-
程序验证Jackson反序列化的规则、Jackson序列化与反序列化关键方法程序详细分析
目录
1. Jackson反序列化时,无参构造、有参构造的执行顺序【附程序截图】
2. Jackson反序列化时,无参构造、有参构造的执行顺序的总结
3.1 public T readValue(String content, Class valueType)
3.1.1 public JsonParser createParser(String content) throws IOException, JsonParseException
3.1.2 public JavaType constructType(Type type)
3.1.3 protected JavaType _fromAny(ClassStack context, Type type, TypeBindings bindings)
3.1.4 protected JavaType _fromClass(ClassStack context, Class rawType, TypeBindings bindings)
3.2 protected Object _readMapAndClose(JsonParser p0, JavaType valueType)【重要方法】
3.2.4 buildBeanDeserializer 中的 addBeanProps
3.2.5 public Object deserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException
3.2.6 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.BeanDeserializer#vanillaDeserialize
java.lang.reflect.Constructor#newInstance
3.2.7 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.impl.MethodProperty#deserializeAndSet
3.2.8 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.NumberDeserializers.IntegerDeserializer#deserialize
3.2.9 com.fasterxml.jackson.core.base.ParserBase#getIntValue
3.2.10 java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
0. 为什么要做这个分析
这个反序列化一般都不会出问题,但是但是但是,墨菲定理,在实习中发现了一年前的代码存在有关反序列化的问题;
具体是原本场景就是直接读数据库,可通过Jackson反序列化读出来的数据,竟然和数据库中的不一样;
所以就针对Jackson反序列化的规则以及源码进行分析
1. Jackson反序列化时,无参构造、有参构造的执行顺序【附程序截图】
1.1 没有无参构造时:
- 如果有参构造的参数全,或者更多(就是有不存在的值),这样还能正常运行:
-
如果参数不全则直接异常:
-
1.2 无参构造和有参构造方法都有的时候先走无参构造;
-
无参构造需要set/get方法来完成序列化和反序列化
- 下图是有无参构造但是没有对应的set/get方法的程序截图,可以看出,age并没有成功读取2;
-
-
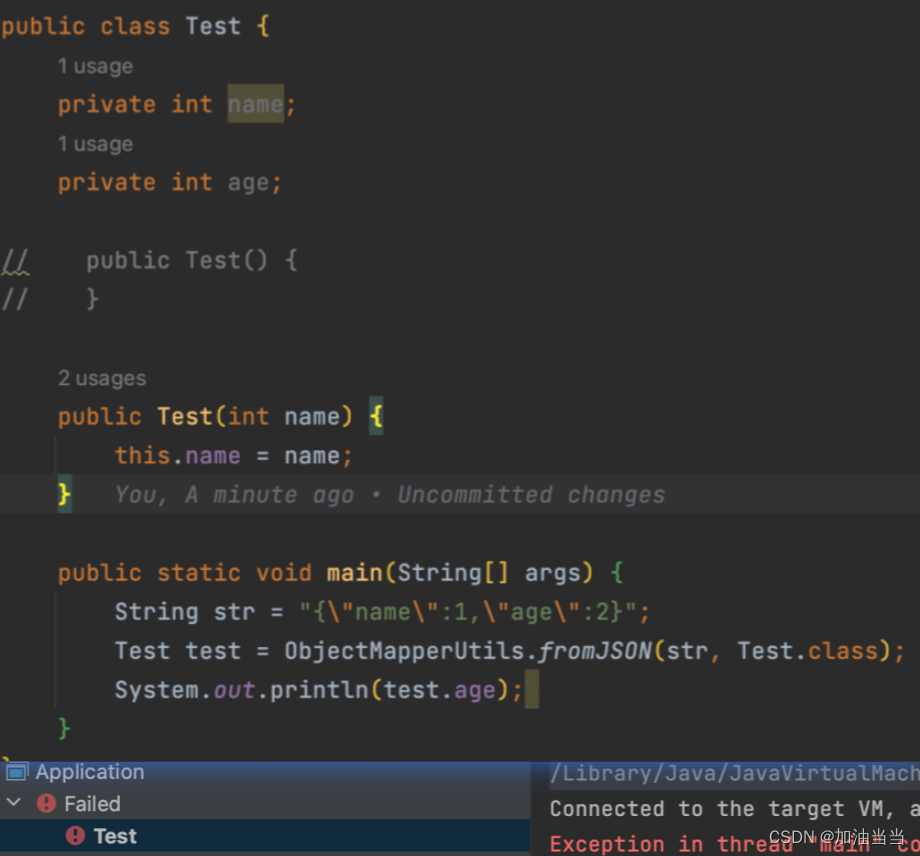
下图是有无参构造且有对应的set/get方法的程序截图,可以看出,age成功读取2;
-
- 下图是有无参构造但是没有对应的set/get方法的程序截图,可以看出,age并没有成功读取2;
2. Jackson反序列化时,无参构造、有参构造的执行顺序的总结
- 没有无参构造时:
- 如果有参构造的参数全,或者更多(就是有不存在的值),这样还能正常运行
- 如果参数不全则直接异常
- 无参构造和有参构造方法都有的时候先走无参构造;
- 无参构造需要set/get方法来完成序列化和反序列化
3. Jackson序列化与反序列化关键方法程序详细分析
3.1 public
T readValue(String content, Class valueType) - readValue
- 从给定的 JSON 内容字符串反序列化 JSON 内容的方法
- 抛出异常:
- IOException – 如果发生低级 IO 问题(意外的输入结束、网络错误)(按原样传递而无需额外包装——请注意,这是 DeserializationFeature.WRAP_EXCEPTIONS 不会导致包装异常的一种情况,即使如果启用)
- DeserializationFeature.WRAP_EXCEPTIONS :确定杰克逊代码是否应捕获和包装异常(但绝不是错误!)以添加有关问题位置(在输入内)的附加信息的功能。如果启用,大多数异常将被捕获并重新抛出(特别是 java.io.IOExceptions 可以按原样传递,因为它们被声明为可抛出);这很方便,因为所有异常都将被检查和声明,因此有更多的上下文信息。但是,有时调用应用程序可能只想按原样传递“原始”未经检查的异常。功能默认启用。
- JsonParseException - 如果基础输入包含 JsonParser 支持的类型的无效内容(默认情况下为 JSON)
- JsonMappingException - 如果输入 JSON 结构与结果类型的预期结构不匹配(或有其他不匹配问题)
- readValue源码:
- /**
- * Method to deserialize JSON content from given JSON content String.
- *
- * @throws IOException if a low-level I/O problem (unexpected end-of-input,
- * network error) occurs (passed through as-is without additional wrapping -- note
- * that this is one case where {@link DeserializationFeature#WRAP_EXCEPTIONS}
- * does NOT result in wrapping of exception even if enabled)
- * @throws JsonParseException if underlying input contains invalid content
- * of type {@link JsonParser} supports (JSON for default case)
- * @throws JsonMappingException if the input JSON structure does not match structure
- * expected for result type (or has other mismatch issues)
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public
T readValue(String content, Class valueType) - throws IOException, JsonParseException, JsonMappingException
- {
- return (T) _readMapAndClose(_jsonFactory.createParser(content), _typeFactory.constructType(valueType));
- }
3.1.1 public JsonParser createParser(String content) throws IOException, JsonParseException
- createParser:
- 构造解析器以解析给定字符串内容的方法;
- 将String生成一个Paser对象,用于后面的解析;
- createParser源码:
- /**
- * Method for constructing parser for parsing
- * contents of given String.
- *
- * @since 2.1
- */
- public JsonParser createParser(String content) throws IOException, JsonParseException {
- final int strLen = content.length();
- // Actually, let's use this for medium-sized content, up to 64kB chunk (32kb char)
- if ((_inputDecorator != null) || (strLen > 0x8000) || !canUseCharArrays()) {
- // easier to just wrap in a Reader than extend InputDecorator; or, if content
- // is too long for us to copy it over
- return createParser(new StringReader(content));
- }
- IOContext ctxt = _createContext(content, true);
- char[] buf = ctxt.allocTokenBuffer(strLen);
- content.getChars(0, strLen, buf, 0);
- return _createParser(buf, 0, strLen, ctxt, true);
- }
3.1.2 public JavaType constructType(Type type)
- _typeFactory.constructType(valueType):
- 通过传⼊的第⼆个参数,即Target类对象获取⼀个Type对象;
- 简要流程:
- 它⾸先⾸先会从缓存尝试获取该Class对应的Type,缓存中有这个数据的前提是,这个objectMapper前有对这个Class进⾏过序列化,之后会经过⼀系列的判断,这些判断包括判断它的Class是否属于某些特殊的Class(Map,Collection,AtomicReference)以及判断这个Class是否是Interface,这些判断在我上⾯的代码中都不成⽴,最终会通过 _newSimpleType ⽅法来创建⼀个Type对象。
- 这个创建的Type记录了Class、superClass等信息;
- constructType源码:
- public JavaType constructType(Type type) {
- return _fromAny(null, type, EMPTY_BINDINGS);
- }
3.1.3 protected JavaType _fromAny(ClassStack context, Type type, TypeBindings bindings)
- _fromAny
- 如果类型信息作为从 getGenericXxx 方法返回的 Java 类型传递(通常用于返回或参数类型),则可以使用工厂方法;
- 根据type的各种不同类型来获取相应的值;
- _fromAny源码:
- /**
- * Factory method that can be used if type information is passed
- * as Java typing returned from
getGenericXxxmethods - * (usually for a return or argument type).
- */
- protected JavaType _fromAny(ClassStack context, Type type, TypeBindings bindings)
- {
- JavaType resultType;
- // simple class?
- if (type instanceof Class) {
- // Important: remove possible bindings since this is type-erased thingy
- resultType = _fromClass(context, (Class) type, EMPTY_BINDINGS);
- }
- // But if not, need to start resolving.
- else if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
- resultType = _fromParamType(context, (ParameterizedType) type, bindings);
- }
- else if (type instanceof JavaType) { // [databind#116]
- // no need to modify further if we already had JavaType
- return (JavaType) type;
- }
- else if (type instanceof GenericArrayType) {
- resultType = _fromArrayType(context, (GenericArrayType) type, bindings);
- }
- else if (type instanceof TypeVariable) {
- resultType = _fromVariable(context, (TypeVariable) type, bindings);
- }
- else if (type instanceof WildcardType) {
- resultType = _fromWildcard(context, (WildcardType) type, bindings);
- } else {
- // sanity check
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unrecognized Type: "+((type == null) ? "[null]" : type.toString()));
- }
- // 21-Feb-2016, nateB/tatu: as per [databind#1129] (applied for 2.7.2),
- // we do need to let all kinds of types to be refined, esp. for Scala module.
- if (_modifiers != null) {
- TypeBindings b = resultType.getBindings();
- if (b == null) {
- b = EMPTY_BINDINGS;
- }
- for (TypeModifier mod : _modifiers) {
- JavaType t = mod.modifyType(resultType, type, b, this);
- if (t == null) {
- throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
- "TypeModifier %s (of type %s) return null for type %s",
- mod, mod.getClass().getName(), resultType));
- }
- resultType = t;
- }
- }
- return resultType;
- }
3.1.4 protected JavaType _fromClass(ClassStack context, Class rawType, TypeBindings bindings)
- _fromClass
- 参数:绑定——将形式参数声明(对于泛型类型)映射到实际类型;
- 会经过⼀系列的判断,这些判断包括判断它的Class是否属于某些特殊的Class(Map,Collection,AtomicReference)以及判断这个Class是否是Interface,这些判断在我上⾯的代码中都不成⽴,最终会通过 _newSimpleType ⽅法来创建⼀个Type对象。

- 这个创建的Type记录了Class、superClass等信息;
- _fromClass源码:
- /**
- * @param bindings Mapping of formal parameter declarations (for generic
- * types) into actual types
- */
- protected JavaType _fromClass(ClassStack context, Class rawType, TypeBindings bindings)
- {
- // Very first thing: small set of core types we know well:
- JavaType result = _findWellKnownSimple(rawType);
- if (result != null) {
- return result;
- }
- // Barring that, we may have recently constructed an instance
- final Object key;
- if ((bindings == null) || bindings.isEmpty()) {
- key = rawType;
- } else {
- key = bindings.asKey(rawType);
- }
- result = _typeCache.get(key); // ok, cache object is synced
- if (result != null) {
- return result;
- }
- // 15-Oct-2015, tatu: recursive reference?
- if (context == null) {
- context = new ClassStack(rawType);
- } else {
- ClassStack prev = context.find(rawType);
- if (prev != null) {
- // Self-reference: needs special handling, then...
- ResolvedRecursiveType selfRef = new ResolvedRecursiveType(rawType, EMPTY_BINDINGS);
- prev.addSelfReference(selfRef);
- return selfRef;
- }
- // no, but need to update context to allow for proper cycle resolution
- context = context.child(rawType);
- }
- // First: do we have an array type?
- if (rawType.isArray()) {
- result = ArrayType.construct(_fromAny(context, rawType.getComponentType(), bindings),
- bindings);
- } else {
- // If not, need to proceed by first resolving parent type hierarchy
- JavaType superClass;
- JavaType[] superInterfaces;
- if (rawType.isInterface()) {
- superClass = null;
- superInterfaces = _resolveSuperInterfaces(context, rawType, bindings);
- } else {
- // Note: even Enums can implement interfaces, so cannot drop those
- superClass = _resolveSuperClass(context, rawType, bindings);
- superInterfaces = _resolveSuperInterfaces(context, rawType, bindings);
- }
- // 19-Oct-2015, tatu: Bit messy, but we need to 'fix' java.util.Properties here...
- if (rawType == Properties.class) {
- result = MapType.construct(rawType, bindings, superClass, superInterfaces,
- CORE_TYPE_STRING, CORE_TYPE_STRING);
- }
- // And then check what flavor of type we got. Start by asking resolved
- // super-type if refinement is all that is needed?
- else if (superClass != null) {
- result = superClass.refine(rawType, bindings, superClass, superInterfaces);
- }
- // if not, perhaps we are now resolving a well-known class or interface?
- if (result == null) {
- result = _fromWellKnownClass(context, rawType, bindings, superClass, superInterfaces);
- if (result == null) {
- result = _fromWellKnownInterface(context, rawType, bindings, superClass, superInterfaces);
- if (result == null) {
- // but if nothing else, "simple" class for now:
- result = _newSimpleType(rawType, bindings, superClass, superInterfaces);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- context.resolveSelfReferences(result);
- // 16-Jul-2016, tatu: [databind#1302] is solved different way, but ideally we shouldn't
- // cache anything with partially resolved `ResolvedRecursiveType`... so maybe improve
- if (!result.hasHandlers()) {
- _typeCache.putIfAbsent(key, result); // cache object syncs
- }
- return result;
- }
3.2 protected Object _readMapAndClose(JsonParser p0, JavaType valueType)【重要方法】
- _readMapAndClose:
- 调用_initForReading方法,以确保给定的解析器已准备好读取数据绑定的内容;
- 进入START_OBJECT的解析,标识开始解析还原一个对象,要还原一个对象要获取这个JSON串对应的Deserializer,最终调用Deserializer#deserilize还原对象:
- 调用_initForReading方法,以确保给定的解析器已准备好读取数据绑定的内容;
- _readMapAndClose源码:
- protected Object _readMapAndClose(JsonParser p0, JavaType valueType)
- throws IOException
- {
- try (JsonParser p = p0) {
- Object result;
- JsonToken t = _initForReading(p, valueType);
- final DeserializationConfig cfg = getDeserializationConfig();
- final DeserializationContext ctxt = createDeserializationContext(p, cfg);
- if (t == JsonToken.VALUE_NULL) {
- // Ask JsonDeserializer what 'null value' to use:
- result = _findRootDeserializer(ctxt, valueType).getNullValue(ctxt);
- } else if (t == JsonToken.END_ARRAY || t == JsonToken.END_OBJECT) {
- result = null;
- } else {
- JsonDeserializer
- if (cfg.useRootWrapping()) {
- result = _unwrapAndDeserialize(p, ctxt, cfg, valueType, deser);
- } else {
- result = deser.deserialize(p, ctxt);
- }
- ctxt.checkUnresolvedObjectId();
- }
- if (cfg.isEnabled(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_TRAILING_TOKENS)) {
- _verifyNoTrailingTokens(p, ctxt, valueType);
- }
- return result;
- }
- }
3.2.1 protected DefaultDeserializationContext createDeserializationContext(JsonParser p, DeserializationConfig cfg)
- createDeserializationContext
- 调用内部辅助方法以创建 DeserializationContext 的实例以反序列化单个根值。如果需要自定义上下文,可以覆盖。
- 依据配置和json串对应的paser获取上下文context,这些信息包括下图,用于解析;
- 可以看到 inputBuffer 中已经缓存了待反序列化的json串
- createDeserializationContext源码:
- protected DefaultDeserializationContext createDeserializationContext(JsonParser p,
- DeserializationConfig cfg) {
- return _deserializationContext.createInstance(cfg, p, _injectableValues);
- }
3.2.2 protected JsonDeserializer
- _findRootDeserializer
- 调用方法来定位传递的根级值的反序列化器。
- 尝试从根节点去获取 反序列化器 ,类似于缓存的操作;
- 因是第⼀次获取 反序列化器 ,所以从根节点取不到;
- 然后进入 findRootValueDeserializer 获取 Deserializer;

- _findRootDeserializer源码:
- /**
- * Method called to locate deserializer for the passed root-level value.
- */
- protected JsonDeserializer
- JavaType valueType)
- throws JsonMappingException
- {
- // First: have we already seen it?
- JsonDeserializer
- if (deser != null) {
- return deser;
- }
- // Nope: need to ask provider to resolve it
- deser = ctxt.findRootValueDeserializer(valueType);
- if (deser == null) { // can this happen?
- return ctxt.reportBadDefinition(valueType,
- "Cannot find a deserializer for type "+valueType);
- }
- _rootDeserializers.put(valueType, deser);
- return deser;
- }
3.2.3 public final JsonDeserializer
- findRootValueDeserializer
- 查找根级值的反序列化器的方法。
- 该⽅法会从尝试从缓存中获取 Deserializer ,这⾥的获取⽅式有点不同了,它不是单纯的从个map中去调⽤get⽅法获取,⽽是会经过⼀系列很复杂的获取⽅式后,判断是否获取到了,如果获取不到,会调⽤ _createAndCacheValueDeserializer(该方法在findValueDeserializer中) 去创建⼀个 Deserializer 并对其进⾏缓存。最后会通过buildBeanDeserializer ⽅法创建⼀BeanDeserializer (因为前⾯的⼀系列判断都不满⾜,⽐如判断Type的类型,如判断是不是Enum,Container,Reference等)
- 通过如下方法为创建好的 BeanDeserializer 对象赋值:
- findRootValueDeserializer源码:
- /**
- * Method for finding a deserializer for root-level value.
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public final JsonDeserializer
- throws JsonMappingException
- {
- JsonDeserializer
- _factory, type);
- if (deser == null) { // can this occur?
- return null;
- }
- deser = (JsonDeserializer
- TypeDeserializer typeDeser = _factory.findTypeDeserializer(_config, type);
- if (typeDeser != null) {
- // important: contextualize to indicate this is for root value
- typeDeser = typeDeser.forProperty(null);
- return new TypeWrappedDeserializer(typeDeser, deser);
- }
- return deser;
- }
- findValueDeserializer源码:
- /**
- * Method called to get hold of a deserializer for a value of given type;
- * or if no such deserializer can be found, a default handler (which
- * may do a best-effort generic serialization or just simply
- * throw an exception when invoked).
- *
- * Note: this method is only called for value types; not for keys.
- * Key deserializers can be accessed using {@link #findKeyDeserializer}.
- *
- * Note also that deserializer returned is guaranteed to be resolved
- * (if it is of type {@link ResolvableDeserializer}), but
- * not contextualized (wrt {@link ContextualDeserializer}): caller
- * has to handle latter if necessary.
- *
- * @param ctxt Deserialization context
- * @param propertyType Declared type of the value to deserializer (obtained using
- * 'setter' method signature and/or type annotations
- *
- * @throws JsonMappingException if there are fatal problems with
- * accessing suitable deserializer; including that of not
- * finding any serializer
- */
- public JsonDeserializer
- DeserializerFactory factory, JavaType propertyType)
- throws JsonMappingException
- {
- JsonDeserializer
- if (deser == null) {
- // If not, need to request factory to construct (or recycle)
- deser = _createAndCacheValueDeserializer(ctxt, factory, propertyType);
- if (deser == null) {
- /* Should we let caller handle it? Let's have a helper method
- * decide it; can throw an exception, or return a valid
- * deserializer
- */
- deser = _handleUnknownValueDeserializer(ctxt, propertyType);
- }
- }
- return deser;
- }
- buildBeanDeserializer源码:
- /**
- * Method that is to actually build a bean deserializer instance.
- * All basic sanity checks have been done to know that what we have
- * may be a valid bean type, and that there are no default simple
- * deserializers.
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public JsonDeserializer
- JavaType type, BeanDescription beanDesc)
- throws JsonMappingException
- {
- // First: check what creators we can use, if any
- ValueInstantiator valueInstantiator;
- /* 04-Jun-2015, tatu: To work around [databind#636], need to catch the
- * issue, defer; this seems like a reasonable good place for now.
- * Note, however, that for non-Bean types (Collections, Maps) this
- * probably won't work and needs to be added elsewhere.
- */
- try {
- valueInstantiator = findValueInstantiator(ctxt, beanDesc);
- } catch (NoClassDefFoundError error) {
- return new ErrorThrowingDeserializer(error);
- } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
- // 05-Apr-2017, tatu: Although it might appear cleaner to require collector
- // to throw proper exception, it doesn't actually have reference to this
- // instance so...
- throw InvalidDefinitionException.from(ctxt.getParser(),
- ClassUtil.exceptionMessage(e),
- beanDesc, null);
- }
- BeanDeserializerBuilder builder = constructBeanDeserializerBuilder(ctxt, beanDesc);
- builder.setValueInstantiator(valueInstantiator);
- // And then setters for deserializing from JSON Object
- addBeanProps(ctxt, beanDesc, builder);
- addObjectIdReader(ctxt, beanDesc, builder);
- // managed/back reference fields/setters need special handling... first part
- addBackReferenceProperties(ctxt, beanDesc, builder);
- addInjectables(ctxt, beanDesc, builder);
- final DeserializationConfig config = ctxt.getConfig();
- if (_factoryConfig.hasDeserializerModifiers()) {
- for (BeanDeserializerModifier mod : _factoryConfig.deserializerModifiers()) {
- builder = mod.updateBuilder(config, beanDesc, builder);
- }
- }
- JsonDeserializer deserializer;
- if (type.isAbstract() && !valueInstantiator.canInstantiate()) {
- deserializer = builder.buildAbstract();
- } else {
- deserializer = builder.build();
- }
- // may have modifier(s) that wants to modify or replace serializer we just built
- // (note that `resolve()` and `createContextual()` called later on)
- if (_factoryConfig.hasDeserializerModifiers()) {
- for (BeanDeserializerModifier mod : _factoryConfig.deserializerModifiers()) {
- deserializer = mod.modifyDeserializer(config, beanDesc, deserializer);
- }
- }
- return (JsonDeserializer
- }
3.2.4 buildBeanDeserializer 中的 addBeanProps
- 调用方法来确定 bean 反序列化器使用的可设置属性。
- 注意:设计为可覆盖,并努力保持版本之间的界面相似。
- 主要的逻辑在于解决字段与setter | getter | 反射的绑定,用于后面解析json串还原对象;
- setter方法调用的条件:(反序列化)
- getSetter()方法调用后能看到name、age两个字段;
- getSetter()方法调用后能看到name、age两个字段;
- getter方法调用的条件:(序列化)
- addBeanProps源码:
- /**
- * Method called to figure out settable properties for the
- * bean deserializer to use.
- *
- * Note: designed to be overridable, and effort is made to keep interface
- * similar between versions.
- */
- protected void addBeanProps(DeserializationContext ctxt,
- BeanDescription beanDesc, BeanDeserializerBuilder builder)
- throws JsonMappingException
- {
- final boolean isConcrete = !beanDesc.getType().isAbstract();
- final SettableBeanProperty[] creatorProps = isConcrete
- ? builder.getValueInstantiator().getFromObjectArguments(ctxt.getConfig())
- : null;
- final boolean hasCreatorProps = (creatorProps != null);
- // 01-May-2016, tatu: Which base type to use here gets tricky, since
- // it may often make most sense to use general type for overrides,
- // but what we have here may be more specific impl type. But for now
- // just use it as is.
- JsonIgnoreProperties.Value ignorals = ctxt.getConfig()
- .getDefaultPropertyIgnorals(beanDesc.getBeanClass(),
- beanDesc.getClassInfo());
- Set
ignored; - if (ignorals != null) {
- boolean ignoreAny = ignorals.getIgnoreUnknown();
- builder.setIgnoreUnknownProperties(ignoreAny);
- // Or explicit/implicit definitions?
- ignored = ignorals.findIgnoredForDeserialization();
- for (String propName : ignored) {
- builder.addIgnorable(propName);
- }
- } else {
- ignored = Collections.emptySet();
- }
- // Also, do we have a fallback "any" setter?
- AnnotatedMember anySetter = beanDesc.findAnySetterAccessor();
- if (anySetter != null) {
- builder.setAnySetter(constructAnySetter(ctxt, beanDesc, anySetter));
- } else {
- // 23-Jan-2018, tatu: although [databind#1805] would suggest we should block
- // properties regardless, for now only consider unless there's any setter...
- Collection
ignored2 = beanDesc.getIgnoredPropertyNames(); - if (ignored2 != null) {
- for (String propName : ignored2) {
- // allow ignoral of similarly named JSON property, but do not force;
- // latter means NOT adding this to 'ignored':
- builder.addIgnorable(propName);
- }
- }
- }
- final boolean useGettersAsSetters = ctxt.isEnabled(MapperFeature.USE_GETTERS_AS_SETTERS)
- && ctxt.isEnabled(MapperFeature.AUTO_DETECT_GETTERS);
- // Ok: let's then filter out property definitions
- List
propDefs = filterBeanProps(ctxt, - beanDesc, builder, beanDesc.findProperties(), ignored);
- // After which we can let custom code change the set
- if (_factoryConfig.hasDeserializerModifiers()) {
- for (BeanDeserializerModifier mod : _factoryConfig.deserializerModifiers()) {
- propDefs = mod.updateProperties(ctxt.getConfig(), beanDesc, propDefs);
- }
- }
- // At which point we still have all kinds of properties; not all with mutators:
- for (BeanPropertyDefinition propDef : propDefs) {
- SettableBeanProperty prop = null;
- // 18-Oct-2013, tatu: Although constructor parameters have highest precedence,
- // we need to do linkage (as per [databind#318]), and so need to start with
- // other types, and only then create constructor parameter, if any.
- if (propDef.hasSetter()) {
- AnnotatedMethod setter = propDef.getSetter();
- JavaType propertyType = setter.getParameterType(0);
- prop = constructSettableProperty(ctxt, beanDesc, propDef, propertyType);
- } else if (propDef.hasField()) {
- AnnotatedField field = propDef.getField();
- JavaType propertyType = field.getType();
- prop = constructSettableProperty(ctxt, beanDesc, propDef, propertyType);
- } else {
- // NOTE: specifically getter, since field was already checked above
- AnnotatedMethod getter = propDef.getGetter();
- if (getter != null) {
- if (useGettersAsSetters && _isSetterlessType(getter.getRawType())) {
- // 23-Jan-2018, tatu: As per [databind#1805], need to ensure we don't
- // accidentally sneak in getter-as-setter for `READ_ONLY` properties
- if (builder.hasIgnorable(propDef.getName())) {
- ;
- } else {
- prop = constructSetterlessProperty(ctxt, beanDesc, propDef);
- }
- } else if (!propDef.hasConstructorParameter()) {
- PropertyMetadata md = propDef.getMetadata();
- // 25-Oct-2016, tatu: If merging enabled, might not need setter.
- // We cannot quite support this with creator parameters; in theory
- // possibly, but right not not due to complexities of routing, so
- // just prevent
- if (md.getMergeInfo() != null) {
- prop = constructSetterlessProperty(ctxt, beanDesc, propDef);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- // 25-Sep-2014, tatu: No point in finding constructor parameters for abstract types
- // (since they are never used anyway)
- if (hasCreatorProps && propDef.hasConstructorParameter()) {
- /* If property is passed via constructor parameter, we must
- * handle things in special way. Not sure what is the most optimal way...
- * for now, let's just call a (new) method in builder, which does nothing.
- */
- // but let's call a method just to allow custom builders to be aware...
- final String name = propDef.getName();
- CreatorProperty cprop = null;
- if (creatorProps != null) {
- for (SettableBeanProperty cp : creatorProps) {
- if (name.equals(cp.getName()) && (cp instanceof CreatorProperty)) {
- cprop = (CreatorProperty) cp;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- if (cprop == null) {
- List
n = new ArrayList<>(); - for (SettableBeanProperty cp : creatorProps) {
- n.add(cp.getName());
- }
- ctxt.reportBadPropertyDefinition(beanDesc, propDef,
- "Could not find creator property with name '%s' (known Creator properties: %s)",
- name, n);
- continue;
- }
- if (prop != null) {
- cprop.setFallbackSetter(prop);
- }
- Class[] views = propDef.findViews();
- if (views == null) {
- views = beanDesc.findDefaultViews();
- }
- cprop.setViews(views);
- builder.addCreatorProperty(cprop);
- continue;
- }
- if (prop != null) {
- // one more thing before adding to builder: copy any metadata
- Class[] views = propDef.findViews();
- if (views == null) {
- views = beanDesc.findDefaultViews();
- }
- prop.setViews(views);
- builder.addProperty(prop);
- }
- }
- }
3.2.5 public Object deserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException
- 用来解析还原对象的Deserializer.deserialize 依据_hashArea的name 与 Method对应还原对象
- deserialize:
- 基于 bean 的对象 (POJO) 的主要反序列化方法。
- deserialize源码:
- /**
- * Main deserialization method for bean-based objects (POJOs).
- */
- @Override
- public Object deserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException
- {
- // common case first
- if (p.isExpectedStartObjectToken()) {
- if (_vanillaProcessing) {
- return vanillaDeserialize(p, ctxt, p.nextToken());
- }
- // 23-Sep-2015, tatu: This is wrong at some many levels, but for now... it is
- // what it is, including "expected behavior".
- p.nextToken();
- if (_objectIdReader != null) {
- return deserializeWithObjectId(p, ctxt);
- }
- return deserializeFromObject(p, ctxt);
- }
- return _deserializeOther(p, ctxt, p.getCurrentToken());
- }
3.2.6 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.BeanDeserializer#vanillaDeserialize
- private final Object vanillaDeserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt, JsonToken t) throws IOException
- vanillaDeserialize:
- final Object bean = _valueInstantiator.createUsingDefault(ctxt); //默认构造器初始化对象
- SettableBeanProperty prop = _beanProperties.find(propName); //获取字段的设置方法
- prop.deserializeAndSet(p, ctxt, bean); //调用初始化字段,调用每个properties对应的方法
- 字段的赋值在 SettableBeanProperty.deserializeAndSet(): 不同的 SettableBeanProperty 有不同的行为
- vanillaDeserialize源码:
- /**
- * Streamlined version that is only used when no "special"
- * features are enabled.
- */
- private final Object vanillaDeserialize(JsonParser p,
- DeserializationContext ctxt, JsonToken t)
- throws IOException
- {
- final Object bean = _valueInstantiator.createUsingDefault(ctxt); //默认构造器初始化对象
- // [databind#631]: Assign current value, to be accessible by custom serializers
- p.setCurrentValue(bean);
- if (p.hasTokenId(JsonTokenId.ID_FIELD_NAME)) {
- String propName = p.getCurrentName();
- do {
- p.nextToken();
- SettableBeanProperty prop = _beanProperties.find(propName); //获取字段的设置方法
- if (prop != null) { // normal case
- try {
- prop.deserializeAndSet(p, ctxt, bean); //调用初始化字段,调用每个properties对应的方法
- } catch (Exception e) {
- wrapAndThrow(e, bean, propName, ctxt);
- }
- continue;
- }
- handleUnknownVanilla(p, ctxt, bean, propName);
- } while ((propName = p.nextFieldName()) != null);
- }
- return bean;
- }
无参构造存在的时候:
- createUsingDefault源码:
- @Override
- public Object createUsingDefault(DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException
- {
- if (_defaultCreator == null) { // sanity-check; caller should check
- return super.createUsingDefault(ctxt);
- }
- try {
- return _defaultCreator.call();
- } catch (Exception e) { // 19-Apr-2017, tatu: Let's not catch Errors, just Exceptions
- return ctxt.handleInstantiationProblem(_valueClass, null, rewrapCtorProblem(ctxt, e));
- }
- }
- call源码:调用构造器的newInstance()方法
- @Override
- public final Object call() throws Exception {
- return _constructor.newInstance();
- }
- Constructor
- newInstance()底层调用的是该类型的无参数构造方法;
全参构造存在时:
- createFromObjectWith源码:com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.StdValueInstantiator#createFromObjectWith
- @Override
- public Object createFromObjectWith(DeserializationContext ctxt, Object[] args) throws IOException
- {
- if (_withArgsCreator == null) { // sanity-check; caller should check
- return super.createFromObjectWith(ctxt, args);
- }
- try {
- return _withArgsCreator.call(args);
- } catch (Exception e) { // 19-Apr-2017, tatu: Let's not catch Errors, just Exceptions
- return ctxt.handleInstantiationProblem(_valueClass, args, rewrapCtorProblem(ctxt, e));
- }
- }
- call源码:调用构造器的newInstance()方法
- @Override
- public final Object call(Object[] args) throws Exception {
- return _constructor.newInstance(args);
- }
java.lang.reflect.Constructor#newInstance
- newInstance
- 使用此 Constructor 对象表示的构造函数,使用指定的初始化参数创建和初始化构造函数的声明类的新实例。各个参数会自动展开以匹配原始形式参数,并且原始参数和引用参数都根据需要进行方法调用转换。
- 如果底层构造函数所需的形参数量为 0,则提供的 initargs 数组的长度可能为 0 或 null。
- 如果构造函数的声明类是非静态上下文中的内部类,则构造函数的第一个参数需要是封闭实例;请参阅 Java™ 语言规范的第 15.9.3 节。
- 如果所需的访问和参数检查成功并且实例化将继续,则如果尚未初始化构造函数的声明类,则将对其进行初始化。
- 如果构造函数正常完成,则返回新创建和初始化的实例。
- 参数:
- initargs – 作为参数传递给构造函数调用的对象数组;原始类型的值被包装在适当类型的包装对象中(例如,浮点数中的浮点数)
- 返回值:
- 通过调用此对象表示的构造函数创建的新对象
- 抛出异常:
- IllegalAccessException – 如果此 Constructor 对象正在强制执行 Java 语言访问控制并且底层构造函数不可访问。
- IllegalArgumentException – 如果实际参数和形式参数的数量不同;如果原始参数的展开转换失败;或者,如果在可能的展开之后,参数值不能通过方法调用转换转换为相应的形参类型;如果此构造函数属于枚举类型。
- InstantiationException – 如果声明底层构造函数的类表示一个抽象类。
- InvocationTargetException – 如果底层构造函数抛出异常。
- ExceptionInInitializerError – 如果此方法引发的初始化失败。
- newInstance源码:
- /**
- * Uses the constructor represented by this {@code Constructor} object to
- * create and initialize a new instance of the constructor's
- * declaring class, with the specified initialization parameters.
- * Individual parameters are automatically unwrapped to match
- * primitive formal parameters, and both primitive and reference
- * parameters are subject to method invocation conversions as necessary.
- *
- *
If the number of formal parameters required by the underlying constructor
- * is 0, the supplied {@code initargs} array may be of length 0 or null.
- *
- *
If the constructor's declaring class is an inner class in a
- * non-static context, the first argument to the constructor needs
- * to be the enclosing instance; see section 15.9.3 of
- * The Java™ Language Specification.
- *
- *
If the required access and argument checks succeed and the
- * instantiation will proceed, the constructor's declaring class
- * is initialized if it has not already been initialized.
- *
- *
If the constructor completes normally, returns the newly
- * created and initialized instance.
- *
- * @param initargs array of objects to be passed as arguments to
- * the constructor call; values of primitive types are wrapped in
- * a wrapper object of the appropriate type (e.g. a {@code float}
- * in a {@link java.lang.Float Float})
- *
- * @return a new object created by calling the constructor
- * this object represents
- *
- * @exception IllegalAccessException if this {@code Constructor} object
- * is enforcing Java language access control and the underlying
- * constructor is inaccessible.
- * @exception IllegalArgumentException if the number of actual
- * and formal parameters differ; if an unwrapping
- * conversion for primitive arguments fails; or if,
- * after possible unwrapping, a parameter value
- * cannot be converted to the corresponding formal
- * parameter type by a method invocation conversion; if
- * this constructor pertains to an enum type.
- * @exception InstantiationException if the class that declares the
- * underlying constructor represents an abstract class.
- * @exception InvocationTargetException if the underlying constructor
- * throws an exception.
- * @exception ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization provoked
- * by this method fails.
- */
- @CallerSensitive
- @ForceInline // to ensure Reflection.getCallerClass optimization
- public T newInstance(Object ... initargs)
- throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
- IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
- {
- if (!override) {
- Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
- checkAccess(caller, clazz, clazz, modifiers);
- }
- if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
- ConstructorAccessor ca = constructorAccessor; // read volatile
- if (ca == null) {
- ca = acquireConstructorAccessor();
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- T inst = (T) ca.newInstance(initargs);
- return inst;
- }
3.2.7 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.impl.MethodProperty#deserializeAndSet
- public void deserializeAndSet(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt, Object instance) throws IOException
- deserializeAndSet:
- 字段的赋值在 SettableBeanProperty.deserializeAndSet(): 不同的 SettableBeanProperty 有不同的行为;
- MethodProperty通过反射调用bean的setter方法;
- FieldProperty通过反射设置Bean的值;
- 字段的赋值在 SettableBeanProperty.deserializeAndSet(): 不同的 SettableBeanProperty 有不同的行为;
- deserializeAndSet源码:
- @Override
- public void deserializeAndSet(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt,
- Object instance) throws IOException
- {
- Object value;
- if (p.hasToken(JsonToken.VALUE_NULL)) {
- if (_skipNulls) {
- return;
- }
- value = _nullProvider.getNullValue(ctxt);
- } else if (_valueTypeDeserializer == null) {
- value = _valueDeserializer.deserialize(p, ctxt);
- // 04-May-2018, tatu: [databind#2023] Coercion from String (mostly) can give null
- if (value == null) {
- if (_skipNulls) {
- return;
- }
- value = _nullProvider.getNullValue(ctxt);
- }
- } else {
- value = _valueDeserializer.deserializeWithType(p, ctxt, _valueTypeDeserializer);
- }
- try {
- _setter.invoke(instance, value);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- _throwAsIOE(p, e, value);
- }
- }
3.2.8 com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.NumberDeserializers.IntegerDeserializer#deserialize
- @Override
- public Integer deserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException {
- if (p.hasToken(JsonToken.VALUE_NUMBER_INT)) {
- return p.getIntValue();
- }
- return _parseInteger(p, ctxt);
- }
3.2.9 com.fasterxml.jackson.core.base.ParserBase#getIntValue
- @Override
- public int getIntValue() throws IOException
- {
- if ((_numTypesValid & NR_INT) == 0) {
- if (_numTypesValid == NR_UNKNOWN) { // not parsed at all
- return _parseIntValue();
- }
- if ((_numTypesValid & NR_INT) == 0) { // wasn't an int natively?
- convertNumberToInt(); // let's make it so, if possible
- }
- }
- return _numberInt;
- }
3.2.10 java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke
- public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
- 这个方法一顿调用,就找到了自己写的set方法;
总结
- 序列化和反序列化,主要通过getXX获取字段值序列化 与 默认构造器+setXX反序列化还原对象。
- 走无参构造的时候,参数赋值需要用到set、get方法;
- 如果是全参构造,则无需走set、gei方法;
- Jackson只支持对象的public属性或者有对象getter方法的属性序列化,即 protected,private,final,static 等属性将不会序列化到json串中,这是JavaBean的向后兼容使然。即Jackson在序列化的时候优先通过getXXX方法获取属性,如果没有则判断该属性是否public访问,是则通过反射获取该属性值。
- Json的反序列化是不论是Fastjson还是Jackson,都限定了从某一个类的constructor默认参数实例化(如Fastjson的的autotype,Jackson在parseObject传入的Target.Class),通过getter or setter方法给成员对象赋值还原对象,利用的仅仅是这个Taget类与Target类的成员的setter or getter方法(这是一个递归的解析还原JSON串)。
参考文献
JavaSec Jackjson反序列化漏洞利用原理 | thonsun's blog
- 如果有参构造的参数全,或者更多(就是有不存在的值),这样还能正常运行:
-
相关阅读:
arraybuffer 转json
619. 只出现一次的最大数字
vivado 串行 I/O 硬件调试流程
iOS17正式版BUG汇总:无法正常拨打电话、小组件不可用、无线充电不可用等问题
LeetCode90. 子集 II
title标签和meta标签怎样设置?有什么含义?
python 抽象类
postgresql并行查询(高级特性)
MobaXterm配置ssh端口转发(tensorboard使用)
双十一买led灯哪个品牌性价比高?2022适合学生使用的护眼灯推荐
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jiayoudangdang/article/details/127813330