-
SpringSecurity Oauth2实战 - 08 SpEL权限表达式源码分析及两种权限控制方式原理
文章目录
- 1. 权限管理介绍
- 2. 权限表达式介绍
- 3. 基于url地址的权限控制
- 4. 基于方法级别的权限控制
- 5. 源码 - 权限表达式
- 6. 资源服务器 server-resource
- 7. 源码分析 - 基于url权限表达式
- 1. 资源服务器配置类 ResourceServerAutoConfiguration
- 2. 业务 knowledge 服务
- 3. 源码流程分析
- 01. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 02. 进入 BearerTokenExtractor#extract 提取token返回待认证的Authentication对象
- 03. 进入 CustomTokenExtractor#extractToken 从request中提取token
- 04. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 05. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate 完成Authentication对象的认证
- 06. 进入 DefaultTokenServices#loadAuthentication 填充完整的Authentication认证信息
- 07. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate
- 08. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 09. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthority 权限表达式
- 10. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName 判断用户是否具备指定的权限
- 11. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#getAuthoritySet 获取用户具备的所有权限
- 12. 回到 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName
- 13. 进入 UserInfoInterceptor#preHandle
- 14. 进入 DocController#getDocList
- 7. 源码分析 - 基于注解的权限表达式
- 1. 资源服务器配置类 ResourceServerAutoConfiguration
- 2. 业务 knowledge 服务
- 3. 源码流程分析
- 01. 进入OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 02. 进入 BearerTokenExtractor#extract
- 03. 进入CustomTokenExtractor#extractToken:
- 04. 回到 BearerTokenExtractor#extract
- 05. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 06. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate
- 07. 进入DefaultTokenServices#loadAuthentication
- 08. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
- 09. 进入 UserInfoInterceptor#preHandle
- 10. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthority 权限表达式方法
- 11. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName 判断用户是否具备指定的权限
- 12. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#getAuthoritySet 获取用户具备的所有权限
- 13. 回到 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName
- 14. 进入 DocController#getDocList
1. 权限管理介绍
SpringSecurity提供的权限管理功能主要有两种类型:
① 基于过滤器的权限管理(FilterSecurityInterceptor):用来拦截HTTP请求,拦截下来之后,根据HTTP请求地址进行权限校验;
请求首先到大过滤器FilterSecurityInterceptor,在其执行过程中,首先会由前置处理器去判断发起请求的用户是否具备响应的权限,如果具备则继续向下走,到达目标方法后执行完毕。拦截请求的url,这种权限管理方式粒度较粗。
② 基于AOP的权限管理(MethodSecurityInterceptor):用来处理方法级别的权限问题。当需要调用某一个方法时,通过AOP将操作拦截下来,然后判断用户是否具备相关的权限,如果具备,则允许方法调用,否则禁止方法调用。
当目标方法的调用被MethodSecurityInterceptor拦截下来之后,再起invoke方法中首先会由前置处理器去判断当前用户是否具备调用目标方法所需的权限,如果具备则继续执行目标方法。
2. 权限表达式介绍
SpringSecurity 内置的SpEL表达式,可以再请求的URL或者访问的方法上,通过SpEL来配置需要的权限:

3. 基于url地址的权限控制
@Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // http.authorizeRequests()主要是对url进行访问权限控制,通过这个方法来实现url授权操作 http.authorizeRequests() // 写法:url匹配规则.权限表达式 // permitAll()权限表达式:用户可以在没有身份验证的情况下访问 /api/v1/login,/api/v1/token 地址 .antMatchers("/api/v1/login", "/api/v1/token").permitAll() // hasAuthority()权限表达式:用户必须具备knowledgeEdit权限才可以访问 /api/v1/hello 地址 .antMatchers("/api/v1/hello").hasAuthority("knowledgeEdit") // url匹配规则.权限表达式 // hasRole()权限表达式:用户必须具备ADMIN角色才可以访问 /api/v1/doc 地址 .antMatchers("/api/v1/doc").hasRole("ADMIN"); // 其他请求只要认证后的用户就可以访问 http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated(); http.formLogin().disable(); http.httpBasic().disable(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
4. 基于方法级别的权限控制
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 该注解是用来开启权限注解,用法如下:
@Configuration @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true,securedEnabled=true, jsr250Enabled=true) public class SecurityConfig extends WebsecurityConfigurerAdapter{}- 1
- 2
- 3
perPostEnabled: 开启 Spring Security 提供的四个权限注解,@PostAuthorize、@PostFilter、@PreAuthorize 以及@PreFilter,注解会将一个描述权限规则的SpEL表达式作为一个值来接收。@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v2") public class UserController { // 在目标方法执行之前进行权限校验 // 通过权限表达式来配置访问该方法需要具备的权限 @PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('superAdmin')") @PostMapping(value = "/domain/users", params = { "_method=GET" }) public List<UserEntity> getUsersByNamesInSameDomain(){ } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
5. 源码 - 权限表达式
SpringSecurity中通 SecurityExpressionOperations 接口定义了基本的权限表达式,他的实现类如下:
1. 源码 SecurityExpressionOperations
public interface SecurityExpressionOperations1 { /** * Gets the Authentication used for evaluating the expressions * * 当用户登录成功后,当前用户信息将保存在 Authentication 对象中, * Authentication#getAuthorities() 方法:返回当前对象所具备的权限信息,也就是已经授予当前登录用户的权限。 */ Authentication getAuthentication(); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. * * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定权限 */ boolean hasAuthority(String authority); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. * * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定权限中的任意一个 */ boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has a particular authority within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. * * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定角色 */ boolean hasRole(String role); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has any of the specified authorities within {@link Authentication#getAuthorities()}. * * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定角色中的任意一个 */ boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles); /** * 允许所有的请求调用 * * @return true */ boolean permitAll(); /** * 拒绝所有的请求调用 * * @return false */ boolean denyAll(); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} is anonymous * * 当前用户是否是一个匿名用户 */ boolean isAnonymous(); /** * Determines ifthe {@link #getAuthentication()} is authenticated * * 判断用户是否已经认证成功 */ boolean isAuthenticated(); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} was authenticated using remember me * * 当前用户是否通过RememberMe自动登录 */ boolean isRememberMe(); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} authenticated without the use of remember me * * 当前登录用户是否既不是匿名用户又不是通过RememberMe登录的 */ boolean isFullyAuthenticated(); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the target given the permission * * 当前登录用户是否具有指定目标的指定权限 */ boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission); /** * Determines if the {@link #getAuthentication()} has permission to access the domain object with a given id, type, and permission. * * 当前登录用户是否具有指定目标的指定权限 */ boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
hasAuthority,hasAnyAuthority,hasRole,hasAnyRole四个方法主要是将传入的参数和authentication对象中保存的方法进行比对,如果用户具有相应的权限就返回true,否则返回false,permitAll方法总是返回true,而denyAll方法总是返回false,isAnonymous,isAuthenticated,isRememberMe,isFullyAuthenticated这四个方法时根据对authentication对象的分析返回true还是false,最后的hasPermission方法则需要调用PermissionEvaluator中对应的方法进行计算,返回true还是false。
2. 源码 SecurityExpressionRoot
/** * 为了创建自定义表达式,我们首先需要实现SecurityExpressionOperations表达式 */ public abstract class SecurityExpressionRoot implements SecurityExpressionOperations { /*用户登录成功后,保存用户信息的Authentication对象*/ protected final Authentication authentication; private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver; private RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy; /*用户角色列表*/ private Set<String> roles; /*角色前缀*/ private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_"; public final boolean permitAll = true; public final boolean denyAll = false; private PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator; public final String read = "read"; public final String write = "write"; public final String create = "create"; public final String delete = "delete"; public final String admin = "administration"; public final Authentication getAuthentication() { return authentication; } /** * 构造方法 */ public SecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication authentication) { if (authentication == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Authentication object cannot be null"); } this.authentication = authentication; } /** * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定权限 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAuthority: @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('superAdmin')") */ public final boolean hasAuthority(String authority) { return hasAnyAuthority(authority); } /** * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定权限中的任意一个 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyAuthority:@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('superAdmin','incidentQuery')") */ public final boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities) { // return hasAnyAuthorityName(null, authorities); } /** * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定角色 * SpEL权限表达式:hasRole:@PreAuthorize("hasRole("ROLE_ADMIN")") */ public final boolean hasRole(String role) { return hasAnyRole(role); } /** * 判断当前用户具备的权限信息,是否存在指定角色中的任意一个 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole("ROLE_ADMIN","ROLE_USER")") */ public final boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles) { // 与 hasAnyAuthority 不同的是,hasRole 会自动给传入的字符串加上 ROLE_ 前缀 // 代码里如果写的是 admin,框架会自动加上 ROLE_ 前缀,所以数据库就必须是 ROLE_admin。 return hasAnyAuthorityName(defaultRolePrefix, roles); } /** * 允许所有的请求调用 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("permitAll()") */ public final boolean permitAll() { return true; } /** * 拒绝所有的请求调用 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("denyAll()") */ public final boolean denyAll() { return false; } /** * 当前用户是否是一个匿名用户 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("isAnonymous()") */ public final boolean isAnonymous() { return trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication); } /** * 判断用户是否已经认证成功 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()") */ public final boolean isAuthenticated() { return !isAnonymous(); } /** * 当前用户是否通过RememberMe自动登录 * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("isRememberMe()") */ public final boolean isRememberMe() { return trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication); } /** * SpEL权限表达式:hasAnyRole:@PreAuthorize("isFullyAuthenticated()") * 前登录用户是否既不是匿名用户又不是通过RememberMe登录的 */ public final boolean isFullyAuthenticated() { return !trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) && !trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication); } public Object getPrincipal() { return authentication.getPrincipal(); } public void setTrustResolver(AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver) { this.trustResolver = trustResolver; } public void setRoleHierarchy(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) { this.roleHierarchy = roleHierarchy; } public void setPermissionEvaluator(PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator) { this.permissionEvaluator = permissionEvaluator; } /** * 当前登录用户是否具有指定目标的指定权限 */ public boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) { return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication, target, permission); } /** * 当前登录用户是否具有指定目标的指定权限 */ public boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) { return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication, (Serializable) targetId, targetType, permission); } private Set<String> getAuthoritySet() { if (roles == null) { roles = new HashSet<>(); // 获取登录用户具备的权限信息 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> userAuthorities = authentication.getAuthorities(); if (roleHierarchy != null) { userAuthorities = roleHierarchy.getReachableGrantedAuthorities(userAuthorities); } roles = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(userAuthorities); } return roles; } private boolean hasAnyAuthorityName(String prefix, String... roles) { Set<String> roleSet = getAuthoritySet(); for (String role : roles) { String defaultedRole = getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(prefix, role); if (roleSet.contains(defaultedRole)) { return true; } } return false; } public void setDefaultRolePrefix(String defaultRolePrefix) { this.defaultRolePrefix = defaultRolePrefix; } private static String getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(String defaultRolePrefix, String role) { if (role == null) { return role; } if (defaultRolePrefix == null || defaultRolePrefix.length() == 0) { return role; } if (role.startsWith(defaultRolePrefix)) { return role; } return defaultRolePrefix + role; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
3. 源码 MethodSecurityExpressionOperations
/** * Interface which must be implemented if you want to use filtering in method security expressions. */ public interface MethodSecurityExpressionOperations extends SecurityExpressionOperations { void setFilterObject(Object filterObject); Object getFilterObject(); void setReturnObject(Object returnObject); Object getReturnObject(); Object getThis(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
4. 源码 MethodSecurityExpressionRoot
class MethodSecurityExpressionRoot extends SecurityExpressionRoot implements MethodSecurityExpressionOperations { private Object filterObject; private Object returnObject; private Object target; MethodSecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication a) { super(a); } public void setFilterObject(Object filterObject) { this.filterObject = filterObject; } public Object getFilterObject() { return filterObject; } public void setReturnObject(Object returnObject) { this.returnObject = returnObject; } public Object getReturnObject() { return returnObject; } void setThis(Object target) { this.target = target; } public Object getThis() { return target; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
6. 资源服务器 server-resource
相关文章:
SpringSecurity Oauth2实战 - 05 /oauth/token请求认证流程源码分析
SpringSecurity Oauth2实战 - 06 拦截器获取用户登录信息并存储到本地线程ThreadLocal
SpringSecurity Oauth2实战 - 07 整合Redis延长页面自动退出登录时间
在前面三篇文章中,我们增加了自定义认证管理器 CustomAuthProvider 获取认证令牌 access_token ,增加了拦截器 UserInfoInterceptor 用来获取用户登录信息并存储搭配本地线程,增加了自定义 CustomTokenExtractor 用来延长页面自动退出登录的时间。
在此基础上我们来继续研究新东西,然后走一遍整个源码流程。
1. 自定义认证管理器 CustomAuthProvider
@Slf4j @Component public class CustomAuthProvider implements AuthenticationProvider { @Autowired private CustomUserDetailService customUserDetailService; /** * 认证 * @param authentication 待认证的对象 principal:loginJsonString, credentials:"" * @return Authentication 认证成功后填充的对象 * @throws AuthenticationException 异常 */ @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { // loginJsonString String contentJsonStr = Objects.isNull(authentication.getPrincipal()) ? StringUtils.EMPTY : authentication.getName(); // 通过authentication获取登录用户信息AuthUser AuthUser authUser = customUserDetailService.loadUserByContent(contentJsonStr); // principal,credentials,authorities UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken( authUser, authentication.getCredentials(), authUser.getAuthorities() ); result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails()); return result; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) { return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
2. 拦截器 UserInfoInterceptor
/** * 拦截器:用户信息本地线程存储 */ public class UserInfoInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { /** * 拦截所有请求,在Controller层方法之前调用 */ @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 判断用户是否被认证,如果没有认证不放行 boolean isAuthenticated = request.authenticate(response); if (!isAuthenticated) { return false; } // 存储用户信息到本地线程 Principal userPrincipal = request.getUserPrincipal(); OAuth2Authentication oAuth2Authentication = (OAuth2Authentication) userPrincipal; AuthUser ngsocUser = (AuthUser) oAuth2Authentication.getUserAuthentication().getPrincipal(); UserInfo userInfo = ngsocUser.getUserInfo(); UserInfoShareHolder.setUserInfo(userInfo); // 放行,继续执行Controller层的方法 return true; } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { UserInfoShareHolder.remove(); super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
@Configuration @EnableWebMvc public class CommonWebMvcAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Bean public UserInfoInterceptor userInfoInterceptor() { return new UserInfoInterceptor(); } @Override public void addInterceptors(@NonNull InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 拦截器会拦截所有请求,需要配置放行的请求 registry.addInterceptor(userInfoInterceptor()) // 放行的请求 .excludePathPatterns("/api/v1/login"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
3. 自定义 CustomTokenExtractor
@Slf4j public class CustomTokenExtractor extends BearerTokenExtractor { @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; /** * 从请求中提取 token */ @Override protected String extractToken(HttpServletRequest request) { String token = null; // 从cookie中获取token,确保tokenCookie.setHttpOnly(true) Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); if (Objects.nonNull(cookies)) { for (Cookie cookie : cookies) { if (cookie.getName().equals(OAuth2AccessToken.ACCESS_TOKEN)) { token = cookie.getValue(); break; } } } // 从header中获取token if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { log.debug("Token not found in cookies. Trying request header."); token = extractHeaderToken(request); } // 从parameters获取token if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { log.debug("Token not found in headers. Trying request parameters."); token = request.getParameter(OAuth2AccessToken.ACCESS_TOKEN); } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { log.debug("Token not found in headers and request parameters and cookie. Not an OAuth2 request."); return null; } request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_TYPE, OAuth2AccessToken.BEARER_TYPE); return freshTimeAndGetRedisToken(request,token); } // 省略延长页面自动退出登录时长逻辑..... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
7. 源码分析 - 基于url权限表达式
1. 资源服务器配置类 ResourceServerAutoConfiguration
在资源服务器配置类中添加url权限表达式,对请求url进行访问权限控制
@Slf4j @Configuration @EnableResourceServer @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) public class ResourceServerAutoConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private TokenStore tokenStore; @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String appName; @Override public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) { resources.resourceId(appName); resources.tokenStore(tokenStore); resources.tokenExtractor(tokenExtractor()); } @Bean @Primary public TokenExtractor tokenExtractor() { CustomTokenExtractor customTokenExtractor = new CustomTokenExtractor(); return customTokenExtractor; } @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // http.authorizeRequests()主要是对url进行访问权限控制,通过这个方法来实现url授权操作 http.authorizeRequests() // permitAll()权限表达式 .antMatchers("/api/v1/login", "/api/v1/token").permitAll() // hasAnyAuthority()权限表达式 .antMatchers("/api/v1/doc").hasAnyAuthority("knowledgeEdit","knowledgeQuery"); // 其他请求只要认证后的用户就可以访问 http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated(); http.formLogin().disable(); http.httpBasic().disable(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
2. 业务 knowledge 服务
@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class DocController { @GetMapping("/doc") public String getDocList(){ return "docList"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3. 源码流程分析

我们在资源服务器中配置了用户具备
knowledgeEdit,knowledgeQuery中的任一权限就可以访问/api/v1/doc地址。那我们先让用户访问/api/v1/login请求获取令牌token,然后通过令牌访问/api/v1/doc接口地址,然后通过源码看一下它是怎么通过权限表达式来进行权限管理的。01. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
当访问
/api/v1/doc接口受限资源时,请求会被过滤器OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter拦截,这个过滤器他的作用就是从请求中获取认证服务器发出去的Token,(因为在调用我们服务的时候请求中都会包含Token),获取到Token后会根据在认证服务器中Token的存储策略去对应的存储中找到Token信息,然后根据用户信息是否存在,是否有权限来判断是否能访问资源。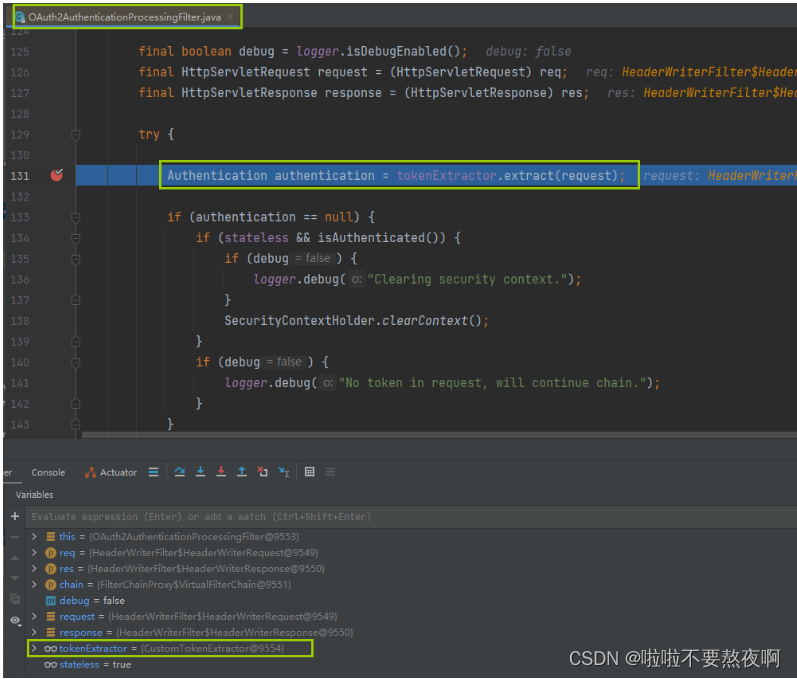
02. 进入 BearerTokenExtractor#extract 提取token返回待认证的Authentication对象
从请求request中获取令牌token,根据tokenValue获取PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken认证对象,该对象是待认证的Authentication对象,需要交给AuthenticationManager认证管理器完成认证。

03. 进入 CustomTokenExtractor#extractToken 从request中提取token

04. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
可以看到获取Authentication对象是待认证的对象,认证的主体是userId,认证的凭证为密码。

05. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate 完成Authentication对象的认证
调用OAuth2AuthenticationManager认证管理器的authenticate(Authentication authentication) 方法完成Authentication对象的认证,OAuth2AuthenticationManager是AuthenticationManager的实现类:

06. 进入 DefaultTokenServices#loadAuthentication 填充完整的Authentication认证信息
该方法就是到认证数据源中获取完整的 Authentication 认证信息。根据 accessTokenValue 到 tokenStore 中获取 OAtuth2AccessToken:

根据 OAuthAccessToken 到 tokenStore 中获取 OAuth2Authentication 对象:

07. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate

08. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter

09. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthority 权限表达式
权限表达式指定的权限:knowledgeEdit,knowledgeQuery

10. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName 判断用户是否具备指定的权限

11. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#getAuthoritySet 获取用户具备的所有权限
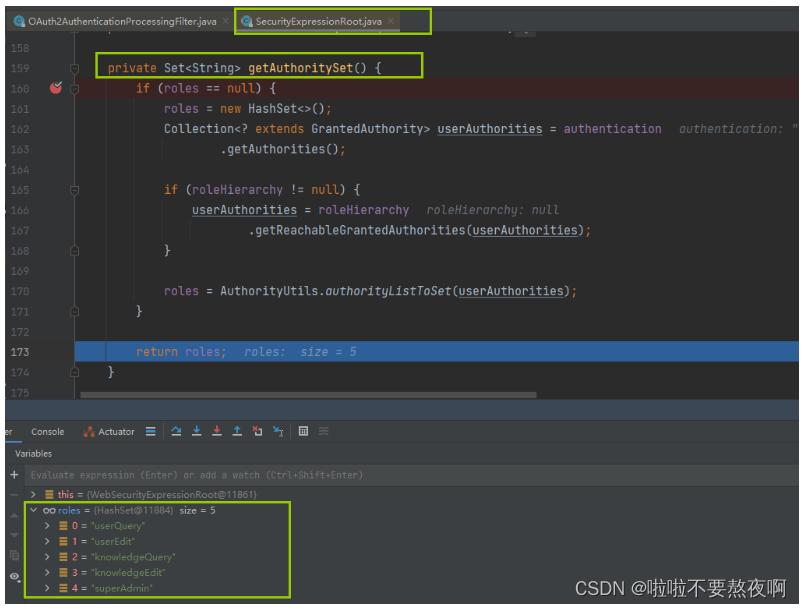
12. 回到 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName

13. 进入 UserInfoInterceptor#preHandle

14. 进入 DocController#getDocList
结论:我们在资源服务器中配置了
antMatchers("/api/v1/doc").hasAnyAuthority("knowledgeEdit","knowledgeQuery");,使用了权限表达式hasAnyAuthority,因此会调用 SecurityExpressionRoot 类的 hasAnyAuthority 方法,在该方法中获取用户具备的所有权限并判断用户具备的权限中是否包含指定的权限,如果包含则放行否则抛出异常。因此,当我们在资源服务器中使用了某个权限表达式时,最终就会调用 SecurityExpressionRoot 类中的权限表达式方法,比如
antMatchers("/api/v1/login", "/api/v1/token").permitAll()使用了 permitAll 这个权限表达式,那么最终就会调用 SecurityExpressionRoot 类中的 permitAll() 方法,该方法始终返回true,代表用户可以在没有任何权限的情况下访问该url接口。7. 源码分析 - 基于注解的权限表达式
1. 资源服务器配置类 ResourceServerAutoConfiguration
@Slf4j @Configuration @EnableResourceServer @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) public class ResourceServerAutoConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private TokenStore tokenStore; @Override public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) { resources.resourceId(appName); resources.tokenStore(tokenStore); resources.tokenExtractor(tokenExtractor()); } @Bean @Primary public TokenExtractor tokenExtractor() { CustomTokenExtractor customTokenExtractor = new CustomTokenExtractor(); return customTokenExtractor; } @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // http.authorizeRequests()主要是对url进行访问权限控制,通过这个方法来实现url授权操作 http.authorizeRequests() // permitAll()权限表达式 .antMatchers("/api/v1/login", "/api/v1/token").permitAll(); // 其他请求只要认证后的用户就可以访问 http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated(); http.formLogin().disable(); http.httpBasic().disable(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
2. 业务 knowledge 服务
@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class DocController { @PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('knowledgeEdit','knowledgeQuery')") @GetMapping("/doc") public String getDocList(){ return "docList"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3. 源码流程分析

我们将资源服务器配置中的 url 权限表达式去掉,改为注解权限表达式,再来看下整个流程。01. 进入OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter

02. 进入 BearerTokenExtractor#extract

03. 进入CustomTokenExtractor#extractToken:


04. 回到 BearerTokenExtractor#extract

05. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
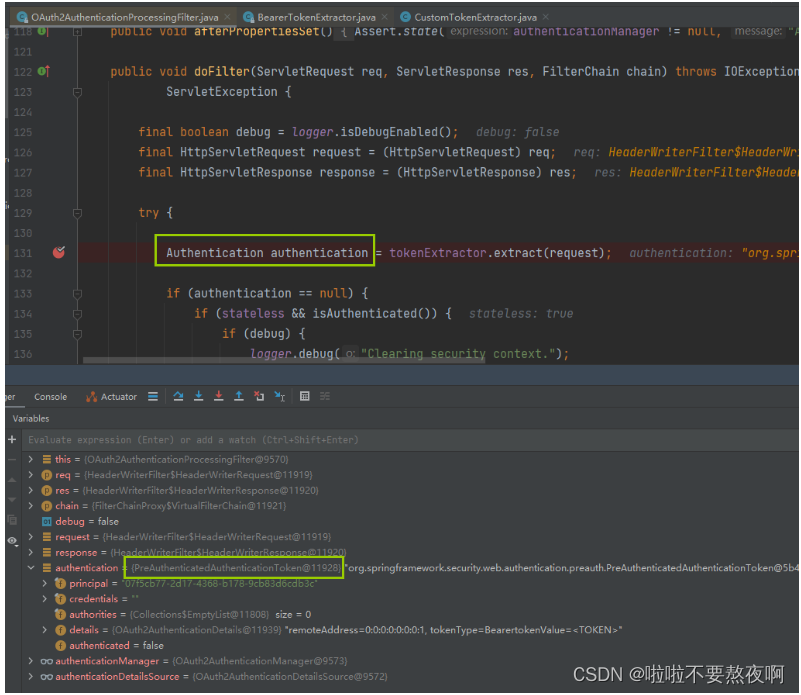
将待认证的 Authentication 对象交给 AuthenticationManager 的实现类 OAuthAuthenticationManager 认证:
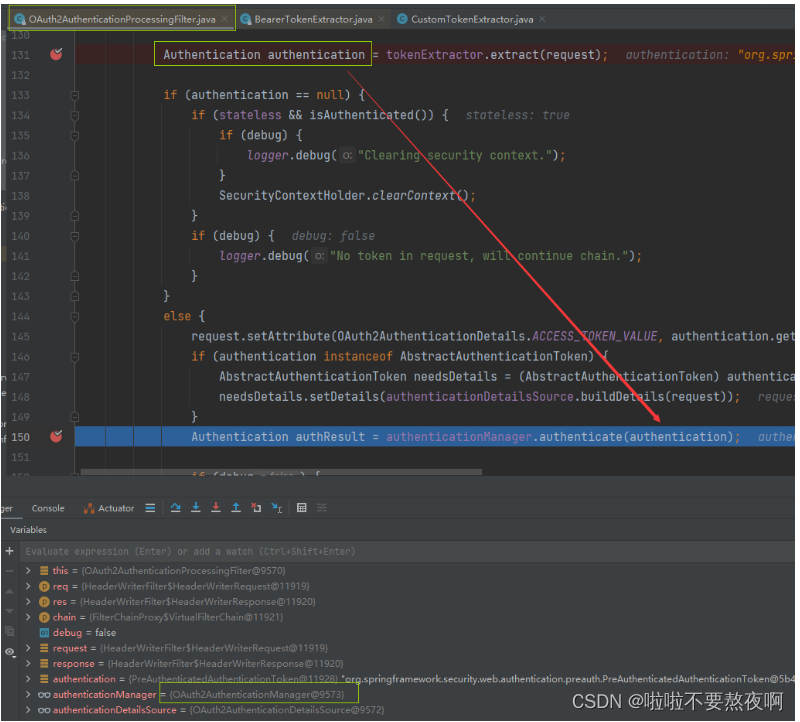
可以看到获取Authentication对象是待认证的对象,认证的主体是userId,认证的凭证为密码。
06. 进入 OAuth2AuthenticationManager#authenticate
这认证管理器中会调用DefaultTokenServices的loadAuthentication方法,到数据源中获取Authentication对象信息:

07. 进入DefaultTokenServices#loadAuthentication

08. 回到 OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter


09. 进入 UserInfoInterceptor#preHandle

10. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthority 权限表达式方法
因为我们使用了注解权限表达式:@PreAuthorize(“hasAnyAuthority(‘knowledgeEdit’,‘knowledgeQuery’)”),最终会调用 hasAnyAuthority 方法判断登录用户是否具备指定的权限中的一个,如果具备就返回true,否则返回false:

11. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName 判断用户是否具备指定的权限

12. 进入 SecurityExpressionRoot#getAuthoritySet 获取用户具备的所有权限

13. 回到 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasAnyAuthorityName

14. 进入 DocController#getDocList

经过上面的分析我们可以看到url权限表达式会在注解权限表达式之前执行,那么如果我们在url权限表达式中配置了permitAll 权限表达式,在注解中配置了hasAnyAuthority权限表达式会怎么样呢?会以哪个权限表达式的执行结果为准呢?这个问题将会涉及到一个新的问题,我们放到后面的文章中去讲。
-
相关阅读:
UDP协议结构及其注意事项
Git命令大全
【TensorFlow】带你搞懂 TensorFlow 中的张量数据结构
【从零开始学习 SystemVerilog】3.1.3、SystemVerilog 控制流—— for 循环
【Rust 日报】2022-06-19 Rust 1.63 新特性令人期待
搭建vue后台管理系统框架
php中进程、线程、协程详细讲解
问题及解决方案汇总
计算机网络八股总结
Android NfcManager 之NFC接入
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42764468/article/details/127782438