorch的clamp接口后,发现能够利用其能正确实现原公式,见实现2。六. 试验验证
① 交叉熵损失正确率,与标准的交叉熵比较:
loss1 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() loss2 = CELoss(label_smooth=None, class_num=3) x = torch.tensor([[1, 8, 1], [1, 1, 8]], dtype=torch.float) y = torch.tensor([1, 2]) print(loss1(x, y), loss2(x, y)) # tensor(0.0018) tensor(0.0018)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
② 标签平滑结果展示:
loss1 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() loss2 = CELoss(label_smooth=0.05, class_num=3) x = torch.tensor([[1, 8, 1], [1, 1, 8]], dtype=torch.float) y = torch.tensor([1, 2]) print(loss1(x, y), loss2(x, y)) # tensor(0.0018) tensor(0.2352)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
另一组结果:
x = torch.tensor([[0.1, 8, 0.1], [0.1, 0.1, 8]], dtype=torch.float) y = torch.tensor([1, 2]) print(loss1(x, y), loss2(x, y)) # tensor(0.0007) tensor(0.2641)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
分析:拉大模型输出数值间的差距后,原始的交叉熵会变小,而增加了标签平滑的反而变大。这也反映了标签平滑后,并不是概率越接近于1越好,而是接近某个小于1的值,这使得模型的输出不再是越高(+∞)越好。
七. 参考链接
-
相关阅读:
使用express连接MySQL数据库编写基础的增、删、改、查、分页等接口
Spring-aop +redssion 实现接口限流注解
Java零基础入门-关系运算符
《在线编程-Python篇》Python入门 01 输入输出
python3中 三个点是啥意思?
SaaSBase:什么是小裂变SCRM?
分布式事务与分布式锁区别及概念学习
【广州华锐互动】智能家居设计3D虚拟还原系统
Java延迟队列——DelayQueue
什么是列间空调?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/flyingluohaipeng/article/details/128060040
