-
【Machine Learning】23.Anomaly Detection 异常检测
异常数据的检测,这实际上也是一种无监督学习(因为不知道什么是异常)1.导入
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from utils import * %matplotlib inline- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
文件utils.py的代码:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def load_data(): X = np.load("data/X_part1.npy") X_val = np.load("data/X_val_part1.npy") y_val = np.load("data/y_val_part1.npy") return X, X_val, y_val def load_data_multi(): X = np.load("data/X_part2.npy") X_val = np.load("data/X_val_part2.npy") y_val = np.load("data/y_val_part2.npy") return X, X_val, y_val def multivariate_gaussian(X, mu, var): """ Computes the probability density function of the examples X under the multivariate gaussian distribution with parameters mu and var. If var is a matrix, it is treated as the covariance matrix. If var is a vector, it is treated as the var values of the variances in each dimension (a diagonal covariance matrix """ k = len(mu) if var.ndim == 1: var = np.diag(var) X = X - mu p = (2* np.pi)**(-k/2) * np.linalg.det(var)**(-0.5) * \ np.exp(-0.5 * np.sum(np.matmul(X, np.linalg.pinv(var)) * X, axis=1)) return p def visualize_fit(X, mu, var): """ This visualization shows you the probability density function of the Gaussian distribution. Each example has a location (x1, x2) that depends on its feature values. """ X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, 35.5, 0.5), np.arange(0, 35.5, 0.5)) Z = multivariate_gaussian(np.stack([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()], axis=1), mu, var) Z = Z.reshape(X1.shape) plt.plot(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], 'bx') if np.sum(np.isinf(Z)) == 0: plt.contour(X1, X2, Z, levels=10**(np.arange(-20., 1, 3)), linewidths=1) # Set the title plt.title("The Gaussian contours of the distribution fit to the dataset") # Set the y-axis label plt.ylabel('Throughput (mb/s)') # Set the x-axis label plt.xlabel('Latency (ms)')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
2.Anomaly Detection 异常检测
2.1 问题描述
在本练习中,您将实现异常检测算法以检测服务器计算机中的异常行为。
数据集包含两个特征:
- 吞吐量(mb/s)和
- 每个服务器的响应延迟(ms)。
当您的服务器运行时,您收集了 m = 307 m=307 m=307它们的行为示例,因此有一个未标记的数据集 { x ( 1 ) , … , x ( m ) } \{x^{(1)}, \ldots, x^{(m)}\} {x(1),…,x(m)}.
- 您怀疑这些示例中的绝大多数是服务器正常运行的“正常”(非异常)示例,但也可能有一些服务器在该数据集中异常运行的示例。
您将使用高斯模型来检测您的数据集。
- 您将首先从2D数据集开始,该数据集将允许您可视化算法正在做什么。
- 在该数据集上,您将拟合高斯分布,然后找到概率非常低的值,因此可以认为是异常。
- 之后,您将把异常检测算法应用于具有多个维度的更大数据集。
2.2 数据集
您将从加载此任务的数据集开始。
- 下面显示的
load_data()函数将数据加载到变量X_train、X_val和y_val中 - 您将使用
X_train拟合高斯分布 - 您将使用
X_val和y_val作为交叉验证集来选择阈值并确定异常与正常示例
# Load the dataset X_train, X_val, y_val = load_data()- 1
- 2
查看前五条数据
# Display the first five elements of X_train print("The first 5 elements of X_train are:\n", X_train[:5]) # Display the first five elements of X_val print("The first 5 elements of X_val are\n", X_val[:5]) # Display the first five elements of y_val print("The first 5 elements of y_val are\n", y_val[:5])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
检查shape
print ('The shape of X_train is:', X_train.shape) print ('The shape of X_val is:', X_val.shape) print ('The shape of y_val is: ', y_val.shape) The shape of X_train is: (307, 2) The shape of X_val is: (307, 2) The shape of y_val is: (307,)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
对于这个数据集,您可以使用散点图来可视化数据(“X_train”),因为它只有两个属性可以绘制(吞吐量和延迟)
# Create a scatter plot of the data. To change the markers to blue "x", # we used the 'marker' and 'c' parameters plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], marker='x', c='b') # Set the title plt.title("The first dataset") # Set the y-axis label plt.ylabel('Throughput (mb/s)') # Set the x-axis label plt.xlabel('Latency (ms)') # Set axis range plt.axis([0, 30, 0, 30]) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

2.3 高斯分布
To perform anomaly detection, you will first need to fit a model to the data’s distribution. 首先要把模型匹配数据分布才能执行异常检测
-
Given a training set { x ( 1 ) , . . . , x ( m ) } \{x^{(1)}, ..., x^{(m)}\} {x(1),...,x(m)} you want to estimate the Gaussian distribution for each of the features x i x_i xi.
-
Recall that the Gaussian distribution is given by
p ( x ; μ , σ 2 ) = 1 2 π σ 2 exp − ( x − μ ) 2 2 σ 2 p(x ; \mu,\sigma ^2) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi \sigma ^2}}\exp^{ - \frac{(x - \mu)^2}{2 \sigma ^2} } p(x;μ,σ2)=2πσ21exp−2σ2(x−μ)2
where μ \mu μ is the mean and σ 2 \sigma^2 σ2 controls the variance.
-
For each feature i = 1 … n i = 1\ldots n i=1…n, you need to find parameters μ i \mu_i μi and σ i 2 \sigma_i^2 σi2 that fit the data in the i i i-th dimension { x i ( 1 ) , . . . , x i ( m ) } \{x_i^{(1)}, ..., x_i^{(m)}\} {xi(1),...,xi(m)} (the i i i-th dimension of each example).
2.3.1 Estimating parameters for a Gaussian
Your task is to complete the code in
estimate_gaussianbelow.Exercise 1
Please complete the
estimate_gaussianfunction below to calculatemu(mean for each feature inX)andvar(variance for each feature inX).You can estimate the parameters, ( μ i \mu_i μi, σ i 2 \sigma_i^2 σi2), of the i i i-th
feature by using the following equations. To estimate the mean, you will
use: 平均值的计算公式μ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 m x i ( j ) \mu_i = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{j=1}^m x_i^{(j)} μi=m1j=1∑mxi(j)
and for the variance you will use: 方差的计算公式
σ i 2 = 1 m ∑ j = 1 m ( x i ( j ) − μ i ) 2 \sigma_i^2 = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{j=1}^m (x_i^{(j)} - \mu_i)^2 σi2=m1j=1∑m(xi(j)−μi)2# UNQ_C1 # GRADED FUNCTION: estimate_gaussian def estimate_gaussian(X): """ Calculates mean and variance of all features in the dataset Args: X (ndarray): (m, n) Data matrix Returns: mu (ndarray): (n,) Mean of all features var (ndarray): (n,) Variance of all features """ m, n = X.shape ### START CODE HERE ### mu = np.mean(X,axis = 0)#别忘了要指定轴 var = np.mean((X - mu)**2,axis = 0) ##注意**2是在sum里面的 ### END CODE HERE ### return mu, var- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
函数调用:
# Estimate mean and variance of each feature mu, var = estimate_gaussian(X_train) print("Mean of each feature:", mu) print("Variance of each feature:", var) Mean of each feature: [14.11222578 14.99771051] Variance of each feature: [1.83263141 1.70974533]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
# Returns the density of the multivariate normal # at each data point (row) of X_train p = multivariate_gaussian(X_train, mu, var) #Plotting code visualize_fit(X_train, mu, var)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2.3.2 选择阈值
已经估计了高斯参数,您可以研究在给定这种分布的情况下,哪些示例具有非常高的概率,哪些示例的概率非常低。
- 低概率的例子更可能是我们数据集中的异常。
- 确定哪些示例是异常的一种方法是基于交叉验证集选择阈值。
在本节中,您将完成“select_threshold”中的代码,以使用交叉验证集上的 F 1 F_1 F1分数选择阈值 ε \varepsilon ε。
- For this, we will use a cross validation set
{ ( x c v ( 1 ) , y c v ( 1 ) ) , … , ( x c v ( m c v ) , y c v ( m c v ) ) } \{(x_{\rm cv}^{(1)}, y_{\rm cv}^{(1)}),\ldots, (x_{\rm cv}^{(m_{\rm cv})}, y_{\rm cv}^{(m_{\rm cv})})\} {(xcv(1),ycv(1)),…,(xcv(mcv),ycv(mcv))}, where the label y = 1 y=1 y=1 corresponds to an anomalous example, and y = 0 y=0 y=0 corresponds to a normal example. y=1代表异常数据,y=0代表正常数据 - For each cross validation example, we will compute
p
(
x
c
v
(
i
)
)
p(x_{\rm cv}^{(i)})
p(xcv(i)). The vector of all of these probabilities
p
(
x
c
v
(
1
)
)
,
…
,
p
(
x
c
v
(
m
c
v
)
)
p(x_{\rm cv}^{(1)}), \ldots, p(x_{\rm cv}^{(m_{\rm cv)}})
p(xcv(1)),…,p(xcv(mcv)) is passed to
select_thresholdin the vectorp_val. - The corresponding labels
y
c
v
(
1
)
,
…
,
y
c
v
(
m
c
v
)
y_{\rm cv}^{(1)}, \ldots, y_{\rm cv}^{(m_{\rm cv)}}
ycv(1),…,ycv(mcv) is passed to the same function in the vector
y_val.
Exercise 2
Please complete the
select_thresholdfunction below to find the best threshold to use for selecting outliers based on the results from a 验证集validation set (p_val) and the ground truth (y_val). 完成下列函数-
In the provided code
select_threshold, 已经有一个循环将尝试 ε \varepsilon ε的许多不同值,并根据 F 1 F_1 F1得分选择最佳 ε \varepsilon ε。 -
通过选择
epsilon作为阈值来计算F1分数,并将值放在“F1”中。-
Recall that if an example x x x has a low probability p ( x ) < ε p(x) < \varepsilon p(x)<ε, then it is classified as an anomaly. 如果x的概率小于阈值,就是异常数据
-
Then, you can compute precision 准确率(预测当中正确预测概率) and recall 召回率(阳性当中被正确预测概率) by:
p r e c = t p t p + f p r e c = t p t p + f n ,precrec==tp+fptptp+fntp, wherep r e c = t p t p + f p r e c = t p t p + f n , - t p tp tp is the number of true positives: the ground truth label says it’s an anomaly and our algorithm correctly classified it as an anomaly. 真阳性
- f p fp fp is the number of false positives: the ground truth label says it’s not an anomaly, but our algorithm incorrectly classified it as an anomaly. 假阳性
- f n fn fn is the number of false negatives: the ground truth label says it’s an anomaly, but our algorithm incorrectly classified it as not being anomalous. 假阴性
-
The F 1 F_1 F1 score is computed using precision ( p r e c prec prec) and recall ( r e c rec rec) as follows: 计算F1分数的公式
F 1 = 2 ⋅ p r e c ⋅ r e c p r e c + r e c F_1 = \frac{2\cdot prec \cdot rec}{prec + rec} F1=prec+rec2⋅prec⋅rec
-
Implementation Note:
In order to compute t p tp tp, f p fp fp and f n fn fn, you may be able to use a vectorized implementation rather than loop over all the examples. 使用向量化的实现方式而不是循环代码填空:
下面代码选择
epsilon的方法是把概率最大值和最小值区间内分成一千份,然后遍历# UNQ_C2 # GRADED FUNCTION: select_threshold def select_threshold(y_val, p_val): """ Finds the best threshold to use for selecting outliers based on the results from a validation set (p_val) and the ground truth (y_val) Args: y_val (ndarray): Ground truth on validation set p_val (ndarray): Results on validation set Returns: epsilon (float): Threshold chosen F1 (float): F1 score by choosing epsilon as threshold """ best_epsilon = 0 best_F1 = 0 F1 = 0 step_size = (max(p_val) - min(p_val)) / 1000 for epsilon in np.arange(min(p_val), max(p_val), step_size): ### START CODE HERE ### predictions = # Your code here to calculate predictions for each example using epsilon as threshold tp = # Your code here to calculate number of true positives fp = # Your code here to calculate number of false positives fn = # Your code here to calculate number of false negatives prec = # Your code here to calculate precision rec = # Your code here to calculate recall F1 = # Your code here to calculate F1 ### END CODE HERE ### if F1 > best_F1: best_F1 = F1 best_epsilon = epsilon return best_epsilon, best_F1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
答案:
for epsilon in np.arange(min(p_val), max(p_val), step_size): ### START CODE HERE ### predictions = (p_val < epsilon) tp = np.sum((predictions == 1) & (y_val == 1)) fp = np.sum((predictions == 1) & (y_val == 0))# Your code here to calculate number of false positives fn = np.sum((predictions == 0) & (y_val == 1))# Your code here to calculate number of false negatives prec = tp / (tp + fp) rec = tp / (tp + fn) F1 = 2 * prec * rec / (prec + rec)# Your code here to calculate F1 ### END CODE HERE ### if F1 > best_F1: best_F1 = F1 best_epsilon = epsilon return best_epsilon, best_F1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
测试代码:
p_val = multivariate_gaussian(X_val, mu, var) epsilon, F1 = select_threshold(y_val, p_val) print('Best epsilon found using cross-validation: %e' % epsilon) print('Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: %f' % F1) Best epsilon found using cross-validation: 8.990853e-05 Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: 0.875000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
可视化异常数据
# Find the outliers in the training set outliers = p < epsilon # Visualize the fit visualize_fit(X_train, mu, var) # Draw a red circle around those outliers plt.plot(X_train[outliers, 0], X_train[outliers, 1], 'ro', markersize= 10,markerfacecolor='none', markeredgewidth=2)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

2.4 在大数据集上的实践
In this dataset, each example is described by 11 features, capturing many more properties of your compute servers.
- The
load_data()function shown below loads the data into variablesX_train_high,X_val_highandy_val_high_highis meant to distinguish these variables from the ones used in the previous part- We will use
X_train_highto fit Gaussian distribution - We will use
X_val_highandy_val_highas a cross validation set to select a threshold and determine anomalous vs normal examples
- 下面显示的“load_data()”函数将数据加载到变量“X_train_high”、“X_val_high”和“y_val_high”中`
- “_high”意在将这些变量与前一部分中使用的变量区分开来
- 我们将使用“X_train_high”来拟合高斯分布
- 我们将使用“X_val_high”和“y_val_high”作为交叉验证集来选择阈值并确定异常与正常示例
加载数据
# load the dataset X_train_high, X_val_high, y_val_high = load_data_multi()- 1
- 2
查看数据维度
print ('The shape of X_train_high is:', X_train_high.shape) print ('The shape of X_val_high is:', X_val_high.shape) print ('The shape of y_val_high is: ', y_val_high.shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
进行异常检测
The code below will use your code to
- Estimate the Gaussian parameters ( μ i \mu_i μi and σ i 2 \sigma_i^2 σi2)
- Evaluate the probabilities for both the training data
X_train_highfrom which you estimated the Gaussian parameters, as well as for the the cross-validation setX_val_high. 评估用于估计高斯参数的训练数据“X_train_high”以及交叉验证集“X_val_high”的概率。 - Finally, it will use
select_thresholdto find the best threshold ε \varepsilon ε.
# Apply the same steps to the larger dataset # Estimate the Gaussian parameters mu_high, var_high = estimate_gaussian(X_train_high) # Evaluate the probabilites for the training set p_high = multivariate_gaussian(X_train_high, mu_high, var_high) # Evaluate the probabilites for the cross validation set p_val_high = multivariate_gaussian(X_val_high, mu_high, var_high) # Find the best threshold epsilon_high, F1_high = select_threshold(y_val_high, p_val_high) print('Best epsilon found using cross-validation: %e'% epsilon_high) print('Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: %f'% F1_high) print('# Anomalies found: %d'% sum(p_high < epsilon_high)) Best epsilon found using cross-validation: 1.377229e-18 Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: 0.615385 # Anomalies found: 117- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
3.课后题
- 监督学习和异常检测的使用:
- 您正在构建一个系统来检测数据中心中的计算机是否出现故障。您有10000个数据点计算机运行良好,并且没有来自计算机的数据发生故障。使用异常检测
- 您正在构建一个系统来检测数据中心中的计算机是否出现故障。你有10000个数据点计算机运行良好,10000个计算机数据点出现故障。使用监督学习
- 上面的使用场景很容易判断,但要是有已知异常数据但极少要怎么办?

将异常发动机的数据(与一些正常发动机一起)进行交叉验证和/或测试
-
阈值变小了,更少的数据会被分配为异常数据

-
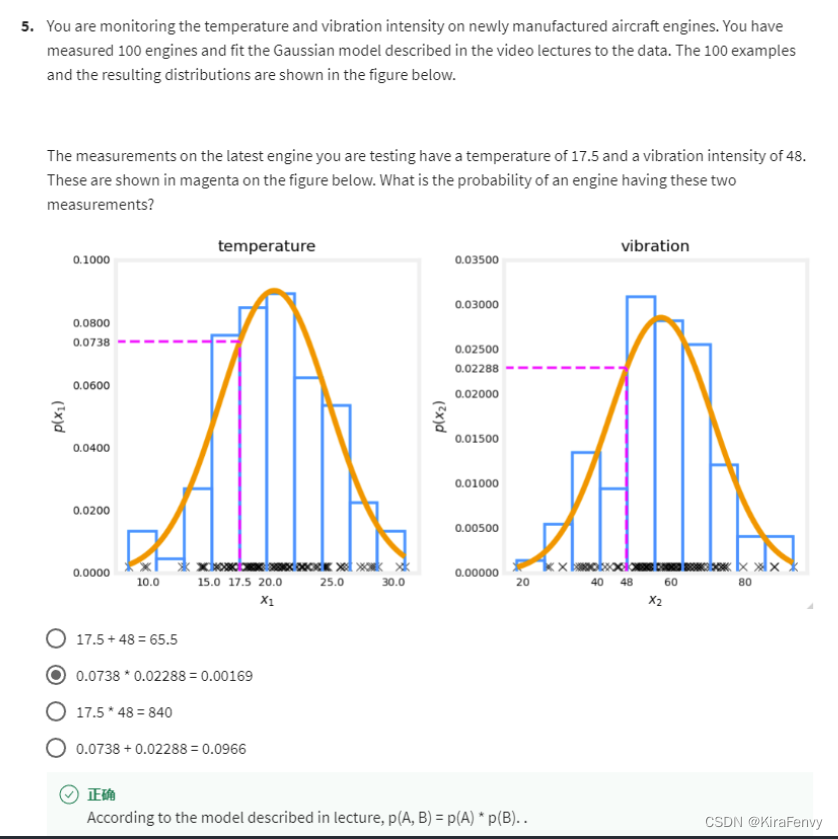
你正在监测新制造的飞机发动机的温度和振动强度。测量了100个引擎,并将视频讲座中描述的高斯模型与数据拟合。100个示例所得分布如下图所示。
您正在测试的最新发动机的测量值温度为17.5,振动强度为48。下图中以洋红色表示。发动机有这两种情况的概率是多少
-
相关阅读:
lua函数定义
分布式事务解决方案Seata
Java 编码那些事(二)
WMS仓储管理系统的主要类型及其特性和适用场景
【C++】C++入门
NC23054 华华开始学信息学
Android开发:Fragment中优雅使用ViewBinding【Java】
数据结构-----树和二叉树的定义与性质
使用Discord机器人和Midjourney构建图像生成服务
基于Java+SpringBoot+Vue的大学生线上心理咨询系统(可随意更改项目主题如医院预约、店铺预约、专家挂号、在线咨询等)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51371693/article/details/127635991
