-
[pytorch] 2D + 3D EfficientNet代码 实现,改写
[pytorch] 2D + 3D EfficientNet实现
本文只介绍EfficientNet的代码实现,需要对EfficientNet有基础的了解。代码参考:
deep-learning-for-image-processing
EfficientNet网络详解网络结构

2D EfficientNet
import math import copy from functools import partial from collections import OrderedDict from typing import Optional, Callable import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch import Tensor from torch.nn import functional as F- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
def _make_divisible(ch, divisor=8, min_ch=None): """ 将传入的channel的个数调整到离其最近的8的整数倍 This function is taken from the original tf repo. It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8 It can be seen here: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py """ if min_ch is None: min_ch = divisor new_ch = max(min_ch, int(ch + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor) # Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%. if new_ch < 0.9 * ch: new_ch += divisor return new_ch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
class ConvBNActivation(nn.Sequential): # 卷积 + BN + Swish激活函数 def __init__(self, in_planes: int, # 输入特征矩阵的channel out_planes: int, # 输出特征矩阵的channel kernel_size: int = 3, stride: int = 1, groups: int = 1, # 卷及类型:普通卷积或者是Depwise卷积 norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, # BN结构 activation_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None): padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if norm_layer is None: norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d if activation_layer is None: activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish (torch>=1.7) super(ConvBNActivation, self).__init__(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_planes, out_channels=out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups, bias=False), norm_layer(out_planes), activation_layer())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

class SqueezeExcitation(nn.Module): # SE模块 def __init__(self, input_c: int, # block input channel MBConv的输入channel expand_c: int, # block expand channel MBConv第一个Conv(1*1)升维之后输出的channel, # 因为Depwise卷积没改变channel个数,所以它也是SE的输入channel squeeze_factor: int = 4): super(SqueezeExcitation, self).__init__() squeeze_c = input_c // squeeze_factor # 第一个全连接层节点个数 self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(expand_c, squeeze_c, 1) # 使用卷积代替全连接层,作用一样 self.ac1 = nn.SiLU() # alias Swish self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_c, expand_c, 1) self.ac2 = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: scale = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, output_size=(1, 1)) scale = self.fc1(scale) scale = self.ac1(scale) scale = self.fc2(scale) scale = self.ac2(scale) return scale * x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
class InvertedResidualConfig: # MBConv参数设置 # kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate def __init__(self, kernel: int, # 3 or 5 input_c: int, # 输入MBConv模块的channel out_c: int, # MBConv模块输出的channel expanded_ratio: int, # 1 or 6 第一个1*1卷积升维大小倍数 MBConv1或者MBConv6 stride: int, # 1 or 2 use_se: bool, # True drop_rate: float, index: str, # 1a, 2a, 2b, ...记录当前MBConv模块名称 width_coefficient: float): # 宽度因子 # 宽度因子是channel维度上的倍率因子,比如在Efficient_B0中Stage1的3*3卷积层中卷积核个数为32 # 那么B6中就是32*1.8 = 57.6 取整到离8最近的倍数即56 self.input_c = self.adjust_channels(input_c, width_coefficient) self.kernel = kernel self.expanded_c = self.input_c * expanded_ratio self.out_c = self.adjust_channels(out_c, width_coefficient) self.use_se = use_se self.stride = stride self.drop_rate = drop_rate self.index = index @staticmethod # 以在不创建类实例的情况下调用方法 def adjust_channels(channels: int, width_coefficient: float): return _make_divisible(channels * width_coefficient, 8) # 调整到离其最近的8的整数倍- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False): """ Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks). "Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth", https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.09382.pdf This function is taken from the rwightman. It can be seen here: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/layers/drop.py#L140 """ if drop_prob == 0. or not training: return x keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device) random_tensor.floor_() # binarize output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor return output class DropPath(nn.Module): """ Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks). "Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth", https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.09382.pdf """ def __init__(self, drop_prob=None): super(DropPath, self).__init__() self.drop_prob = drop_prob def forward(self, x): return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
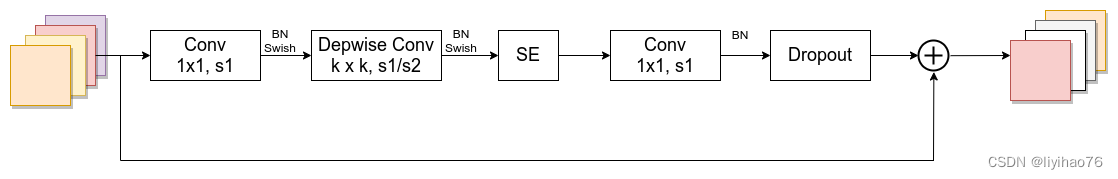
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module): # MBConv模块 def __init__(self, cnf: InvertedResidualConfig, norm_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module]): super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__() if cnf.stride not in [1, 2]: raise ValueError("illegal stride value.") self.use_res_connect = (cnf.stride == 1 and cnf.input_c == cnf.out_c) # 仅当输入MBConv结构的特征矩阵与输出的特征矩阵shape相同时才使用shortcut链接 layers = OrderedDict() activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish # expand 1*1升维卷积层 if cnf.expanded_c != cnf.input_c: # 当expendeed = 1的时候,不需要第一个升维的1*1卷积层 layers.update({"expand_conv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.input_c, cnf.expanded_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer)}) # depthwise 输入输出channel不变 layers.update({"dwconv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.expanded_c, cnf.expanded_c, kernel_size=cnf.kernel, stride=cnf.stride, groups=cnf.expanded_c, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer)}) if cnf.use_se: layers.update({"se": SqueezeExcitation(cnf.input_c, cnf.expanded_c)}) # project 1*1卷积层,这里没有激活函数所以使用nn.Identity layers.update({"project_conv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.expanded_c, cnf.out_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=nn.Identity)}) self.block = nn.Sequential(layers) self.out_channels = cnf.out_c self.is_strided = cnf.stride > 1 # 只有在使用shortcut连接时且drop_rate大于零才使用dropout层 if self.use_res_connect and cnf.drop_rate > 0: self.dropout = DropPath(cnf.drop_rate) # self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=cnf.drop_rate,inplace=True) else: self.dropout = nn.Identity() def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: result = self.block(x) result = self.dropout(result) if self.use_res_connect: result += x return result- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
class EfficientNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, width_coefficient: float, # 宽度倍率因子 depth_coefficient: float, # 深度倍率因子 num_classes: int = 1000, dropout_rate: float = 0.2, # stage9 FC层前面的失活比例 drop_connect_rate: float = 0.2, # MBConv层中的失活比例 block: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None ): super(EfficientNet, self).__init__() # B0默认配置表 stage2-stage8的参数 # kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats default_cnf = [[3, 32, 16, 1, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1], [3, 16, 24, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [5, 24, 40, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [3, 40, 80, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 80, 112, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 112, 192, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 4], [3, 192, 320, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1]] def round_repeats(repeats): # 深度倍率因子仅针对stage2-stage8,比如在efficient_B0中stage7的L=4, # 那么在B6中就是4*2.6=10.4,向上取整即11 """Round number of repeats based on depth multiplier.""" return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats)) if block is None: block = InvertedResidual if norm_layer is None: norm_layer = partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.1) # partial方法传入函数的默认参数 adjust_channels = partial(InvertedResidualConfig.adjust_channels, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) # build inverted_residual_setting bneck_conf = partial(InvertedResidualConfig, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) b = 0 num_blocks = float(sum(round_repeats(i[-1]) for i in default_cnf)) # 根据B0默认配置表中最后一个参数(B0的重复次数)和倍率因子来计算当前网络(B0-B7)的重复次数 inverted_residual_setting = [] for stage, args in enumerate(default_cnf): # 遍历stage cnf = copy.copy(args) for i in range(round_repeats(cnf.pop(-1))):# 遍历MBConv模块 if i > 0: # strides equal 1 except first cnf cnf[-3] = 1 # strides cnf[1] = cnf[2] # input_channel equal output_channel cnf[-1] = args[-2] * b / num_blocks # update dropout ratio # 对于MBConv中的随机失活比例是从0慢慢增长到给定的值 index = str(stage + 1) + chr(i + 97) # 1a, 2a, 2b, ... inverted_residual_setting.append(bneck_conf(*cnf, index))# 每一个MBConv的配置 b += 1 # create layers layers = OrderedDict() # first conv layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3, out_planes=adjust_channels(32), kernel_size=3, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # building inverted residual blocks for cnf in inverted_residual_setting: layers.update({cnf.index: block(cnf, norm_layer)}) # build top last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280) layers.update({"top": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c, out_planes=last_conv_output_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # 1*1的卷积层 self.features = nn.Sequential(layers) self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) classifier = [] if dropout_rate > 0: classifier.append(nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate, inplace=True)) classifier.append(nn.Linear(last_conv_output_c, num_classes)) self.classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier) # initial weights for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out") if m.bias is not None: nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): nn.init.ones_(m.weight) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) def _forward_impl(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: x = self.features(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = torch.flatten(x, 1) x = self.classifier(x) return x def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: return self._forward_impl(x)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114

num_classes = 3 efficientnet_b0 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.0, depth_coefficient=1.0, dropout_rate=0.2, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b1 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.0, depth_coefficient=1.1, dropout_rate=0.2, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b2 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.1, depth_coefficient=1.2, dropout_rate=0.3, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b3 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.2, depth_coefficient=1.4, dropout_rate=0.3, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b4 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.4, depth_coefficient=1.8, dropout_rate=0.4, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b5 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.6, depth_coefficient=2.2, dropout_rate=0.4, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b6 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.8, depth_coefficient=2.6, dropout_rate=0.5, num_classes=num_classes) efficientnet_b7 = EfficientNet(width_coefficient=2.0, depth_coefficient=3.1, dropout_rate=0.5, num_classes=num_classes)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
实现三分类
x=torch.randn(1,3,224,224) X=efficientnet_b0(x) print(X.shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
可视化
import netron import torch.onnx import onnx modelData ='demo.onnx' # 定义模型数据保存的路径 torch.onnx.export(efficientnet_b0, x, modelData) # 将 pytorch 模型以 onnx 格式导出并保存 onnx.save(onnx.shape_infe- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7


# first conv layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3, out_planes=adjust_channels(32), kernel_size=3, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer)})- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
因为silu (x)=x∗ sigmoid(x) 所以是双支路.


当n = 1时(MBConv1),不要第一个升维的1x1卷积层,即Stage2中的MBConv结构都没有第一个升维的1x1卷积层(这和MobileNetV3网络类似)
所以输入特征直接经过Depwise卷积,SE模块和Conv1*1, 因为输入和输出channel不同,所以不使用shortcut和dropout_rate.


第一层MBConv,n=6, 通过第一个1*1卷积将channel升维6倍,因为输入和输出channel不同,所以不使用shortcut和dropout_rate.

第二层MBConv,使用shortcut.
MBConv模块参数

通过对网络构建中inverted_residual_setting的分析,我们可以确定Efficient网络stage2-stage8每层的配置class EfficientNet(nn.Module): def __init__(): ... self.conf = inverted_residual_setting ... def forward(): ... for i in self.conf: print(i.kernel,i.input_c,i.out_c,i.expanded_c,i.use_se,i.stride,i.drop_rate,i.index)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
kernel // input_c // out_c // expanded_c // use_se // stride // drop_rate // index-
efficientnet_b0

-
efficientnet_b1

-
efficientnet_b2

-
efficientnet_b3

-
efficientnet_b4

-
efficientnet_b5

-
efficientnet_b6

-
efficientnet_b7

改写Efficienet_b0
class EfficientNet_b0_2d(nn.Module): def __init__(self, width_coefficient: float, # 宽度倍率因子 depth_coefficient: float, # 深度倍率因子 num_classes: int = 1000, dropout_rate: float = 0.2, # stage9 FC层前面的失活比例 drop_connect_rate: float = 0.2, # MBConv层中的失活比例 block: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None ): super(EfficientNet_b0_2d, self).__init__() # B0默认配置表 stage2-stage8的参数 # kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats default_cnf = [[3, 32, 16, 1, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1], [3, 16, 24, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [5, 24, 40, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [3, 40, 80, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 80, 112, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 112, 192, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 4], [3, 192, 320, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1]] def round_repeats(repeats): # 深度倍率因子仅针对stage2-stage8,比如在efficient_B0中stage7的L=4, # 那么在B6中就是4*2.6=10.4,向上取整即11 """Round number of repeats based on depth multiplier.""" return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats)) if block is None: block = InvertedResidual if norm_layer is None: norm_layer = partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.1) # partial方法传入函数的默认参数 adjust_channels = partial(InvertedResidualConfig.adjust_channels, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) # build inverted_residual_setting bneck_conf = partial(InvertedResidualConfig, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) # 这里定义宽度因子,InvertedResidualConfig剩下的变量由default_cnf变化得到 b = 0 num_blocks = float(sum(round_repeats(i[-1]) for i in default_cnf)) # 根据B0默认配置表中最后一个参数(B0的重复次数)和倍率因子来计算当前网络(B0-B7)的重复次数 inverted_residual_setting = [] for stage, args in enumerate(default_cnf): # 遍历stage cnf = copy.copy(args) for i in range(round_repeats(cnf.pop(-1))):# 遍历MBConv模块 if i > 0: # strides equal 1 except first cnf cnf[-3] = 1 # strides cnf[1] = cnf[2] # input_channel equal output_channel cnf[-1] = args[-2] * b / num_blocks # update dropout ratio # 对于MBConv中的随机失活比例是从0慢慢增长到给定的值 index = str(stage + 1) + chr(i + 97) # 1a, 2a, 2b, ... inverted_residual_setting.append(bneck_conf(*cnf, index))# 每一个MBConv的配置 b += 1 # create layers # layers = OrderedDict() # first conv self.stage1_2d = ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3, out_planes=adjust_channels(32), kernel_size=3, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer) self.stage2_2d = block(inverted_residual_setting[0], norm_layer) self.stage3_2d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[1], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[2], norm_layer)) self.stage4_2d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[3], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[4], norm_layer)) self.stage5_2d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[5], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[6], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[7], norm_layer)) self.stage6_2d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[8], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[9], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[10], norm_layer)) self.stage7_2d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[11], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[12], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[13], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[14], norm_layer)) self.stage8_2d = block(inverted_residual_setting[15], norm_layer) # build top last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280) self.stage9_2d = ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c, out_planes=last_conv_output_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer) self.conf = inverted_residual_setting # layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3, # out_planes=adjust_channels(32), # kernel_size=3, # stride=2, # norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # building inverted residual blocks # for cnf in inverted_residual_setting: # layers.update({cnf.index: block(cnf, norm_layer)}) # build top # last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c # last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280) # layers.update({"top": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c, # out_planes=last_conv_output_c, # kernel_size=1, # norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # 1*1的卷积层 #self.features = nn.Sequential(layers) self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) classifier = [] if dropout_rate > 0: classifier.append(nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate, inplace=True)) classifier.append(nn.Linear(last_conv_output_c, num_classes)) self.classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier) # initial weights for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out") if m.bias is not None: nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): nn.init.ones_(m.weight) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: x = self.stage1_2d(x) x = self.stage2_2d(x) x = self.stage3_2d(x) x = self.stage4_2d(x) x = self.stage5_2d(x) x = self.stage6_2d(x) x = self.stage7_2d(x) x = self.stage8_2d(x) x = self.stage9_2d(x) #x = self.features(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = torch.flatten(x, 1) x = self.classifier(x) # print('stage2-7 total layer = ',len(self.conf)) # for i in self.conf: # print(i.kernel,i.input_c,i.out_c,i.expanded_c,i.use_se,i.stride,i.drop_rate,i.index) return x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
3D EfficientNet_b0
import math import copy from functools import partial from collections import OrderedDict from typing import Optional, Callable import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch import Tensor from torch.nn import functional as F- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
def _make_divisible(ch, divisor=8, min_ch=None): """ 将传入的channel的个数调整到离其最近的8的整数倍 This function is taken from the original tf repo. It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8 It can be seen here: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py """ if min_ch is None: min_ch = divisor new_ch = max(min_ch, int(ch + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor) # Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%. if new_ch < 0.9 * ch: new_ch += divisor return new_ch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
class ConvBNActivation_3d(nn.Sequential): # 卷积 + BN + Swish激活函数 def __init__(self, in_planes: int, # 输入特征矩阵的channel out_planes: int, # 输出特征矩阵的channel kernel_size: int = 3, stride: int = 1, groups: int = 1, # 卷及类型:普通卷积或者是Depwise卷积 norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, # BN结构 activation_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None): padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if norm_layer is None: norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm3d if activation_layer is None: activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish (torch>=1.7) super(ConvBNActivation_3d, self).__init__(nn.Conv3d(in_channels=in_planes, out_channels=out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups, bias=False), norm_layer(out_planes), activation_layer())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
class SqueezeExcitation_3d(nn.Module): # SE模块 def __init__(self, input_c: int, # block input channel MBConv的输入channel expand_c: int, # block expand channel MBConv第一个Conv(1*1)升维之后输出的channel, # 因为Depwise卷积没改变channel个数,所以它也是SE的输入channel squeeze_factor: int = 4): super(SqueezeExcitation_3d, self).__init__() squeeze_c = input_c // squeeze_factor # 第一个全连接层节点个数 self.fc1 = nn.Conv3d(expand_c, squeeze_c, 1) # 使用卷积代替全连接层,作用一样 self.ac1 = nn.SiLU() # alias Swish self.fc2 = nn.Conv3d(squeeze_c, expand_c, 1) self.ac2 = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: scale = F.adaptive_avg_pool3d(x, output_size=(1, 1, 1)) scale = self.fc1(scale) scale = self.ac1(scale) scale = self.fc2(scale) scale = self.ac2(scale) return scale * x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
class InvertedResidualConfig_3d: # MBConv参数设置 # kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate def __init__(self, kernel: int, # 3 or 5 input_c: int, # 输入MBConv模块的channel out_c: int, # MBConv模块输出的channel expanded_ratio: int, # 1 or 6 第一个1*1卷积升维大小倍数 MBConv1或者MBConv6 stride: int, # 1 or 2 use_se: bool, # True drop_rate: float, index: str, # 1a, 2a, 2b, ...记录当前MBConv模块名称 width_coefficient: float): # 宽度因子 # 宽度因子是channel维度上的倍率因子,比如在Efficient_B0中Stage1的3*3卷积层中卷积核个数为32 # 那么B6中就是32*1.8 = 57.6 取整到离8最近的倍数即56 self.input_c = self.adjust_channels(input_c, width_coefficient) self.kernel = kernel self.expanded_c = self.input_c * expanded_ratio self.out_c = self.adjust_channels(out_c, width_coefficient) self.use_se = use_se self.stride = stride self.drop_rate = drop_rate self.index = index @staticmethod # 以在不创建类实例的情况下调用方法 def adjust_channels(channels: int, width_coefficient: float): return _make_divisible(channels * width_coefficient, 8) # 调整到离其最近的8的整数倍- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
class InvertedResidual_3d(nn.Module): # MBConv模块 def __init__(self, cnf: InvertedResidualConfig_3d, norm_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module]): super(InvertedResidual_3d, self).__init__() if cnf.stride not in [1, 2]: raise ValueError("illegal stride value.") self.use_res_connect = (cnf.stride == 1 and cnf.input_c == cnf.out_c) # 仅当输入MBConv结构的特征矩阵与输出的特征矩阵shape相同时才使用shortcut链接 layers = OrderedDict() activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish # expand 1*1升维卷积层 if cnf.expanded_c != cnf.input_c: # 当expendeed = 1的时候,不需要第一个升维的1*1卷积层 layers.update({"expand_conv": ConvBNActivation_3d(cnf.input_c, cnf.expanded_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer)}) # depthwise 输入输出channel不变 layers.update({"dwconv": ConvBNActivation_3d(cnf.expanded_c, cnf.expanded_c, kernel_size=cnf.kernel, stride=cnf.stride, groups=cnf.expanded_c, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer)}) if cnf.use_se: layers.update({"se": SqueezeExcitation_3d(cnf.input_c, cnf.expanded_c)}) # project 1*1卷积层,这里没有激活函数所以使用nn.Identity layers.update({"project_conv": ConvBNActivation_3d(cnf.expanded_c, cnf.out_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=nn.Identity)}) self.block = nn.Sequential(layers) self.out_channels = cnf.out_c self.is_strided = cnf.stride > 1 # 只有在使用shortcut连接时且drop_rate大于零才使用dropout层 if self.use_res_connect and cnf.drop_rate > 0: #self.dropout = DropPath(cnf.drop_rate) self.dropout = nn.Dropout3d(p=cnf.drop_rate,inplace=True) else: self.dropout = nn.Identity() def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: result = self.block(x) result = self.dropout(result) if self.use_res_connect: result += x return result- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
class EfficientNet_b0_3d(nn.Module): def __init__(self, width_coefficient: float, # 宽度倍率因子 depth_coefficient: float, # 深度倍率因子 num_classes: int = 1000, dropout_rate: float = 0.2, # stage9 FC层前面的失活比例 drop_connect_rate: float = 0.2, # MBConv层中的失活比例 block: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None ): super(EfficientNet_b0_3d, self).__init__() # B0默认配置表 stage2-stage8的参数 # kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats default_cnf = [[3, 32, 16, 1, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1], [3, 16, 24, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [5, 24, 40, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2], [3, 40, 80, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 80, 112, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 3], [5, 112, 192, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 4], [3, 192, 320, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1]] def round_repeats(repeats): # 深度倍率因子仅针对stage2-stage8,比如在efficient_B0中stage7的L=4, # 那么在B6中就是4*2.6=10.4,向上取整即11 """Round number of repeats based on depth multiplier.""" return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats)) if block is None: block = InvertedResidual_3d if norm_layer is None: norm_layer = partial(nn.BatchNorm3d, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.1) # partial方法传入函数的默认参数 adjust_channels = partial(InvertedResidualConfig_3d.adjust_channels, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) # build inverted_residual_setting bneck_conf = partial(InvertedResidualConfig_3d, width_coefficient=width_coefficient) # 这里定义宽度因子,InvertedResidualConfig剩下的变量由default_cnf变化得到 b = 0 num_blocks = float(sum(round_repeats(i[-1]) for i in default_cnf)) # 根据B0默认配置表中最后一个参数(B0的重复次数)和倍率因子来计算当前网络(B0-B7)的重复次数 inverted_residual_setting = [] for stage, args in enumerate(default_cnf): # 遍历stage cnf = copy.copy(args) for i in range(round_repeats(cnf.pop(-1))):# 遍历MBConv模块 if i > 0: # strides equal 1 except first cnf cnf[-3] = 1 # strides cnf[1] = cnf[2] # input_channel equal output_channel cnf[-1] = args[-2] * b / num_blocks # update dropout ratio # 对于MBConv中的随机失活比例是从0慢慢增长到给定的值 index = str(stage + 1) + chr(i + 97) # 1a, 2a, 2b, ... inverted_residual_setting.append(bneck_conf(*cnf, index))# 每一个MBConv的配置 b += 1 # create layers # layers = OrderedDict() # first conv self.stage1_3d = ConvBNActivation_3d(in_planes=3, out_planes=adjust_channels(32), kernel_size=3, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer) self.stage2_3d = block(inverted_residual_setting[0], norm_layer) self.stage3_3d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[1], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[2], norm_layer)) self.stage4_3d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[3], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[4], norm_layer)) self.stage5_3d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[5], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[6], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[7], norm_layer)) self.stage6_3d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[8], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[9], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[10], norm_layer)) self.stage7_3d = nn.Sequential(block(inverted_residual_setting[11], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[12], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[13], norm_layer), block(inverted_residual_setting[14], norm_layer)) self.stage8_3d = block(inverted_residual_setting[15], norm_layer) # build top last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280) self.stage9_3d = ConvBNActivation_3d(in_planes=last_conv_input_c, out_planes=last_conv_output_c, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer) self.conf = inverted_residual_setting # layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3, # out_planes=adjust_channels(32), # kernel_size=3, # stride=2, # norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # building inverted residual blocks # for cnf in inverted_residual_setting: # layers.update({cnf.index: block(cnf, norm_layer)}) # build top # last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c # last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280) # layers.update({"top": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c, # out_planes=last_conv_output_c, # kernel_size=1, # norm_layer=norm_layer)}) # 1*1的卷积层 #self.features = nn.Sequential(layers) self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d(1) classifier = [] if dropout_rate > 0: classifier.append(nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate, inplace=True)) classifier.append(nn.Linear(last_conv_output_c, num_classes)) self.classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier) # initial weights for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv3d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu') elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm3d): nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1) nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: x = self.stage1_3d(x) x = self.stage2_3d(x) x = self.stage3_3d(x) x = self.stage4_3d(x) x = self.stage5_3d(x) x = self.stage6_3d(x) x = self.stage7_3d(x) x = self.stage8_3d(x) x = self.stage9_3d(x) #x = self.features(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = torch.flatten(x, 1) x = self.classifier(x) # print('stage2-7 total layer = ',len(self.conf)) # for i in self.conf: # print(i.kernel,i.input_c,i.out_c,i.expanded_c,i.use_se,i.stride,i.drop_rate,i.index) return x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
num_classes = 3 efficientnet_b0 = EfficientNet_b0_3d(width_coefficient=1.0, depth_coefficient=1.0, dropout_rate=0.2, num_classes=num_classes)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
x=torch.randn(1,3,224,224,224) X=efficientnet_b0(x) print(X.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3])- 1
- 2
- 3
import netron import torch.onnx import onnx modelData ='demo.onnx' # 定义模型数据保存的路径 torch.onnx.export(efficientnet_b0, x, modelData) # 将 pytorch 模型以 onnx 格式导出并保存 onnx.save(onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx.load(modelData)), modelData) netron.start(modelData)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
相关阅读:
ServletContext详解
练[ZJCTF 2019]NiZhuanSiWei
leetcode marathon [复习] 8.24 - 9道
7.Vue常用属性
【第29天】给定一个整数 n ,请你求出它的因子数
10个适合后端程序员的前端框架
Java Stream Map的使用
初级项目经理 如何快速提升能力?
科教导刊杂志科教导刊杂志社科教导刊编辑部2022年第27期目录
局域网内部如何实现文件夹共享
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38736504/article/details/127561201
